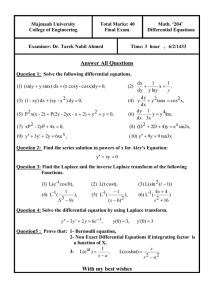
Identifying Strategies of Jio Telecom by Ankit Kumar (2019IMG-007) Submitted in partial Dr. Gaurav Agrawal ABV INDIAN INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT GWALIOR-474 015 2023 1. Introduction Jio Telecom, a subsidiary of Reliance Industries, stands as a pioneering force in the Indian telecommunications sector, reshaping the industry landscape with its introduction in 2016. Led by Chairman and Managing Director Mukesh Ambani, the company has not only provided affordable 4G services but also diversified into an array of digital products and services. 2. History ● Founded in 2016 by Reliance Industries, Jio Telecom aimed to transform the telecommunications landscape by delivering high-quality yet affordable services to the masses. In September 2016, the company made a groundbreaking entry into the market, offering free voice calls and remarkably low-cost data plans, triggering a surge in subscribers and compelling established competitors to adapt. ● Jio Telecom swiftly expanded its 4G network infrastructure nationwide, reaching even remote areas and providing internet access to millions who were previously underserved. This rapid expansion played a pivotal role in establishing Jio as a key player in India's telecom sector. ● Jio introduced a suite of digital services to complement its telecom offerings. Notable services include JioTV, JioCinema, and JioSaavn, providing customers with a comprehensive entertainment experience. This strategic move enhanced customer engagement and diversified the company's portfolio. ● In 2020, Jio made significant strides in diversifying its business portfolio. The introduction of JioMart, an online grocery delivery platform, marked the company's entry into the e-commerce sector. Simultaneously, Jio Platforms attracted substantial investments from global technology giants, including Facebook and Google, solidifying Jio's position at the intersection of telecommunications and technology. ● Jio's disruptive entry into the market not only redefined industry standards but also forced competitors to reevaluate their strategies. The company's innovative pricing models and commitment to widespread connectivity reshaped consumer expectations and set new benchmarks for the telecom sector. 3. Industry Analysis This section elucidates the industry landscape in which Jio operates. It explores the transformative influence of Jio Telecom, a subsidiary of Reliance Industries, on the sector, highlighting the introduction of affordable 4G services, a suite of digital products, and the subsequent diversification into e-commerce and technology. Fig. 3.1 - Telecom Market Share FY-22 Fig. 3.2 - Number of wireless telecommunications subscribers in India by service provider Fig. 3.3 - Comparison between data usage and data tariff for Jio Fig. 3.4 - Revenue vs Year for Jio Fig. 3.5 - Tele-density(%) vs Year for Jio 3.1 Porter’s Five Forces ● Threat of New Entrants(Moderate) ○ Capital Requirements: The telecom industry demands significant capital for network expansion and technological upgrades. Larger players enjoy cost advantages, while smaller entrants face monumental financial challenges, especially in keeping pace with rapid technological changes. ○ Product Differentiation: In a sector with limited product differentiation, players seek to stand out through strategic partnerships and value-added services. Reliance Jio, for instance, collaborates with platforms like Amazon Prime, Hotstar, and Netflix to offer unique content experiences, showcasing a differentiated approach. ○ Switching Cost: Low switching costs in the telecom sector enabled Jio to attract 50 million subscribers within 83 days of launch swiftly. Predatory pricing strategies and a seamless Mobile Number Portability (MNP) process played a crucial role in eroding the market positions of established players. ○ Brand Identity: While brand loyalty has some impact, the telecom industry's sensitivity to pricing makes it less influential. Jio's entry resulted in a substantial decline in incumbent subscriber bases, indicating that price considerations often outweigh brand loyalty. ○ Access to Distribution Channel: Ease of access to distribution channels is facilitated by strategic planning. Jio, for instance, leveraged Aadhaar-based digital SIM activation and later introduced home delivery, streamlining its distribution channels. ● Bargaining Power of Buyers(Strong) ○ Low Information Asymmetry: Consumers in the telecom industry are well-informed, leading to significant pressure on operators. With easy switching options, customers with awareness of competing carriers can exert considerable influence on their current operator. ○ T-Services Crucial to Buyers: Telecommunication services have become critical across various industries, increasing the bargaining power of buyers. The ease of switching carriers and the importance of telecom services amplify customer influence. ○ Operators Concentration: With only four major players dominating the Indian market, operators enjoy a degree of concentration. Regulatory bodies like TRAI and DOT ensure a balanced playing field, preventing the formation of a monopoly. ○ Low Switching Cost: The low switching cost contributes less to reducing the commanding position of buyers, allowing flexibility in choosing telecom operators. ● Bargaining Power of Suppliers(Strong) ○ Concentrated Suppliers: The dominance of Huawei and ZTE as T-Equipment providers, especially in the 5G network rollout, presents a concentrated supplier scenario. The Indian government's restrictions on Chinese giants create an opportunity for European players, potentially altering supplier dynamics. ○ Backward Integration of Reliance Jio: Reliance Jio's backward integration into developing its 5G solutions reduces dependence on foreign vendors. Acquisitions and in-house development diminish the bargaining power of traditional T-Equipment suppliers. ○ Status Quo of Airtel and Vi: Huawei's diminishing role in the 5G network rollout increases the bargaining power of Vi and Airtel's suppliers, raising switching costs and dominance of suppliers. ● Rivalry among Players(Strong) ○ No Clear Leader and Few Players: The absence of a clear leader and the presence of a limited number of major players (Jio, Airtel, Vi) contribute to significant rivalry. Despite Jio's market leadership, industry dynamics still need to establish a clear leader. ○ High Fixed Costs: High fixed costs, particularly in spectrum auctions and network expansion, intensify competition. The capital-intensive nature of the telecom business adds to the rivalry among operators. ○ Moderately Differentiated Offerings: Limited differentiation in telecom products prompts operators to introduce innovative services like free OTT subscriptions. However, offerings remain moderately differentiated, contributing to competitive intensity. ○ High Exit Barriers: Exiting the telecom sector poses challenges, with regulatory approvals and asset sales complexities. High exit barriers hinder companies from winding up operations quickly. ● Threat of Substitutes(Weak) ○ Voice Communication: An alternative for voice communication through transmission equipment has yet to be discovered globally. However, in the future, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AIML) may introduce a novel technique for voice communication, potentially replacing traditional transmission equipment. It's important to note that any such technology would be subject to control by regulatory bodies like TRAI, and its distribution would likely be restricted to carriers. Consequently, there is currently no substitute for this product that would exert pressure on the profitability of incumbent operators. ○ Data and Internet Services: In Internet communication, cable TV and satellite operators emerge as contenders for the same consumer base. Cable providers, utilising direct lines into homes, offer broadband internet services, while satellite links provide alternatives to the high networking services delivered by telecom operators. Despite this competition, these substitutes do not pose significant pressure on the profitability of the telecom industry. The impact on profitability from these substitutes is notably minimal. 4. SWOT Analysis Examining Reliance Jio's internal strengths and weaknesses, coupled with external opportunities and threats, provides a comprehensive SWOT analysis, offering valuable insights into the company's strategic positioning within the telecommunications industry. 4.1 Strengths 1. Strongest Strategy for Customer Acquisition: Reliance Jio's most potent strategy for customer acquisition lies in its innovative and disruptive pricing model. By offering free trials and extremely affordable data and voice plans during its launch, Jio rapidly attracted millions of subscribers, setting a benchmark for customer acquisition in the Indian telecommunications market. 2. Huge Customer Base: Jio boasts an extensive and rapidly growing customer base, with millions of subscribers nationwide. This sizable customer base not only reflects the success of its customer acquisition strategies but also provides a significant competitive advantage, creating a robust foundation for the company's market presence and influence. 3. Reliance Industries Parent Company's Strong Backing: As a subsidiary of Reliance Industries, one of India's largest conglomerates, Jio benefits from robust financial backing and strategic support. This backing empowers Jio to invest heavily in infrastructure, technology, and expansion, contributing to its resilience and competitiveness in the dynamic telecommunications sector. 4. Jio Owns Pan India License, Spectrum Valid Until 2035: Jio holds a pan-India license for telecommunications services, allowing it to operate across the country. Additionally, the spectrum owned by Jio is valid until 2035, providing long-term strategic advantages in terms of network stability, service continuity, and the ability to plan for future technological advancements. 5. Strong Brand Management: Jio has effectively managed and cultivated a robust brand image since its inception. Through strategic partnerships, innovative digital services, and a focus on customer experience, Jio has positioned itself as synonymous with affordability, innovation, and reliability, contributing to customer loyalty and trust in the market. 4.2 Weakness 1. Anti-Competitive Predatory Pricing: Reliance Jio has faced criticism for adopting anti-competitive predatory pricing strategies, leveraging extremely low-cost plans and free trial offers during its entry into the market. While these tactics attracted a massive customer base, they also raised concerns about their impact on fair competition within the telecommunications industry. 2. Too Many Freebies: Jio's extensive use of freebies, such as free voice calls and data during its initial launch, has been both a strength and a point of contention. While it contributed significantly to customer acquisition, the sustained provision of freebies raised questions about the long-term sustainability of such promotional strategies and their potential impact on industry dynamics. 3. Late Entry into the Telecom Market: Reliance Jio entered the telecommunications market later than some competitors. While its disruptive entry reshaped the industry, the late start meant that Jio had to play catch-up in terms of network infrastructure and market share, facing established competitors who had already established their presence. 4. People with No Access to Smartphones: Jio's reliance on data-driven services and smartphone usage could pose a challenge in reaching individuals with no access to smartphones. As smartphone penetration in certain segments of the population remains limited, this could potentially limit Jio's reach and market share in specific demographic segments. 4.3 Internal Logic ● ● ● ● ● ● Jio offered all its customers their services free for 3-6 months. In the first 170 days of its launch, it managed to reach a subscriber base of 100 million customers. (W1) Strong backing from Reliance Industries allows Jio to bring aggressive strategies. (S1) Providing data services at low prices to attract more customers. Jio currently provides many free services, and that is one of the reasons for the increased market share. (S3) Jio uses VoLTE technology, which can support 6G as well. (S4) Jio focuses on providing a stable and efficient network with zero connectivity issues in all 22 telecom circles in India. (W3) 4.4 Opportunities 1. 5G and 6G Technologies: Reliance Jio's potential adoption and integration of 5G and future 6G technologies represent strategic opportunities for staying at the forefront of technological advancements. Embracing these cutting-edge technologies could enhance network capabilities, provide faster and more reliable services, and position Jio as an industry leader in the evolving landscape of telecommunications. 2. Competitive Strategy for Pricing: Jio's competitive strategy for pricing has been a critical driver of its success in the Indian market. Continuously innovating and adapting pricing models to offer affordable yet robust services will be crucial for maintaining and expanding its customer base. Implementing flexible and attractive pricing structures can give Jio a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving telecom industry. 3. Expansion to Other Countries: Exploring opportunities for expansion into other countries presents a strategic avenue for Reliance Jio's growth. Leveraging its experience and success in the Indian market, Jio could replicate its business model in regions with similar market dynamics, establishing a global footprint and diversifying its revenue streams. 4. Foreign Investment Opportunities: Foreign investment opportunities can further strengthen Reliance Jio's financial position and support its ambitious growth plans. Actively seeking partnerships or investments from international entities can provide not only the necessary capital but also bring invaluable expertise and technology, contributing to Jio's competitiveness on a global scale. 4.5 Threats 1. Customer Loss Risk on Price Increase or Removal of Free Services: There is a potential risk for Reliance Jio in terms of customer loss if it decides to increase prices or remove certain free services. Given the market's sensitivity to pricing and the competitive landscape, any such move must be carefully managed to mitigate the risk of customer churn. 2. Criticism and Negative Image: Reliance Jio may face criticism and negative public perception, especially if its business practices, service quality, or pricing strategies are perceived as unfair or detrimental to consumers. Maintaining a positive image through transparent communication and customer-centric policies mitigates reputational risks. 3. Weak Code of Ethics: A weak or perceived lack of a robust code of ethics could expose Reliance Jio to ethical and governance challenges. Establishing and enforcing a robust ethical framework is essential to ensure compliance, build trust among stakeholders, and mitigate risks associated with potential ethical lapses. 4. TRAI Regulations: Compliance with Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) regulations is imperative for Reliance Jio. Adhering to regulatory standards ensures legal standing and prevents potential legal challenges, penalties, or sanctions that may arise from non-compliance with industry-specific guidelines. 5. Government Policies and Health Policies Regarding Radio Frequencies: Reliance Jio may face challenges from government policies, especially those related to radio frequencies used for telecommunication services. Changes in regulations or health policies related to radio frequencies could impact the company's operations. Staying informed and adapting to evolving policies is crucial to mitigate risks associated with regulatory changes. 4.6 External Logic 1. Embracing 5G and 6G technologies as opportunities for bandwidth expansion (O3). 2. Maintaining competitive pricing strategies in response to market dynamics (T1). 3. Exploring international expansion options in neighbouring regions (O1). 4. Leveraging India's cultural diversity to attract foreign investors (T4). 5. Prioritising customer service excellence and efficient MNP processes (O2). 6. Navigating regulatory and policy changes, such as TRAI regulations and government policies, as potential threats to the business (O4). 5. Jio’s Strategy This segment discusses Jio's strategic approach, emphasising its disruptive innovation, unwavering commitment to affordability, and visionary pursuit of accessibility. 5.1 Jio’s 2A and 3R strategy Reliance Jio adopted the strategy by Mr C.K Prahald (The fortune at the bottom of the Pyramid), which targeted the bottom of the pyramid. Jio decided that addressing the needs of the average and below-average earners in the market would garner maximum profit. Jio's operational framework revolved around a 2A and 3R strategy, strategically focusing on Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Referral, and Revenue. ● Acquisition: Jio's innovative approach commenced with providing a free 3-month service, leading to a remarkable addition of 16 million subscribers within just one month. ● Activation: Jio prioritised ensuring users had an unprecedented experience, setting a new standard in telecom service provision. ● Retention: To maintain customer loyalty, Jio extended its free trial period for an additional three months, reinforcing its commitment to customer satisfaction. ● Referral: Jio's commitment to exceptional customer service and user experience transformed its customers into ardent advocates, pivotal in the company's extraordinary growth. ● Revenue: Jio disrupted the market by slashing prices to one-tenth of the existing cost, catapulting its revenue and securing a substantial leap in market prominence. 5.2 Jio’s Digital Marketing Strategy Reliance Jio boasts a solid digital marketing presence, with over 960k Instagram followers, 2.36 million YouTube subscribers with regional language ad campaigns, and 2.5 million Facebook followers. However, their Twitter following of 666k lags behind their top competitor, suggesting room for improvement, while YouTube and Facebook stand out as their primary strengths. ● ● Digital India, Home Delivered: Jio's campaign reached 26 million potential customers in 20 weeks. The campaign achieved a Click-Through Rate (No. of clicks divided by total views or impressions) of 0.72%, three times the industry average. Jio generated nearly 30,000 leads daily, setting a high standard in the industry. Jio Cheers Cricket: The campaign was rolled out to increase the hype of the India-Pakistan Match. They leveraged the Thunderclap tool for a broad reach, prompting #JioforIndia to trend on Facebook and Twitter. The campaign achieved over 24.8 million organic reach and received over 35,000 messages across various platforms. 5.3 Financial Figures Fig. 5.1- Profit vs Year for the last five quarters Fig. 5.2- Number of Jio Subscribers in India over the year 6. Competitive Advantage of Jio ● ● ● Disruptive Pricing: Jio's disruptive pricing transformed the market with remarkably low data and voice tariffs, pushing competitors to reexamine their pricing. In 2022, Jio's 4G data average revenue per user (ARPU) was Rs. 128, well below the industry average of Rs. 161, showcasing their commitment to affordable data services for a broader audience. Extensive Coverage: Jio's 4G network offers unparalleled coverage, spanning over 99% of India's population, even in remote regions. With more than 35% market share in 4G cell sites in 2022, Jio's extensive network is a formidable competitive edge, enabling widespread access to high-speed data services throughout the country. Vertical Integration: Jio's vertical integration and development of its 5G technology have led to cost savings, greater network control, and performance enhancements. By using its 5G tech for backhauling and offloading 4G traffic, Jio offers higher-quality 4G services and expands its feature set, including ultra-fast speeds and low latency, benefiting both the company and its customers. This strategic move has proven successful in reducing reliance on third-party vendors and enhancing overall network capabilities. 7. Conclusion Jio Telecom, a disruptive force in the Indian telecommunications market, has rapidly emerged as a critical player, reshaping the industry landscape. The company's success is grounded in its strategic approach of delivering affordable and high-quality services, effectively addressing the diverse needs of Indian consumers. Since its inception, Jio has employed innovative pricing models and a commitment to customer satisfaction, leading to substantial growth and a considerable impact on the telecommunications sector. The company's transformative strategy has not only garnered a significant market share but has also set new standards for accessibility and affordability in the rapidly evolving Indian telecom market.