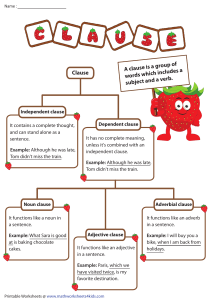
Clauses BY ASEP SAEPULOH, S.S., M.PD How do you translate these sentences? The woman who lives next door is a registered nurse. That dog that you found belongs to the Olsons. Larry's letter, which he mailed Tuesday, reached me on Thursday. Math, which is Dave's favorite subject, has always been easy for him. What is clause? Group of words that forms part of a sentence, has a subject & a predicate of its own Kinds of Clause Clause Independent Clause Subordinate Clause Independent of Clause An independent (or main) clause expresses a complete thought. It can stand by itself as a sentence. It has both a subject and a verb. Examples Halle ate a late dinner. Kevin went to the movies. Travis and Eric gave donations to help others. Savannah collected money. Mercy offered us a ticket. Subordinate of Clause A subordinate (or dependent) clause does not express a complete thought. It does have a subject and a verb. Examples But… it cannot stand alone as a sentence. after Kedon ate dinner because Mary saved the drowning girl when Amy gave a party that we thought was right before Sam left the room whom Mrs. Brooks knew Types of clause Types of Clause Adjective clause Adjective Clause – is a subordinate clause used as an adjective to modify a noun or pronoun Adverb clause Adverb Clause – is a subordinate clause used as an adverb to modify an adjective, adverb, or a verb Noun clause Noun Clause – is a subordinate clause used as a noun. Adjective Clause Play the role of an adjective Examples: The umbrella with a broken handle is mine (phrase) The umbrella which has a broken handle is mine (clause ) Adjective clause is a clause that modifies a noun or a pronoun. It begins with a relative pronoun. Some clauses function as modifiers in the same way adjective and adjective phrases do. Adjective clauses give more information about a noun or pronoun. They are easy to find because they usually begin with these words: These words are relative pronouns. Ellen is the girl who wishes to study law. She reads everything that she can on the subject. Her aunt, who is a lawyer, encourages her. Adjective Clause Function Simple Forms Examples Who Subject person • The people live next door. • They are good neighbors. The people who live next door are good neighbors Whom Object person • He is the man. • We all respect him. He is the man whom we all respect Whose Possessivit y • Do you know the woman? • His picture is in the magazine. Do you know the woman whose picture is in the magazine? Which Thing • The game was played yesterday. • It ended in a tie. The game, which was played yesterday, ended in a tie. Where Place • I visited the town. • They met there. I visited the town where they met When Time • The boat leaves. • The time is not yet fixed. The time when the boat leaves is not yet fixed That Person/thi ng • She bought the cake. • It was delicious. The cake that she bought was delicious Identifying Adjective Clauses. Underline the adjective clause in each of the following sentences. Circle the word it modifies. Example: The book that he wrote has just been published. 1. Mike, whose ancestors came from Ireland, marched in the St. Patrick's Day parade. 2. Williamsburg, Virginia, is a place that I'd like to visit. 3. Summer, which is my favorite season, will be here in another week. 4. Phil is reading The Call of the Wild, which is Jack London's most famous book. 5. We live just twenty miles from O'Hare Airport, which is the world's busiest airport. 6. Newton, Iowa, is the town where Barbara was born. 7. I'm taking golf lessons from Erika Lavery, who is a pro at the country club. 8. Mr. Hartman is a history teacher who also coaches track. 9. The Harveys have a dog that is fourteen years old. 10. For dinner, we had chicken fried steak, which is my favorite dish. Find and copy the adjective clauses in the following sentences. Underline the relative pronoun. Tell what word each clause modifies. 1. The boy who sits next to Sally asked her for a book. 2. He told a story that was absolutely unbelievable. 3. Amy saw a bird that she couldn’t identify. 4. Ms. Finkelstein is a teacher who works very hard. 5. The girl who won the Debating Club award is planning to go to law school and enter politics later. 6. The Diary of Anne Frank is the book that I read. 7. Lan-Hua Yin is a friend whom I always trust. 8. The jester performed tricks that amused the monarch. Adverbial clause An adverb, and adverb phrase, and an adverb clause can modify a verb, and adjective, or another adverb. Adverbs and groups of words that function as adverbs answer where, when, why, how, and how much. Adverb : Suddenly, we were completely lost. Adverb phrase : We were lost in an underground cave. Adverb clause : After Lonnie fell and broke the compass, we were lost. Adveb clauses begin with a special kind of connective called a subordinating conjunction. After As long as Since Though When Wherever Although Because So that Unless Whenever Whether As Before Than Until Where While As if If That A clause that modifies a verb, and adjective, or and an other adverb is an adverb clause. An adverb clause begins with a subordinating conjunction. Find and copy the adverb clause in each of the following sentences. Underline the subordinating conjuction. 1. She pointed a rainbow on the closet door when she redecorated her room. 2. No one can go into the kitchen until the floor dries. 3. Whenever I stay up late, I become very hungry. 4. Carl is baby-sitting and looking for other jobs because he needs the money. 5. Since Alison moved away, no one has heard from her. Noun clause A noun clause does the work of a noun. A noun clause may function as a subject, a direct object, a predicate noun, or an object of a preposition. Mr. Jorgensen showed us his repair kit. Mr. Jorgensen showed us how he repairs television sets. Another example of noun clauses. What you say interest me. (subject) Kathy knows when the dog is hungry. (direct object) Here is a list of what I need. (object of preposition) Copy the following sentences. Underline the noun clauses. 1. His parents give him whatever he wants. 2. The police suspect that the witness is lying. 3. I hope that you are right. 4. The solution is that Regina play the part. 5. He eats whatever he finds in the referigator. 6. Please take whichever one you like.