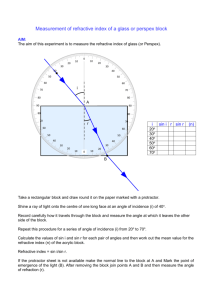
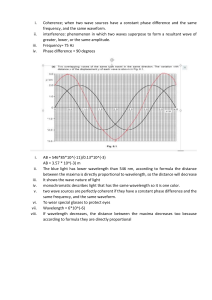
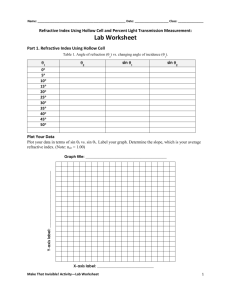
Electricity E= P x T Electrical Energy(J)= Power(w) x time(s) Q= I x T Charge= Current x time E = W/Q Electromotive force(V)= Energy Supplied to the charge of the power source (J) / charge on each carrier (C) V=W/Q Potential difference (V) = Energy transfer to the components from the charge carrier(J) / Charge on each carrier (C) Ohms Law: R=V/I Resistance (Ω) = voltage (v) /current (A) R = K x L (length) Resistance is directly proportional to length. R = K/A Resistance is inversely proportional to the cross section area. Series: Resistance (total)= R1+R2+R3… Current (total)= I1=I2=I3… Parallel: 1/resistance(total)= 1/R1+1/R2+1/R3… Current total= I1+I2+I3… Voltage total= V1+V2+V3… Wave F=1/T Frequency (hz)= 1/period(s) V=λ x f V=Wave speed (m/s) λ=Wavelength(m) f= frequency (hz) Wave speed(m/s)=Wavelength(m) x Frequency(hz) n= C/V Refractive index = Speed of light in Vacuum (3x10^8m/s) / Speed of light in medium n= sin i/sin r refractive index= incident angle/refractive angle