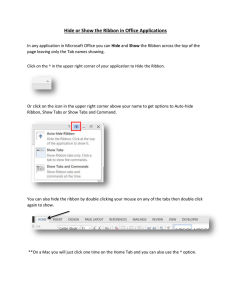
IT APPLICATION TOOLS IN BUSINESS IT APPLICATIONS INTRODUCED IT Application - refers to a program that is designed and developed to facilitate the work handling of users. It is also called Application Program or Application Software. - - an application can manipulate text, numbers, audio, graphics, and a combination of these elements. Made up of many interrelated programs. Purpose of IT Application in Business intended to aid users in accomplishing and fasttracking theexecution of their tasks. These software include the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Productivity Tools Database Software Multimedia Software Educational Software Simulation Software Enterprise Software Productivity tools - also known as office automation tools, are prominently used by personnel in most offices as such are considered being essentials in the disposal of daily tasks. Includes: word processors, spreadsheets, and presentation applications. Most Popular: Microsoft Office Suite Others: WPS Office Suite, MobiSystems Suite RELATIONSHIPS OF PROCESSES, PROCEDURES, AND BUSINESS RULES Every organization is made up of many complex business processes which may be broken down into basic business processes. Procedure - sequence of action steps which a functionary undertakes to perform a work function. - LOTUS 1-2-3 - One of the first spreadsheets and used to be very popular. should indicate Inputs, Files, Outputs and Smart Devices Used. Cell - is a point of intersection of a row and a column in the table. Procedural Steps - best described with narrative form of action statements instead of flowchart or structured English form for better understanding of Functionary/User. PURPOSE OF SPREADSHEETS 1. functions, 2. computations, 3. statistical analysis 4. formatting BUSINESS RULES a procedural step may be conditional or unconditional. in the case of a conditional procedural step, a business rule should be provided. Business rules provide the policies for handling different conditions. algorithms and formulae are also provided to stipulate decision-actions. therefore, a conditional procedural step is qualified by its decision-action policies called business rules. PROGRAM LOGIC FORMULATION is the process of creating a specific program logic that will carry out a required computing work or solve an issue utilizing a computer. This process involves selecting the best approach. - Sequential flow of procedures in order to carry out a given job or function. - Requires an in-depth understanding of how something is to be done to produce an expected output. Written in procedural steps (numbered procedures) format which are qualified as to whether each step is conditional or unconditional in nature. - The use of flowchart depicts procedural steps in graphical form. ESSENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND FEATURES OF A SPREADSHEET INTRODUCED Functions - pre-defined formulas in a spreadsheet which perform calculations in the order specified by its parameters. Function SUM AVERAGE COUNT COUNTA IF TRIM MAX and MIN Description It usually aggregates values from a selection of columns or rows from your selected range. Reminds you of simple averages of data, such as the average number of shareholders in a given shareholding pool. Counts all cells in a given range that contain only numeric values. Counts all cells in a given rage. However, it counts all cells regardless of type. Often used when you want to sort your data according to a given logic. Makes sure your functions do not return errors due to extra spaces in your data. It ensures that all empty spaces are eliminated. Help in finding the maximum number and the minimum number in a range of values. Functionary – personnel assigned to perform basic business processes. EXPLORING THE USE OF SPREADSHEETS WORD FOR DUMMIES Business Process - defined by its component Work Functions which are performed to respond to a given request. SPREADSHEET - computer application for computation, organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. - Developed as computerized analogs of paper-based accounting worksheets. Starting Word the Traditional Way RELATIONSHIPS OF PROCESSES, PROCEDURES, AND BUSINESS RULES 1. Press the Windows key on the keyboard. 2. Look for Microsoft Word on the Start menu. 3. Click the Word icon or button to start the program. Starting Word the Best Way 1. Find the Word icon on the Start menu. 2. Right-click the Word icon. 3. Choose the command More, Pin to Taskbar. Opening a Document to Start Word 1. Locate the Document icon. 2. Double-click the icon. Working the Word Start screen You can use the Start screen to open a previously opened document, start a new document based on a template, or start with a blank document. Template - document that contains preset elements, such as formatting, styles, text, and possibly graphics. Ribbon - where a majority of Word’s commands dwell and where settings are made. Showing and Hiding the Ribbon Use the Ribbon Display Options menu, located in the upper right area of the Word window and illustrated in Figure 1-3. Choose an item to determine how to display the Ribbon. Your choices are 1. Auto-Hide Ribbon: The most annoying choice, the Ribbon appears only when you hover the mouse pointer near the top of the document. 2. Show Tabs: With this choice, only the Ribbon’s tabs appear. Click a tab to show the bulk of the Ribbon, which disappears again after you’ve chosen a command. 3. Show Tabs and Commands: This option shows the entire Ribbon — tabs and commands — as illustrated in Figures 1-2 and 1-3. To temporarily hide the Ribbon, click the Collapse the Ribbon button, Working With Word on a Tablet If you’re using Word on a tablet, you can adjust the spacing between buttons on the Ribbon by activating Touch mode. 1. Click or touch the Customize Quick Access Toolbar button. 2. Choose Touch/Mouse Mode. Changing the Document View Print Layout view - standard way to view a document. Other Views are: 1. Read Mode: The Ribbon and pretty much the rest of Word is hidden while in Read mode. 2. Web Layout: This view presents your document as a web page. 3. Outline: This mode helps you organize your thoughts. 4. Draft: Draft view presents only basic text, not all the formatting and fancy features, such as graphics. To switch between Read Mode, Print Layout, and Web Layout views, click one of the View buttons, found in the lower right corner of the Word program window. When your document looks weird in the Word program window, switch back to Print Layout view to fix the problem. Click the Print Layout button on the status bar, or click the View tab and choose Print Layout in the Views group. Making Text Look Larger or Smaller Zoom Command - To set specific zoom sizes, click the 100% button on the status bar. Use the Zoom dialog box to set a size based on percentage, page width, or even multiple pages. Cajoling Word to Help You Help system - Press the F1 key to summon this support, which displays the Word Help pane on the side of the document window. There you can type a topic, a command name, or even a question in the box to search for help. Little buttons that look like question marks appear in various places in the program. Click one of these buttons to also summon Word Help. Tell Me What You Want to Do help box on the Ribbon - Type a topic or question in the box and press the Enter key to see a quick list of commands or suggestions, or to obtain online help.