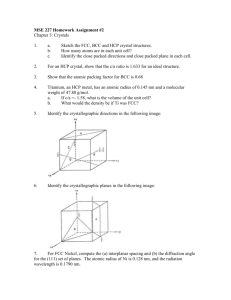
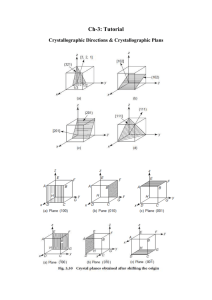
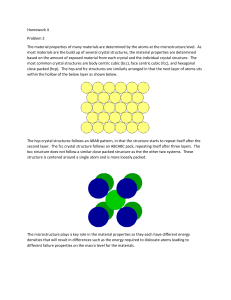
Lecture – 6 & 7 Atomic arrangements, Directions and Planes, Linear and Planar Densities Md. Fakhrul Islam Crystallographic Plane in FCC : (100) Crystallographic Plane in FCC : (110) Crystallographic Plane in FCC : (111) Determination of FCC Unit Cell Volume From the right triangle on the face Computation of the Atomic Packing Factor for FCC FCC : Linear Density [110] FCC : Linear Density [111] Determination of BCC Unit Cell Volume Centre and corner atoms touch one another along cube diagonals, and unit cell length a and aomic radius R are related through BCC : Planar Density (100) Plane BCC : Planar Density (110) Plane Crystal System Below is a unit cell for a hypothetical metal (a) The unit cell belongs to the tetragonal crystal system since a=b=0.30 nm, c=0,40nm, and a=b=g=90o. (b) The crystal structure would be called body-centered tetragonal. (c) As with BCT, n=2 atoms/unit cell, (a) To which crystal system does this unit cell belong? (b) What would this crystal structure be called? (c) Calculate the density of the material, given that its atomic weight is 141 g/mol. Determine the indices for the directions shown in the following cubic unit cells: Determine the Miller indices for the planes shown in the following unit cells: Determination of HCP Unit Cell Volume For the HCP crystal structure, show that the ideal c/a ratio is 1.633 Basal Plane in the Hexagonal unit cell Crystallographic Plane in HCP HCP : Planar Density Thanks