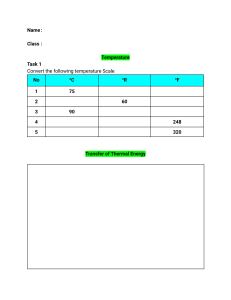
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DESCRIPTIVE QUESTIONS (As per Bloom’s Taxonomy) Name of Course Instructor :Dr. K.AppaRao Course Name & Code : Heat Transfer &17ME 20 UNITS : I Program/Sem/Sec : B.Tech., ME., VI-Sem., Sections- A A.Y : 2019-20 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Q.No. Question Description (Minimum 10 Questions) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. CO BL Formulate the general 3-dimensional heat conduction equation in Cartesian coordinate system. Deduce the general 3-dimensional heat conduction equation in Cylindrical coordinate system. Develop the expression for critical radius of insulation for cylinder What is overall heat transfer coefficient and express the relation for plane and cylinder? Derive general heat conduction equation in spherical coordinate system. Obtain the expression for 1D-steady state heat transfer for plane wall and explain CO1 the terms involved. Distinguish the Conduction, Convection and Radiation mechanisms Explain the physical significance of thermal conductivity, convective heat transfer coefficient, thermal diffusivity, thermal resistance, thermal conductance and thermal contact resistance. Obtain the expression for 1D-steady state heat transfer for composite cylinder when it exposes to inside and outside heat transfer coefficient and explain the terms involved. How the thermal conductivity is varied for solids, liquids, gases and insulating materials when temperature is raised. Discuss it with physical mechanisms. Class/Tutorial/ Date Assignment L1 Class L3 Assignment L3 L1 Tutorial Class L3 L3 Assignment Tutorial L2 L2 Assignment Class L3 Assignment L4 Assignment Note: BL-Bloom’s Taxonomy Level (L1/L2/L3/L4/L5/L6) Course Instructor Course Coordinator Module Coordinator HOD Dr.P.Ravindra Kumar Dr.P.RavindraKumar Dr.P.VijayKumar Dr.S.Pichi Reddy DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL 1QUESTIONS (As per Bloom’s Taxonomy) Name of Course Instructor : Dr. P.Ravindra Kumar Course Name & Code : Heat Transfer &17ME 20 UNITS : I Program/Sem/Sec : B.Tech., ME., VI-Sem., Sections- C A.Y : 2019-20 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Q.No. Question Description (Minimum 10 Questions) 1. 2. 3. 4. CO BL A furnace wall consists of an inside layer of silica brick 10 cm thick (k = 6.28 kJ/m hr0C) and magnasite brick thickness 5 cm (k = 20.35 kJ/m hr0C) on the outside. The inside surface of the silica brick wall is maintained at 750 0C while the outside surface of magnasite is at 125 0C. What is the rate of heat loss per unit area of the wall? Also calculate the temperature at the interface. A pipe carrying steam at 2300 C has an internal diameter of 12 cm and the pipe thickness is 15 mm. The conductivity of the pipe material is 49 W/m K. The convective heat transfer coefficient on the inside is 85 W/m2 K. The pipe is insulated by two layers of insulation one of 5 cm thickness of conductivity 0.15 W/m K and over it another 5 cm thickness of conductivity 0.48 W/m K. The outside is exposed to air at 35 0C with a convective coefficient of 18 W/m2 K. CO1 Determine heat loss for 5 m length. Also determine the interface temperatures and the overall heat transfer coefficient based on inside and outside temperatures An insulated pipe of 50 mm outside diameter (ε=0.8) is laid in a room at 30 0C. If the surface temperature is 250 0C and the convective heat transfer coefficient is 10 W/m2 K. Calculate the heat loss per unit length of the pipe by considering convection and radiation. A hollow sphere is made up of two materials; first with k=70 W/m K is having an I.D. of 10 cm and O.D. of 30 cm and the second with k=15 W/m K, forms the outer layer with O.D. of 40 cm. The inside and outside temperatures are 300 0C and 30 0C respectively. Estimate the rate of heat flow through this sphere assuming perfect contact between two materials. Class/Tutorial/ Date Assignment L3 Tutorial L3 Tutorial L3 L3 Tutorial Tutorial Course Instructor Course Coordinator Module Coordinator HOD Dr.P.Ravindra Kumar Dr.P.Ravindra Kumar Dr.P.VijayKumar Dr.S.Pichi Reddy DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Quiz Questions (Combination of Multiple Choice(Single & Multiple Answers), Fill in the Blanks and matching type) Name of Course Instructor : Dr. K.AppaRao Course Name & Code Program/Sem/Sec : Heat Transfer &17ME 20 : B.Tech., ME., VI-Sem., Sections- A UNITS : I A.Y : 2019-20 Q.No. Question Description(Minimum 10 Questions) 1. 2. Unit of thermal diffusivity is (1). m²/hr (2). m²/hr °C (3). kcal/m²hr (4). kcal/m. hr °C Thermal conductivity of wood depends on (1). Moisture (2). Density (3). Temperature (4). All of the above Ans 1 4 3. The unit of overall coefficient of heat transfer is (1). W/m²K (2). W/m² (3). W/mK(4). W/m 1 4. The transfer of heat by molecular collision is smallest in (1). Solids (2). Liquids (3). Gases (4). None of these 3 5. Fourier's law of heat conduction gives the heat flow for (1). Irregular surfaces (2). Non-uniform temperature surfaces (3). One dimensional cases only (4). Two dimensional cases only Unit of thermal conductivity in M.K.S. units is (1). K cal/kg m² °C, (2). K cal m/hr m² °C (3). K cal/hr m² °C (4). K calm/hr °C 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Which of the following statement is wrong? (1). The heat transfer in liquid and gases takes place according to convection (2). The amount of heat flow through a body is dependent upon the material of the body (3). The thermal conductivity of solid metals increases with rise in temperature (4). Logarithmic mean temperature difference is not equal to the arithmetic mean temperature difference Thermal conductivity of non-metallic amorphous solids with decrease in temperature (1). Increases (2). Decreases (3).Remain constant (4). May increase or decrease depending on temperature Heat transfer takes place as per (1).Zeroth law of thermodynamics (2).First law of thermodynamics (3). Second law of thermodynamics(4).Fouriers law of heat conduction The heat transfer by conduction through a thick sphere is given by (1). Q = 2πkr1 r2 (T1 - T2)/ (r2 - r1) (2). Q = 4πkr1 r2 (T1 - T2)/ (r2 - r1) (3).Q = 6πkr1 r2 (T1 - T2)/ (r2 - r1) (4).Q = 8πkr1 r2 (T1 - T2)/ (r2 - r1) In descending order of magnitude, the thermal conductivity of a. Pure iron, b. Liquid water, c. Saturated water vapour, and d. Pure Aluminium can be arranged as (1). a b c d (2).b c a d (3). d a b c (4).d c b a Consider the following statements: The Fourier heat conduction equation Q=- kA dT/dxpresumes a. Steady-state conditions b. Constant value of thermal conductivity. c. Uniform temperatures at the wall surfaces d. One-dimensional heat flow. 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 4 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. Of these statements: (1) a, b and c are correct (2) a, b and d are correct (3) b, c and d are correct (4) a, c and d are correct Assertion (A): Cork is a good insulator. Reason (R): Good insulators are highly porous. (1) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A (2) Both A and R individually true but R in not the correct explanation of A (3) A is true but R is false (4) A is false but R is true A furnace is made of a red brick wall of thickness 0.5 m and conductivity 0.7 W/mK. For the same heat loss and temperature drop, this can be replaced by a layer of diatomite earth of conductivity 0.14 W/mK and thickness (1) 0.05 m (2) 0.1 m (3) 0.2 m (4) 0.5 m A plane wall is 25 cm thick with an area of 1 m2, and has a thermal conductivity of 0.5 W/mK. If a temperature difference of 60°C is imposed across it, what is the heat flow? (1) 120W (2) 140W (3) 160W (4) 180W A copper block and an air mass block having similar dimensions are subjected to symmetrical heat transfer from one face of each block. The other face of the block will be reaching to the same temperature at a rate: (1) Faster in air block (2) Faster in copper block (3) Equal in air as well as copper block (4) Cannot be predicted with the given information For a given heat flow and for the same thickness, the temperature drop across the material will be maximum for (1) Copper (2) Steel (3) Glass-wool (4) Refractory brick A steel ball of mass 1kg and specific heat 0.4 kJ/kg is at a temperature of 60°C. It is dropped into 1kg water at 20°C. The final steady state temperature of water is: (1) 23.5°C (2) 300°C(3) 35°C (4) 40°C Which one of the following expresses the thermal diffusivity of a substance in terms of thermal conductivity (k), mass density (ρ) and specific heat (c)? (1) k2ρc (2) 1/ρkc(3) k/ρc(4) ρc/k2 When heat is transferred from one particle of hot body to another by actual motion of the heated particles, it is referred to as heat transfer by (1) Conduction (2) Convection (3) Radiation (4) Conduction and convection Heat transfer in liquid and gases takes place by (1) Conduction (2) Convection (3) Radiation (4) Conduction and convection Which of the following is the case of heat transfer by radiation? (1) Blast furnace (2) Heating of building (3) Cooling of parts in furnace (4) Heat received by a person from fireplace Pick up the wrong case. Heat flowing from one side to other depends directly on (1) Face area (2) Time (3) Thickness (4) Temperature difference 1 2 1 2 3 1 3 1 2 4 3 24. The critical radius is the insulation radius at which the resistance to heat flow is (1) Maximum (2) Minimum (3) Zero (4) None of these 2 25. Cork is a good insulator because it has (1) Free electrons (2) Atoms colliding frequency 4 (3) Low density (4) Porous body Note: As per GATE, IES, NPTEL, etc type Questions Course Instructor Course Coordinator Module Coordinator HOD Dr.P.Ravindra Kumar Dr.P.Ravindra Kumar Dr.P.VijayKumar Dr.S.Pichi Reddy DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Topic Covered through ICT Name of Course Instructor Course Name & Code Program/Sem/Sec : : Dr. P.Ravindra Kumar : Heat Transfer &17ME 20 : B.Tech., ME., VI-Sem., Sections- C Slide-1 Slide-2 Slide-3 Slide-4 Slide-5 Slide-6 Date: UNITS : I A.Y : 2019-20 Course Instructor Course Coordinator Module Coordinator HOD Dr.P.Ravindra Kumar Dr.P.Ravindra Kumar Dr.P.VijayKumar Dr.S.Pichi Reddy