Occupational Health & Safety in Workplace Presentation
advertisement

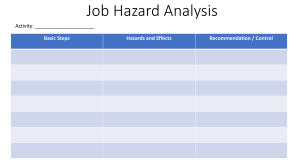
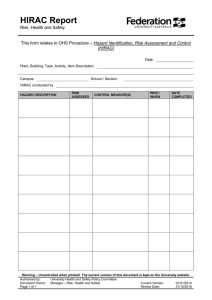
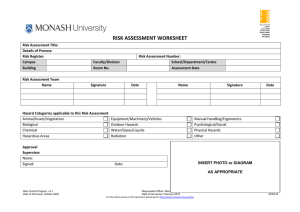
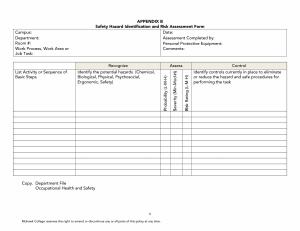
F2023 HRP103-200 Human Resource Management (Peter Villanueva) Group 5 Preet Kawal Kaur (A00149044) Manjit Kaur (A00152453) Lekha Prabakaran (A00166845) Itmam Sanjid Sparshan (A00159525) Md. Siam Sad Alif (A00151415) Occupational Health & Safety in Workplace The Importance of OHS in the Modern Workplace 1. SAFETY PROGRAMS CREATE PRODUCTIVE WORK ENVIRONMENTS: Properly managed safety programs show commitment to safety by the management in turn creating a great safety culture where everyone ‘wants’ to be safe. 2. A COMPANY’S MOST VALUABLE ASSET IS PROTECTED: A company's most valuable asset is protected its people are its strength and priority. 3. ENABLES A COMPANY TO WIN AND RETAIN BUSINESS CUSTOMERS: Safety compliance is crucial for securing the next contract with an owner-client. A well-managed and maintained safety program will help you secure future work. 4. REDUCES BUSINESS COSTS AND DISRUPTION: To reduce business costs, creating productive work environments is essential. Role of OHS in Organizational Success OHS ensures a safe and healthy work environment. Reduced accidents and injuries lead to better physical and mental health. Employee well-being contributes to job satisfaction and morale. Improved well-being enhances overall quality of life. Enhanced Employee Productivity Reduced Downtime and Costs Occupational Injury & Illness Occupational Injury: • Slip and falls • Falling objects • Malfunctioning machinery • Strains from lifting • Work-related vehicle accidents Occupational Injury: • Carpel Tunnel Syndrome • Chemical poisoning • Poison from pesticides • Asbestos Management Model of OHS The image illustrates safety management across three company levels: strategic, tactical, and operational. At the strategic level, safety policy creation, goal setting, and nurturing safety culture drive continuous improvement. In the tactical realm, training, safe environment design, and risk-reduced work processes for managers and employees are central. Operationally, adherence to safety protocols, responsive handling of accidents, and the application of corrective measures are prioritized. The image's compass symbolizes the Plan-DoCheck-Act cycle, guiding continuous learning and improvement within safety management processes. Connection Between HRM AND OHS STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT: RECRUITMENT AND SELECTION: TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT: HRM INTEGRATES OHS POLICIES WITHIN THE ORGANIZATIONAL STRATEGIES, EMPHASIZING THE IMPORTANCE OF EMPLOYEE HEALTH AND SAFETY. HRM ENSURES HIRING PRACTICES THAT CONSIDER CANDIDATE QUALIFICATIONS REGARDING HEALTH AND SAFETY STANDARDS, PROMOTING A SAFE WORK ENVIRONMENT. HRM DESIGNS PROGRAMS TO EDUCATE EMPLOYEES ON OHS REGULATIONS, PROCEDURES, AND BEST PRACTICES TO MITIGATE RISKS. EMPLOYEE WELLBEING INITIATIVES: HRM IMPLEMENTS WELLNESS PROGRAMS THAT PRIORITIZE PHYSICAL AND MENTAL HEALTH, CONTRIBUTING TO A SAFER WORKPLACE AND REDUCING ABSENTEEISM DUE TO HEALTH ISSUES. COMPLIANCE AND REGULATIONS: INCIDENT MANAGEMENT: HRM ENSURES THE ORGANIZATION COMPLIES WITH OHS LAWS, PROMOTING A CULTURE OF SAFETY AND AVOIDING LEGAL ISSUES. HRM COLLABORATES WITH OHS TEAMS TO MANAGE AND ADDRESS WORKPLACE INCIDENTS PROMPTLY, SUPPORTING AFFECTED EMPLOYEES AND IMPLEMENTING PREVENTIVE MEASURES. WHMIS & ELEMENTS OF WHMIS WHMIS stands for the Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System. It is a comprehensive system for providing health and safety information on hazardous products intended for use, handling, or storage in Canadian workplaces. Types of Hazards Biological Hazard: Biological hazards are organisms or substances produced by organisms that pose a threat to human health. Example: Pathogenic bacteria or viruses in a healthcare setting, such as HIV or Hepatitis B, are a significant biological hazard. Physical Hazard: Physical hazards are environmental factors within the workplace that can cause harm without direct contact. Example: Noise-induced hearing loss in a factory due to excessive noise levels is an example of a physical hazard. Chemical and Dust Hazard: Chemical hazards are substances that can cause harm or damage to individuals' health. Example: Exposure to toxic chemicals like asbestos in a construction site leading to respiratory issues is a significant chemical hazard. Ergonomic Hazard: Ergonomic hazards arise from improper workstation design, repetitive tasks, or uncomfortable working conditions that can lead to physical strain or injury. Example: Poorly designed workstations causing back pain. Work Organization Hazard: Work organization hazards involve issues with job design, workload, lack of control, and poor management that can affect mental and physical health. Example: High job demands leading to chronic stress or burnout among employees is an example of a work organization hazard. Safety Hazard: Safety hazards are conditions within the workplace that have the potential to cause accidents or injuries. Example: Slippery floors or exposed electrical wiring without proper insulation leading to tripping is common safety hazards. THE HIERARCHY OF CONTROLS Concepts of Violence & Source of Workplace Violence Violence: It is defined as physical assault with intent to harm or injure others. However, all aggression does not lead to violence, but intent to harm others remains at the root of violence. Source of Workplace Violence: Type 1 Violence- External Perpetrator Type II Violence- Client/Customer Type III Violence- Employment Related Type IV Violence-Domestic Violence Ways to Reduce Workplace Violence 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Complete background checks on new employees. Establish a strict anti-violence policy. Prevent conflicts from turning into harassment or violence. Encourage everyone to report any and all violent incidents. Identify organizational risk factors that could lead to violence. Conclusion Reference