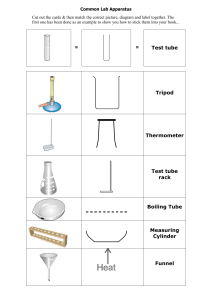
1, BASICLABORATORYTECHNIQUES. 1. TEST TUBE Test tubes are used for conducting various tests with small amount of reagents Test tubes of different sizes are available .Small test tubes (called semimicro test tubes) are used for salt analysis. Test tubes like boiling tubes and centrifiuging tubes are also avaiable 2. BEAKER Beakers are used for mixing, holding, boiling and transferring various liquids .Beakers are of different sizes such as 150 ml,250 ml,500 ml etc. made of soft glass and corning glass are available. 3. FUNNEL Funnel is used for transfering liquids and for filtration It is acone shaped wide glass tube ended in to along narrow neck. Glass or polythene funnels having different diameters are available for different operations in the laboratory. 4. WASH BOTTLES The wash bottle is a convenient water container used for rinsing apparatus, washing precipitates , makingup of solution etc. For this purpose either a glass wash bottle or a polythene wash bottle can be used. i Glass Wash Bottle: The glass wash bottle consists of (a) a flat bottomedglass flask, (b) a long glass tube (30cm) bend at 5cm from one end to an angle of 600,(c)a short glastube (15cm) bend at the middle to an angle of 1200,()aglass jettube (S cm). (e) a piece of rubber tube for connecting the jet tube, () the longer glass tube and (g) a suitable two-holed rubber cork (stopper) fortheflask. These parts are assembled and fitted into the flask as shown in the diagram. Middie rone Hotest purion Barrol (Burner tube) Alr holc -Arregulator Pin hole D-Side tube Basc TEST T Test tul tubes used fe 250 ml 2. BEA Beal are gla Funnel Test Tube 3. FU Beaker F e Jet Tube Short Glass Tube Rubber Tube Jet Tube 4. Long Glass Tube Rubber cork -- Washer Flask Lid Tube Bottle Parts of glass wash bottle Water Polythene wash bottle with water Glass wash bottle with wate Test for airtightness : The stoper is removcd with its fittings .About halfthe the flask is filled with water randthe stopperis replaced. The outer end ofthe is finly closed with thetip ofa finger and air is blown into theflask through .The waterlevel inthe longertube rises above the water level and remains the vshoonluemre je,it shows that the bottle is air-tight. s t e a d y wash t .Waterrises the longer tube and discharges through thejet.. s h ot e r iü. Polythene Wash bottle: The polythene wash bottle consists of an elongated bottle that screwed.The lid its through polythene tube can be inserted air-tight by whi c h a l o n, The above the lid and tube isbe the bottle and the connectedI with apolythene jettube at its outer end. Wateriis with tube screwed air-tight on to bottle. f i l e d i n By bottle ,water brought tthrough the jettube. pr e ssi n ghe THE BUNSEN BURNER How to use the in with alid 5. bottle. Air is blown into the bottle thrOugh the can be : is lid can be has a hole in centre tby means ofapolythene washer. its iis the out The bunsen burner is used for heating3purposes .Petrol gas or LPG mixedi used as the fuel. with air is Partsof the bunsen burner:The burmer, the barrel(bumer tube) and theBunsen burner consists of the base .nipple of the air regulator. 0. Base :Base is made of cast side tube called 'the gas tube`iron It keeps the burner in astable upright for the entry ofthe gas and position.It hasa can be connected through arubber tube. to the gas tap ii. Nipple of the burner : It is made of brass rod and has a Atits lower end,the nipple is screwed into fine pin-hole runing the base .The gas throughit. enters the base through the gas coming from the gas holders tube and passes through the pressure. nipple of the burner under ii, The Barrel tube): It is ametallic tube with lower end.The(Burner gas two from the air holes. passing out the nipple enters into the opposite air holes near its burner tube and mixes with air iv. :This is a Airregulator tube .It is pierced with smal metallic ring that loosely fits on the lower end of the two holes that burner tube.It can be rotated exactly burner to the two air to correspond holes of the wholly closing the air holes. regulate supply of air into the burner tube by partialy or Howto ight the The air holes are the gasescapesburner: tely closed. When the gas tapis the nipple,there iscompl affalleof sucked inthroughthrough the air holes .On and pressure a result of opened as lighting ,the gas burns with a vwhich air is The air rgultor is then ajustexd until ablue non-luminoUs flame is obtained. Non-luminous flamet Anon-uminous flnme is ustunlly used for heating lt consists of three zones. The dark blue inner ozone of unbunt gas -Mar 20 Conlcal Fsk Stoppor Nole Mrk Plpette 48 20 Noler cOck Burette Measuring Cylinder iüThe pale blue middle ozone (reducing region) of partially bunt gas and. üi.The nearly colourless outer ozone (oxidising region) of completely burnt gas .The hotest portion of theflame, about 1600 Kis near the foot ofthe oxidising region. 6. CONICAL FLASK Conicial flask is used in volumetric titrations and filtrations It has flat bottom. 7. MEASURING CYLINDER where high The measuring cylinder is used to measure out adefinite volume ofaliquid gradu precisions is not needed.It is auniformglass cylinder withaflattened base .It is is marked ated in cm or in ml begining from the bottom. The total volume ofthecylinder cm,500 cm (ml) etc.are onthetop.Measuring cylinders with capacities of 10cm,100 in availabe. stopper. Athin line etched 9. aroundthe neck indicates the volume that it can particular tempenture. Standard flasks with capacitics of 100 cm' ( ml), 250 are in commonuse. PIPETTE hold The pippette is to withdrawa definite volume ofa liquid from one intended transfer it into another.It consistssofa cylindrical bulb joined at both ends tovessel the: andy tubing.The lower (delivery) tube is drawn out to a finetip(nozzle).A mark is nar gwe around the upper (suction) into the volume ofthe pipute uptothe mark is indicatedetchea onte Bulb. 10.BURETTE t1sa long graduated glass tube of uniformbore fused with a glass stop -cock and. nozzle at the lower end. The burette is graduated in ml or cm3 from top to bottom.The graduation begins from zero at the top and proceeds downwards to fifty at the botom Each ml or cm' is sub-divided into tenequal parts. Each small division thus corespoNds to 0.1 ml or 0.lcm².