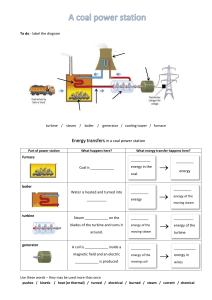
STEAM TURBINE By group :- Ruqaya Raad Abbas Talib Zahraa Awad Huda Ahmed Hala Adil Naba'a Tariq Dr. Aws AL-Akam INTRODUCTION TO STEAM TURBINES Steam turbines are used in all of our major coal fired power stations to drive the generators or alternators, which produce electricity. The turbines themselves are driven by steam generated in ‘Boilers‘ or ‘Steam Generators‘ as they are sometimes called. Energy in the steam after it leaves the boiler is converted into rotational energy as it passes through the turbine. The turbine normally consists of several stages with each stage consisting of a stationary blade (or nozzle) and a rotating blade. Stationary blades convert the potential energy of the steam (temperature and pressure) into kinetic energy (velocity) and direct the flow onto the rotating blades. The rotating blades convert the kinetic energy into forces, caused by pressure drop, which results in the rotation of the turbine shaft. STEAM TURBINE PART The main parts of a steam turbine are : the rotor that carries the blading to convert the thermal energy of the steam into the rotary motion of the shaft the casing, inside of which the rotor turns, that serves as a pressure vessel for containing the steam (it also accommodates fixed nozzle passages or stator vanes through which the steam is accelerated before being directed against and through the rotor blading) the speed-regulating mechanism the support system, which includes the lubrication STEAM TURBINE PRINCIPLE In simple terms, a steam turbine works by using a heat source (gas, coal, nuclear, solar) to heat water to extremely high temperatures until it is converted into steam. As that steam flows past a turbine’s spinning blades, the steam expands and cools. The potential energy of the steam is thus turned into kinetic energy in the rotating turbine’s blades. Because steam turbines generate rotary motion, they’re particularly suited for driving electrical generators for electrical power generation. The turbines are connected to a generator with an axle, which in turn produces energy via a magnetic field that produces an electric current. TYPES OF STEAM TURBINE The two types of steam turbines most widely used are the backpressure and the extractioncondensing types .The choice between backpressure turbine and extractioncondensing turbine depends mainly on the quantities of power and heat, quality of heat, and economic factors. The extraction points of steam from the turbine could be more than one, depending on the temperature levels of heat required by the processes. ADVANTAGES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. S Ability to utilize high pressure and high temperature steam. High efficiency. High rotational speed. High capacity/weight ratio. Smooth, nearly vibration-free operation. No internal lubrication.Soil free exhaust steam. Can be built in small or very large units (up to 1200 MW). DISADVANTAGES Although approximately 90% of all electricity generation in the world is by use of steam turbines, they have also some disadvantages :1. Relatively high overnight cost 2. Steam turbines are less efficient than reciprocating engines at part load operation. 3. They have longer startup than gas turbines and surely than reciprocating engines. 4. Less responsive to changes in power demand compared with gas turbines and with reciprocating engines. APPLICATION Steam turbines are part of various industries, from medium to large, and include dozens of institutional applications:1. 2. 3. 4. Chemical Industry: Providing heat and electricity to drive various processes In the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, steam turbines are integrated into the power production process. Waste plants: Steam turbines help generate the energy needed to harness energy from waste. Oil and Gas: Steam turbines are used as a pump or compressor motor, and support dozens of processes in the oil and gas industry Sugar Mills: Steam turbines offer high levels of efficiency and sustainable operations, and are used to produce green carbon dioxide energy from bagasse. THANK YOU