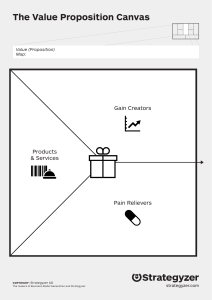
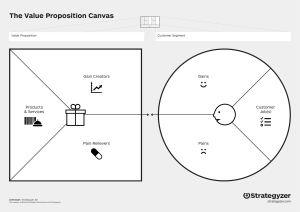
UNIT III. THE VALUE PROPOSITION Keywords: customer, customer segment, end-user, infuencer, stakeholder 3 – 2 The Value Proposition A value proposition pertains to the benefits that customers would get upon buying a product as promise by the company who owns it. A value proposition is a vital part of every company’s approach on its marketing strategy. It provides an information on consumer about a certain company’s brand by telling them the primary goal of the company, how it operates, and why it is worth trusting them. It is actually a statement which serves as a window for the consumer to see clearly what a certain brand could offer. A value proposition are sets of plans and actions that is being crafted by a company in order to market its products to the consumers. It can be introduced as business or marketing statement which when worded sufficiently can also be a very significant tools to convince a set of consumers that the products they are offering is more beneficial than others that offers the same services –thus providing a competitive edge on the part of the enterprise. In our daily living we commonly encounter value propositions from different enterprise, an example of this is thru sales talk. The words "value proposition" is credited to Michael Lanning and Edward Michaels and they originally defines it as "a clear, simple statement of the benefits, both tangible and intangible, that the company will provide, along with the approximate price it will charge each customer segment for those benefits". Visit reference number four to see a brief historical note on value proposition. 3 – 3 Value The word value in the phrase value proposition is the same value as being mentioned in Unit Two. The first aspect of value is benefit. This referred to as the needs, pain points, or problems of customers that the company will solve via offerings of solution (technology). In the original definition of value proposition, it gave reference to the word tangible benefits and intangible benefits. Tangible benefits are measurable quantities such as: sales, profits, assets, discount, etc. while intangible benefits are those which cannot be measured, example of this are customer satisfaction, morale of employees, feeling of proudness, etc. The second aspect of value is differentiation. This referred to as the advantage of a certain product over the other, the reasons that a product can be more preferable as compare to its competitor. When we want to eat outside along with families or friends. This can be done in a variety of ways. We can go to different places that offers food services; fast foods, fine dining restaurant, bar, carinderia, school canteen, or even to a street vendor offering the so-called street – foods. Each of them offers different way of satisfying our needs for food, they may have an edge over the other in terms of food quality, price, place ambience, etc. 3 – 4 Constructing a Good Value Proposition In the construction of a good value proposition, there is actually no precise rules, but the following facts and step by step scheme below could be very helpful. List down all benefits that your product could offer. Describe how these benefits could be very valuable. Determine your customer's primary needs Relate this value to your target customer’s needs. Differentiate the enterprise you belong to as the preferred provider of this value The company’s value proposition could serve as its primary competitive edge. It soundly states all important facts why the product that a certain company’s offer is a worthy choice than its competitor. Referring to reference number four, below is a successive figures illustrating a detailed guide on establishing a good value propositions. Summary The value proposition is a company’s statement that mentions all the benefits that a customer could get upon buying their products. It also illustrates its advantages over its competitor. Benefits can either be tangible or intangible. Value is measured in terms of benefits and differentiation and can be maximized when these two measurements greatly fits one another. 3 – 5 Review Questions All review questions should be submitted individually. Only two file formats are allowed; word and pdf only. Files of other format will not be accepted. Follow the scheme below for the filename: First name initial, Middle Initial, Surname underscore Activity underscore Number e.g. C.A. Cruz_Activity_1 On the last part of your files, provide a list of reference that you have used as basis for answering all questions. Use APA format for citing of reference. Plagiarism checker will be used to check your files, the minimum similarity index is 10%. For further clarification, feel free to post it on our group chat. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Define value proposition. Give three value propositions that you commonly encountered. Give the definition of value in terms of value proposition. Referring to figure 3.1, what are values that are being promised? Do you agree in the definition of value as portrayed in figure 3.1? Explain. If you agree, give some examples of it. Define tangible benefits and intangible benefits and give five examples each. A value proposition id presented as “A non – toxic paint for the interior and exterior wall of your house, a smell that will never harm your family, even babies”. Who are the customers involved here? What are the implied benefits? Give the difference between taglines/slogans to value propositions. Give three examples each of the following and give also the sources. Taglines Slogans Value Propositions