Cell Transport Activity: Membrane Components & Types
advertisement

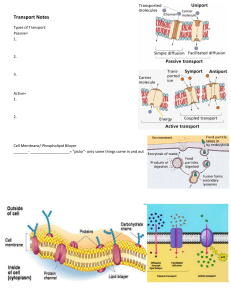
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 ACTIVITY 2 Name: Dzeethan Val B. Almoguerra Grade / Section: 12-Timios Date: 9/24/2023 CELL TRANSPORT I. Identify the cell membrane's different components and give each description below. 1. Integral Protein- reside within the bilayer membranes that surround cells and organelles, playing critical roles in movement of molecules across them and the transduction of energy and signals. 2. Peripheral Protein- a protein that is found temporarily attached to the cell or mitochondrial membrane. 3. Carbohydrate Chain- attached to various proteins and lipids and modify their functions. 4. Phospholipid bilayer- Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail. 5. Cholesterol- a waxy substance found in your blood. 6. Glycoprotein- proteins containing glycans attached to amino acid side chains. 7. Glycolipid- lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. 8. Phosphate Head- A single phospholipid molecule has a phosphate group on one end. 9. Lipid Tail- made up of esterified fatty acids. 10. BONUS II. Answer the following: Use the back of the paper. 10. What is a cell membrane? Give its functions and characteristics. The cell membrane is a dynamic, selectively permeable structure composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrate chains. Its functions include controlling substance passage, facilitating cellular communication, providing structural support, and protecting the cell. 11. What are the types of Cellular transport and give each type? Passive Transport: Diffusion: Molecules move from high to low concentration. Osmosis: Water moves through a membrane. Filtration: Molecules pass through a porous barrier. Active Transport: Primary: Uses ATP to move molecules against their gradient. Secondary (Cotransport): Indirectly uses energy. Bulk Transport: Involves vesicles. Endocytosis: Engulfing large particles. Exocytosis: Expelling substances. These processes maintain cell functions, regulating nutrient intake, waste disposal, and specialized tasks. Prepared by: Maureen Barbosa-Cabredo