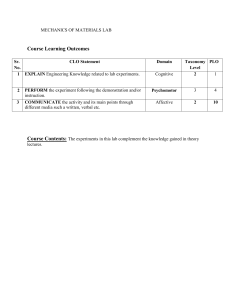
Xavier Institute of Management XIM University Course Name Macroeconomic Theory and Policy (MTP) Programme Batch Term Credits Course Instructor MBA-BM 2023-25 Second Three Prof. Biswa Swarup Misra 1. Course Introduction and Objectives This course introduces the key economic principles and theories which help to understand how the macro economy works. We will focus on five key macroeconomic indicators i.e. growth, employment, inflation, interest rates and exchange rates which help to assess the state of the macroeconomy of a country. The discussions in the class would be oriented to appreciate the factors governing the above five indicators, theories that study the inter-relationship among these indicators. Being a course designed for managers, emphasis will be on the discussion of theories that explain the short term fluctuation in economic activity. The efficacy of monetary and fiscal policies which are used as stabilization measures will be discussed in the course. The theories governing trade and effectiveness of monetary, fiscal and trade policies under different exchange rate frameworks will covered in the course. The discussion will be centering round the Indian context so that participants can relate what is covered in the classroom to what is happening around them in the real life situations and appreciate the subject of discussion. 2. Course Content The significancy of studying macroeconomics Introduce key macroeconomic indicators which help to assess the state of the macroeconomy of a country How economic activity is measured and what are the limitations associated with them How price pressure in the economy is assessed How unemployment is measured in an economy What factors govern whether a country is rich or poor How we depict equilibrium of an economy Why economic activity fluctuates in the short run Why there is a need for economic policy and how economic activity can be stabilized using policy Under what conditions monetary policy is more effective than fiscal policy How the central banks controls money supply in an economy 1 How interest rates and exchange rates are determined in an economy Should countries promote free trade What is Balance of Payment crisis and why it occurs 3. Course Learning Outcomes (CLO) CLO 1: Learn to measure performance of an economy through key macroeconomic indicators. CLO 2: Understand the characteristics of business cycles CLO 3 Understand how the central banks controls money supply in the economy CLO 4 Understand how government influences economic activity CLO 5 Learn efficacy as well limitations of monetary and fiscal policy in stabilizing economic activity CLO 6: Understand the theoretical basis for trade and implications of monetary, fiscal and trade policy under fixed and flexible exchange rate frameworks. 4. Session Plan Sessions Topics Session Learnings Session-1 What Macroeconomics is all about and Why we should be studying macroeconomics Sessions 2- Measuring the 3 Value of Economic Activity through National Income Accounting Sessions 45 Distinction between GDP at Reading Materials Distinction between Micro Presentation Slides and Macro economics Important Macroeconomic Variables: Growth, Inflation, Unemployment Kinds of Macroeconomic Policy: Monetary and Fiscal Distinction between Stock and Flow Distinction between Output and Wealth Circular flow of Income Concepts of GDP, GNP, NDP, NNP Interrelations amongst different concepts of GDP Reading Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 10 Nominal vs. real GDP Implication of Rebasing Reading Principles of Macroeconomics - 2 Presentation Slides Session-6 Current prices and Constant prices Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 10 GDP Deflator based Inflation Presentation Slides Case let GDP at 2011-12 base Limitations of GDP as a measure of economic welfare Session-7 Inflation: Measuring Price pressure in an Economy Sessions-8 Meaning and and 9 measurement of Unemployment GDP at basic price, market price and factor cost GDP at 2011-12 baseMethodological Changes Limitations of GDP Prices are not values. Nonmarket activities are excluded. The shadow economy is missing. Environmental degradation isn’t counted. Leisure doesn’t count. GDP ignores distribution. Reading Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 10 Meaning of Inflation Measurement Inflation through alternate indicators in India- GDP Deflator, WPI, CPI-IW,CPIAL, CPI-Rural, Cpi -Urban and CPI-Combined Biases in measurement of Inflation Costs of inflation Reading Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 11 Computation of Labour Force Participation rate and Unemployment rate Typology of Unemployment-Frictional, Structural Cyclical and Natural rate of unemployment Unemployment Measurement in India Usual Status, CDS, CWS Readings Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 15 3 Presentation Slides Presentation Slides Presentation Slides Session-10 Why trade is beneficial for an Economy Session-11 Capturing interaction of an economy with the rest of the world through the Balance of Payments Session-12 Supply side approach to Growth-Factors that determine living standards of countries Session-13 Determination of equilibrium income The absolute advantage theory The comparative advantage theory Reading Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 3 Presentation Slides Current, Capital and Financial Account in the BoP Classification of credit and debit entries in BoP Why Balance of Payments always balances Concept of deficit in the BoP How exchange rates are determined Role of different factors on exchange rate Purchasing power parity theory of exchange rate Reading Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 18 Long run determinants of Growth through production function Importance of Productivity Concept of Natural Rate of Output Catch up effect and Convergence of Income across nations Proximate and Ultimate causes of growth Role of Institutions in Growth Reading Income and Expenditure model to determine Equilibrium Income Concept of Multiplier Role of fiscal policy in equilibrium income Reading 4 Presentation Slides Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 12 Presentation Slides Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 21 Session 14- Business Cycles and 16 Monetary and Fiscal Policy to Stabilise economic activity Session-17 How money supply is defined and is influenced through policy Fiscal Policy and Its Presentation Slides Limitations Schools of Macroeconomic Thought-Mercantilism, Classical, Marxian, Neoclassical and Keynesian Stylized facts about Short run economic fluctuations Predicting business cycles with leading Indictor Analysis. Real Business Cycle Theory Framework of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate supply to study business cycles. Models of aggregate supply Sticky wage, Sticky Price and the ImperfectInformation models Aggregate supply CurveShort run vs. Long run Hard Landing vs. Soft Landing Use of monetary and fiscal Policy to stabilize economic activity Four step approach to study economic fluctuations Demand pull vs Cost push Inflation Stagflation Reading Money-Functions The definition of Money Banks and Money Supply Deposit Multiplier Role of Central banks in influencing money supply Money Multiplier Reading 5 Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapters- 20 and 21 Presentation Slides Teaching Notes Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 16 Presentation Slides Session18-19 How output and interest rates are decided in an Economy through the IS-LM Model Session 20 Exchange Rate Determination Alternate characterization of goods market equilibrium: SavingInvestment equality vs. Equilibrium Derivation of the IS Curve The theory of liquidity Preference Derivation of the LM Curve Equilibrium in the short run Impact of monetary and fiscal policy on short run equilibrium Reading Macroeconomics Mankiw (10th edition) Exchange rates; Fixed vs. Flexible Dirty Floating or Managed Exchange rate regime Mundell- Fleming model Effectiveness of monetary vs fiscal policy under fixed and flexible exchange rate regimes Impossible Trinity Reading Macroeconomics Dornbusch, Fisher and Statrtz (11th edition) Presentation slides Principles of Macroeconomics Mankiw (8th edition) Chapter- 18 Presentation Slides 5. Readings and References Text Book (Readings from these Books are Mandatory): 1. Principles of Economics: Mankiw (Eighth Edition), 2017. Cengage 2. Macroeconomics: Mankiw (Ninth Edition), 2015. Worth Publishers Further Readings: Latest edition of the following Books 1. Macroeconomics - Abel and Bernanke 2. Macroeconomics: Dornbusch, Fischer, and Startz. Tata McGraw-Hill 3. Macroeconomics: Principles and policy: Baumol and Blinder, South-Western Publishing. 4. Macroeconomics: Olivier Blanchard, Pearson Education 6 Assessment Scheme Component Weight (Per cent) Assessment of Course Leaning Outcome(s) Review Quizzes 10 CLO 1, CLO 2, CLO 3 and CLO 4 Quizzes 25 CLO 1, CLO 2, CLO 3 and CLO 4 Mid Term 20 CLO 1, CLO 2, CLO 3 and CLO 4 End Term 30 CLO 1, CLO 2, CLO 3 and CLO 4 Class Notes 10 CLO 1, CLO 2, CLO 3 and CLO 4 Classroom Engagement 5 CLO 1, CLO 2, CLO 3 and CLO 4 7. Academic Discipline and Integrity Students are expected to come to class on time. Students are expected to come to the class prepared after doing the necessary preparatory studies Late coming will award no attendance and sometimes barring from the class, if the reason for coming late is found not satisfactory. Utmost care will be taken to maintain class decorum, follow the exact evaluation norms, conduct fair examinations, fair and transparent evaluation of examination papers, etc. 8. Mapping Course Leaning Outcomes (CLO) with the Program Learning Goals (PLG) PLG# Program Learning Goals Trait PLG 1 Functional and Business Skills The students will demonstrate understanding of elements of all functional areas 7 Addressed by Course Yes No PLG 2 Analytical Skills PLG 3 Collaboration and Teamwork Attributes PLG 4 Ethical Responsibility PLG 5 Communication The students will use analytical techniques to identify a business problem, and suggest a solution The students will exhibit voluntary cooperation and effective teamwork in a group setting The students will understand the ethical complexities of conducting business. The students will adopt techniques in scenarios involving ethical dilemma and offer resolution The students will produce reasonably good quality business documents. The students will become effective and confident communicators 8