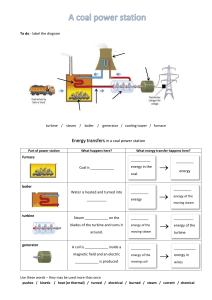
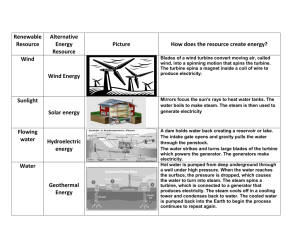
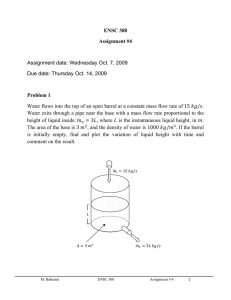
EXERCISE 1 The report is mandatory for the exam Part 1 Calculate the energy density for these forms of energy. Natural gas, Hu= 8 570 kcal/Nm³, 𝜌 = 0,8 𝑘𝑔/𝑁𝑚3 𝑘𝑔 Coal, Hu= 6000 kcal/kg, 𝜌 = 1300 𝑚3 Wind, 𝜌 = 1,2 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 𝑣 = 10 𝑚/𝑠; 𝑘𝑔 𝑘𝐽 Air, thermal energy, 𝜌 = 0,53 𝑚3 , 𝑇 = 400°𝐶, 𝑐𝑝 = 1,09 𝑘𝑔𝐾 Water flow, kinetic energy, 𝜌 = 1000 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3, 𝑣 = 10 𝑚/𝑠; Water, potential energy, h= 400 m, 𝜌 = 1000 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 Part 2 Calculate the energy and power density of the energy conversion systems listed below and represent the points corresponding to the calculated values on a diagram Ev-PA • • • • • • • • • • • • • Combustion chamber for steam generator Convection superheater Steam condenser Pelton turbine Kaplan turbine Centrifugal pump Steam turbine element with reaction degree 0.5 Axial gas turbine element 4-stroke naturally aspirated petrol engine 2-stroke supercharged slow diesel engine Wind turbine Solar collector (PA only) BWR nuclear reactor Combustion chamber for steam generator (suppose that 35% of the generated thermal energy is exchanged by radiation in the combustion chamber, the remaining energy flows through the other heat exchangers): gas pressure 1.02 * 105 N/m2; temperature 1600 K; air / fuel ratio 17; flue gas velocity 16 m/s; gas density 1.1 * air density in the same thermodynamic conditions; irradiation constant 4 W/(m2 K4); external temperature of the evaporator pipes 673 K; Hu = 10000 kcal/kg. Convection superheater (65% of the thermal energy generated in the combustion chamber passes through this element): α = 42 W/(m2 K); flue gas temperature 1150°C to 900°C; steam temperature from 470°C to 538°C. Steam condenser: pressure 0.05 bar; steam density 0.035 kg/m3; α = 4000 W/(m2 K); rx = 500 kcal/kg = 2.1 * 106 J/kg; steam speed 100 m/s. Turbines and pumps Pelton turbine Kaplan turbine Centrifugal pump Steam turbine stage Gas turbine stage ϕ 2.0 0.4 0.12 0.4 0.7 ψ 2.0 0.1 0.5 1.0 1.0 u[m/s] 80 70 70 300 300 ρ[kg/m3] 103 103 103 0.05 1.1 • 4-stroke naturally aspirated petrol engine: 𝑣𝑚 = 14 𝑚/𝑠; ∆= 14; 𝜂 = 0,27; 𝐻𝑢 = 10000 𝑘𝑐𝑎𝑙/𝑘𝑔. • 2-stroke supercharged slow diesel engine: 𝑣𝑚 = 6.7 𝑚/𝑠; ∆= 38; 𝜂 = 0,42; 𝜌 = 2,78 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 ; 𝐻𝑢 = 9500 𝑘𝑐𝑎𝑙/𝑘𝑔. • Wind turbine: 𝑣 = 10 𝑚/𝑠; 𝜌 = 1,2 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 . • Solar collector: 𝑃𝐴 = 1000 𝑊/𝑚2 . • BWR nuclear reactor: 𝜌 = 104 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3; 𝑃𝐴𝑆 ≤ 1000 𝑘𝑊/𝑚2; 𝐸ℎ = 2,38 ∗ 1012 𝐽/𝑘𝑔.