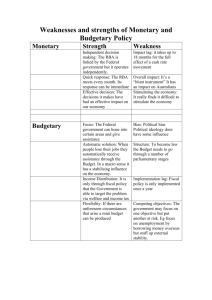
Assignment 5 EC2406 – Empirical Methods in Economics I Exercise 1 You are interested in learning more about economic growth in your country. a) Download time series data on the real GDP in Sweden between 2000 and 2020. Make sure that you obtain quarterly data and that you state the source for your data (where did you find it?). Read the data into STATA and prepare it to be able to analyze it. b) Plot the data (the time series of the quarterly GDP) and provide a screenshot. c) Briefly describe the data. Which patterns can you detect? d) There is an upward trend in Sweden’s GDP over time, so it is nonstationary. To find out if the nonstationarity is due to stochastic or deterministic trends, which test should you run and what is the result? e) Based on your answer in d), what can you do to correct for the nonstationarity in GDP? Exercise 2 The policy rate is the central bank’s key monetary policy tool to control inflation. How quickly the monetary policy can affect inflation, then, is of major concern to central banks. You are interested in the lag in the transmission of the policy rate to the mortgage rate of a small commercial bank. Specifically, your research question is: how long does the change in the central bank policy rate take to affect the 1-year mortgage rate of Danske bank in Sweden? The questions that follow guide you through the steps in finding the answer to your research question. a) You have data on the following two variables. – 𝑑𝑎𝑛𝑠𝑘𝑒𝑡 : 1-year mortgage rate of Danske Bank, monthly frequency Source: Compricer – 𝑟𝑖𝑘𝑠𝑏𝑎𝑛𝑘𝑡 : Riksbank policy rate, monthly frequency Source: Bank of International Settlements These two variables are plotted below. From the figure, why would you be concerned that they might have unit roots? 1 b) You decide to perform the Dickey-Fuller test of unit roots. For 𝑑𝑎𝑛𝑠𝑘𝑒, the p-value of this test is 0.0453 and for 𝑟𝑖𝑘𝑠𝑏𝑎𝑛𝑘, it is 0.0046. Do the two variables suffer from stochastic trends? c) You think that the p-values from the Dickey-Fuller tests are still too large (it is common that the p-value from this test is 0.0000), and you want absolutely no doubt about the variables having unit roots. How would you transform the variables? d) Write down the specification of the Distributed Lag model which you can use to estimate the lag in the pass-through of policy rate on Danske Bank’s mortgage rate, for lags of up to 12 months. e) You are actually interested in the cumulative dynamic multiplier. How would you transform the Distributed Lag model in d)? f) In order for the coefficient estimates to capture the true causal cumulative effects, I need to ensure that Δ𝑟𝑖𝑘𝑠𝑏𝑎𝑛𝑘 is exogenous, i.e. 𝑢𝑡 cannot be correlated with Δ𝑟𝑖𝑘𝑠𝑏𝑎𝑛𝑘𝑡 , Δ𝑟𝑖𝑘𝑠𝑏𝑎𝑛𝑘𝑡−1 , Δ𝑟𝑖𝑘𝑠𝑏𝑎𝑛𝑘𝑡−2 , ..., Δ𝑟𝑖𝑘𝑠𝑏𝑎𝑛𝑘𝑡−12 . There are five possible causes of bias in the coefficients. Discuss whether you would be worried about each: 1. Measurement error in Δ𝑟𝑖𝑘𝑠𝑏𝑎𝑛𝑘𝑡 2. Sample selection bias 3. Functional form misspecification 4. Simultaneity bias 5. Omitted variable bias 2 g) To estimate the specification in d) or e), why do you need to use HAC (heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation-consistent) standard errors? h) The following is the plot of the dynamic cumulative multiplier that you obtained from the specification in e). What can you say about the lag in the transmission from the policy rate to Danske’s mortgage rate? i) What can you say about external validity of this study? 3