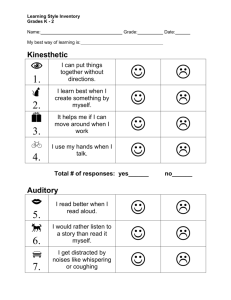
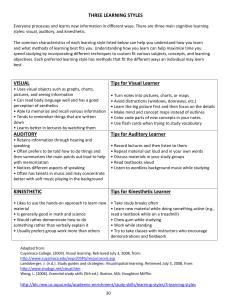
LEARNING STYLES Learning styles is a theory that suggests people learn better using different methods of learning. We perceive information using our senses. The three most practical senses in learning environments are sight, hearing and touch. The VAK model categorizes these sensory methods of learning as Visual (V), Auditory (A) and Kinesthetic (K) learning styles. While most people have a dominant learning style, nobody has just one learning style. Everyone uses each of the learning styles to some degree. Some are stronger in one style while others have even strength in all styles. The reality is that we all have a custom “learning style” that is, in varying degrees, a combination of Visual, Auditory and Kinesthetic learning. It is useful to know the strength of your learning styles as they relate to each other. This allows you to focus on maximizing your learning potential. Recognizing your strengths also helps you to seek learning opportunities that cater to your combination of learning style strengths. In recent years, many educators have started using knowledge of learning styles (and multiple intelligences) to improve teaching methods in order to reach learners of all types. VISUAL LEARNING STYLE Visual learning is a style in which a learner utilizes graphs, charts, maps and diagrams. It is one of the three basic types of learning styles in the Fleming VAK/VARK model that also includes kinesthetic learning and auditory learning.[1] If you use the visual style, you prefer using images, pictures, colors, and maps to organize information and communicate with others. You can easily visualize objects, plans and outcomes in your mind's eye. You also have a good spatial sense, which gives you a good sense of direction. You can easily find your way around using maps, and you rarely get lost. When you walk out of an elevator, you instinctively know which way to turn. Visual learners are those who learn things best through seeing them. Visual learners often prefer to sit in the front of the class and "watch" the lecture closely. Often, these students will find that information makes more sense when it is explained with the aid of a chart or picture. A visual learner: • • • • • • • • Is good at spelling but forgets names of people you see only occasionally. Needs quiet study time and enjoys being alone. Has to think and ponder before understanding a speech or lecture. Likes colors & fashion. Dreams in color. Understands/likes charts. Is good with sign language. Is creative and may enjoy creating artwork or writing stories. AUDITORY LEARNING STYLE If you are an auditory learner, you learn by hearing and listening. You understand and remember things you have heard. You store information by the way it sounds, and you have an easier time understanding spoken instructions than written ones. You often learn by reading out loud because you have to hear it or speak it in order to know it. As an auditory learner, you probably hum or talk to yourself or others if you become bored. People may think you are not paying attention, even though you may be hearing and understanding everything being said. Auditory learners retain information more thoroughly when the information is reinforced through sound. Auditory learning methods could include anything from using musical notes to memorize lists, to using voice recordings or chants to memorize history terms. Students with strong auditory learning preferences may prefer listening class lectures over reading assigned segments of a difficult text. They may struggle to understand a chapter that covers a complex topic, but then experience a full understanding as they listen to the same information as it is delivered through a class lecture. An auditory learner may benefit from using the speech recognition tool available on many PCs and on cell phones. Auditory learners may have a knack for ascertaining the true meaning of someone's words by listening to audible signals like changes in tone. When memorizing a phone number, an auditory learner will say the numbers out loud and then remember how the series of numbers sounded to recall it. If this sounds familiar to you, you might be an auditory learner! You may be an auditory learner if you are someone who: • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Likes to read to self out loud. Is not afraid to speak in class. Likes oral reports Is good at explaining Remembers names Notices sound effect in movies Enjoys music Is good at grammar and foreign language Reads slowly Follows spoken directions well Can’t keep quiet for long periods Enjoys acting, being on stage Is able to memorize lines for a skit easily Is good in study groups Auditory Learners Can Benefit from: • • • • • • • • Using word association to remember facts and lines. Recording lectures. Using the recording feature of a cell phone to memorize lists and terms. Watching videos. Repeating facts with eyes closed. Participating in group discussions. Using audiotapes for language practice. Taping notes after writing them. KINESTHETIC LEARNING STYLE The bodily kinesthetic learning style is one of eight types of learning styles defined in Howard Gardner's theory of Multiple Intelligences. Bodily kinesthetic learning style or intelligence refers to a person's ability to process information physically through hand and body movement, control, and expression. It is also known as the physical learning style or tactile-kinesthetic learning style. Characteristics • • • • • • • • Bodily kinesthetic learners prefer bodily information over other forms. Movement serves as an aid to their memory and they remember movement from others as well as their own. They may seek out touching and manipulating objects when learning about them. Kinesthetic learning styled people enjoy school activities such as drawing, modeling, sculpting, drafting, shop, athletics, dance, and hands-on sciences. Bodily kinesthetic learners enjoy creating work with their hands, may have a lot of energy and need to move, and may be talented athletes. People with bodily kinesthetic learning styles learn best when they are permitted to use their tactile senses and fine and gross motor movement as part of the learning process. They often prefer direct involvement with the material they are learning rather than worksheets or reading from a book. Bodily kinesthetic learning style students understand and remember material longer when they use it in an active way. • • • • • • • • The act of writing can also help them retain and process the information they are writing about. Writing an answer to a question before saying it out loud may be of value to them. Interacting with a computer or keyboard is also of more interest to them than reading. Projects that involve the student in creating displays and props that explain subject matter, such as shadow boxes, models, animations, or videos may be useful to them. They may like to create a game to review information. They will enjoy taking things apart and constructing things. Acting out subjects, role-playing games, demonstrations, and experiments and lab work will be of more interest to them. Students may enjoy field trips and scavenger hunts. They often enjoy physical games, exercise, dance, drama, and sports. They do less well when the learning is focused only on reading or listening to lecture without being able to manipulate an object or move. In such cases, a teacher might offer a sports-related example so the student can at least connect the material to physical actions. The bodily kinesthetic learning style student may be drawn to careers that involve physical interaction. In health professions, these can include surgery, nursing, physical therapy, occupational therapy, emergency medical technician, and recreation therapy. In the arts, this can include being an actor, dancer, artist (painting, sculpting), craft artist, or designer. Physical education and sports professions include athletic coach, personal trainer, aerobics instructor, physical education teacher, and professional athlete. Trades include carpentry, woodworking, mechanic, and factory work with moving systems. Other professions include a postal carrier, firefighter, police officer, forest ranger, or the military.