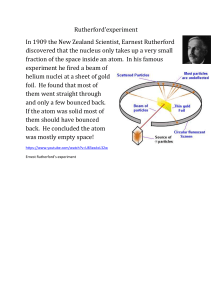
CHE1001 Applied Chemistry Lecture 2 Historical Perspective of Chemistry • By late 1800 it was well accepted that atom is the basic constituent of matter. • It was believed that nature was understood. There were no big discoveries to be made yet. • Newtonian mechanics, thermodynamics , statistical mechanics were formulated. • Maxwell equation was verified. It proposed that propose that light is an electromagnetic phenomenon J. J. Thompson •Let’s talk that atom is not the most basic constituent of matter. •So, we are going to start here with this gentle man named J. J. Thompson. •He was a British physicist and Nobel Laureate in Physics, credited with the discovery of the electron, the first subatomic particle to be discovered. •He was interested in doing what a discharge was. Cathode rays Cathode rays • He constructed a partially evacuated glass tube called cathode ray tube • Applied high electrical voltage between the two electrodes Findings1. Cathode rays travel from the negatively charged electrode to the positively charged electrode 2. The particles that compose the cathode rays travel in straight lines 3. These are independent of the composition of the material from which they originate 4. These carry a negative electrical charge Cathode rays Experiment Findings • There is a particle that is less massive than hydrogen. • You can chop the hydrogen atom up. • The atom is not the most basic constituent of matter. Rutherford Atomic Model Rutherford Experiment Rutherford Atomic Model Based on the above observations and conclusions, Rutherford proposed the atomic structure of elements. According to the Rutherford atomic model: 1. The positively charged particles and most of the mass of an atom was concentrated in an extremely small volume. He called this region of the atom as a nucleus. 2. Rutherford model proposed that the negatively charged electrons surround the nucleus of an atom. He also claimed that the electrons surrounding the nucleus revolve around it with very high speed in circular paths. He named these circular paths as orbits. 3. Electrons being negatively charged and nucleus being a densely concentrated mass of positively charged particles are held together by a strong electrostatic force of attraction. Rutherford Atomic Model Failures •Rutherford proposed that the electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed paths called orbits. • Calculations have shown that as per the Rutherford model, an electron would collapse in the nucleus in less than 10-8 seconds. So, Rutherford model was not in accordance with Maxwell’s theory and could not explain the stability of an atom. •One of the drawbacks of the Rutherford model was also that he did not say anything about the arrangement of electrons in an atom which made his theory incomplete. Classical Description of an Atom Classical Description of an Atom Classical Description of an Atom Classical Description of an Atom Failure Of Classical Mechanics Assumptions made by Quantum Mechanics Atomic Absorption Atomic Emission