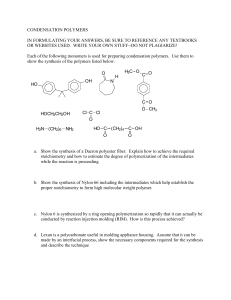
Lesson objective: Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Key Words: Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw . the structure of proteins. • • • • Monomer Polymer Addition polymers Condensation polymers Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Definition POLY Mer + Units Many Polymer Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. ➢Very large molecules having high molecular mass (103-107u). ➢The repeating structural units are derived from monomers and are linked to each other by covalent bonds. ➢This process of formation of polymers from respective monomers is called polymerisation. 4 Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. TYPES OF REACTIONS POLYMERISATION Addition Polymerisation Condensation Polymerisation Unsaturated Monomer undergo Bi-Functional monomer undergo polymerization. polymerization. Examples Examples: Nylon-6,6 Polythene Polyester Polypropene Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. 5 Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Addition polymerisation or Chain Growth Polymerisation Molecules of same monomer or different monomers add together on a large scale to form polymer. The monomers are unsaturated compounds eg : polyethene Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. 6 Lesson objective: Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Formation of poly(ethene) All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Ethene-Monomers Polyethene-Polymer Lesson objective: All Describe the ) differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Condensation Polymerisation or step growth polymerisation It involves a repetitive condensation reaction between two bi-functional monomers with the loss of some simple molecule like water,alcohol etc. In this reaction product of each step is again bifunctional . Since each step produce distinct species ,this is also called step growth polymerisation. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. 9 Lesson objective: All Describe the ) differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Forming Nylon •Nylon is a polyamide made from dicarboxylic acid monomers (a carboxylic with a -COOH group at either end) and diamines (an amine with an NH2 group at either end) •Each -COOH group reacts with another -NH2 group on another monomer •An amide linkage is formed with the subsequent loss of one water molecule per link Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Lesson objective: Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Forming Polyesters All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. •PET or polyethylene terephthalate to give its full name, is a polyester made from dicarboxylic acid monomers (a carboxylic with a -COOH group at either end) and diols (alcohol with an -OH group at either end) •Each -COOH group reacts with another -OH group on another monomer •An ester linkage is formed with the subsequent loss of one water molecule per link Most Describe and draw •For every ester linkage formed in condensation polymerisation, one molecule of water is formed from the structure of the combination of a proton (H+) and a hydroxyl ion (OH–) addition and •PET is also used in synthetic fibres as is sold under the trade name of terylene condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Deducing the polymer from the monomer • Polymer molecules are very large compared with most other molecule • Repeat units are used when displaying the formula • To draw a repeat unit, change the double bond in the monomer to a single bond in the repeat unit • Add a bond to each end of the repeat unit • The bonds on either side of the polymer must extend outside the brackets (these are called extension or continuation bonds) • A small subscript n is written on the bottom right hand side to indicate a large number of repeat units • Add on the rest of the groups in the same order that they surrounded the double bond in the monomer Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. •Deducing the monomer from the polymer • Identify the repeating unit in the polymer • Change the single bond in the repeat unit to a double bond in the monomer • Remove the bond from each end of the repeat unit Lesson objective: Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Plastics & their Disposal All Describe the ) differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. •Synthetic polymers are ones made in a factory, for example nylon, terylene and lycra •Nylon is a polyamide used to produce clothing, fabrics, nets and ropes •PET, also known as Terylene, is a polyester made from monomers which are joined together by ester links •PET is used extensively in the textile industry and is often mixed with cotton to produce clothing Lesson objective: All Describe the ) differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Non-biodegradable plastics •These are plastics which do not degrade over time or take a very long time to degrade, and cause significant pollution problems. •In particular plastic waste has been spilling over into the seas and oceans and is causing huge disruptions to marine life •In landfills waste polymers take up valuable space as they are non-biodegradable Most Describe and draw so microorganisms cannot break them down. This causes the landfill sites to the structure of quickly fill up. addition and •Polymers release a lot of heat energy when incinerated and condensation produce carbon dioxide which is a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate polymers. change •If incinerated by incomplete combustion, carbon monoxide will be produced Some which is a toxic gas that reduces the capacity of the blood to carry oxygen Describe and draw •Polymers can be recycled but different polymers must be separated from each the structure of other which is a difficult and expensive process. proteins. Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. PET Re-polymerisation •PET stands for polyethylene terephthalate, a common polymer used to make things like plastic bottles •It is a condensation polymer consisting of repeating ester units, so it is type of polyester, like terylene •One of the problems with recycling polymers is that the condition needed to break them down, which are usually high temperatures and pressures, can degrade the monomers making them unusable for re-polymerisation •PET is relatively easy to convert back into the monomers •It can be depolymerised either using enzymes or by chemical methods •Enzymes present in microbes breakdown the PET into the original monomers •The same can be achieved using solvents a catalyst and mild heating Lesson objective: Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. The breakdown of PET into its two monomers takes place using enzymes or chemical catalysts and mild conditions •The monomers are recovered and be polymerised into new PET •This saves on resources and energy, reducing the carbon footprint of the production process Lesson objective: Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Proteins All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. •Proteins are condensation polymers which are formed from amino acid monomers joined together by amide links (in proteins also known as a peptide link) similar to the structure in nylon •The units in proteins are different however, consisting of amino acids •Amino acids are small molecules containing NH2 and COOH functional groups General structure of an amino acid •There are twenty common amino acids, each differing by their side chain, represented by R •Proteins can contain between 60 and 600 of these amino acids in different orders •These are the monomers which polymerise to form the protein Lesson objective: All Describe the ) differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Lesson objective: All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers. Check your progress 1. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Ans 1 1 Lesson objective: 2 All Describe the differences between addition and condensation polymerization. Most Describe and draw the structure of addition and condensation polymers. Some Describe and draw the structure of proteins. Describe the structure and bonding in polymers.
![\t<L Your Name: _[printed]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/013223479_1-5f2dc062f9b1decaffac7397375b3984-300x300.png)