NSAIDs & Acetaminophen Study Guide: Indications & Side Effects
advertisement

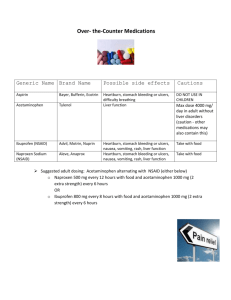
Define the meds based on the Acronym: N- naproxen S- salicylate acid A- acetylsalicylic acid I- ibuprofen & Indomethacin K- Ketorolac (Toradol) Which NSAID can be given IV per video? Ketorolac What is the indication for NSAID’s? We give NSAID’s to reduce a fever (antipyretioc) as well as anti-inflamation (typically for gout and arthritis) What is the mechanism of action? NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin response and they decrease platelet aggregation. Summarize the keypoints using acronym based on the video N- not good for the entire body S- sticky blood clots A- asthma worsening I- increase bleed risk D- dysfunctional kidneys S- swelling heart Summarize Aspirin Education: (based on video) Monitor for the toxicity, which means we are looking for tinnitus and notify the health care provider. Tinnitus is the earliest sign of aspirin toxicity. Also look out for tachycardia or hypertension, could mean a bleed (gi bleed from medication) Aspirin, avoid kids, DO NOT GIVE! Summarize Do NSAID’s alter the brain (CNS system)? Is there hypotension with the medication? Is their sedation? NSAIDS are anti-inflammatory, they do not affect the CNS (like opioids). Which means it doesn’t cause anything go low and slow (hypotension). Also means it’s not a sedative. Acetaminophen: Name some reason acetaminophen may be used instead of aspirin It might be used instead of NSAIDS/acetaminophen because of its decrease bleeding risk. That means patients with peptic ulcers or hemophilia would take acetaminophen. Which organ does acetaminophen have the potential effect? It has the potential to effect the liver, so avoid ETOH and alcoholics. Which labs should be monitored for tylenol? Watch out for ALT and AST labs.