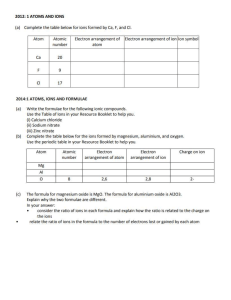
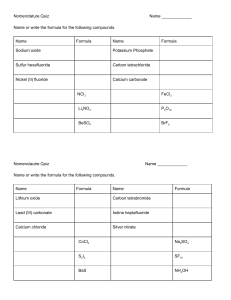
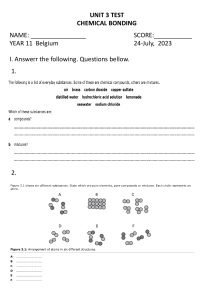
Chemical reactions and equations A reaction in which 2 or more substances react to form new products with new properties is called a chemical reaction Burning of a magnesium ribbon in air When magnesium ribbon is burnt in air it burns with a dazzling white flame and this flame changes into a white powder called magnesium oxide The magnesium ribbon has to be cleaned before performing a chemical rxn because it is coated with a layer of magnesium oxide to prevent it from reacting with atmospheric oxygen and to get the desired chemical reaction it has to be cleaned. Reaction between lead nitrate solution and potassium iodide When lead nitrate is added to potassium iodide 2 new compounds are formed. 1. Yellow solid –lead iodide 2. White solid –potassium nitrate. Reaction between zinc and sulphuric acid When sulphuric acid is added to zinc granules it results in the formation of zinc sulphate in aqueous form and evolution of hydrogen gas. Observations in a chemical reaction Change in state Change in temperature Change in colour Evolution of gas Chemical formulae The chemical formula of a substance is the symbolic representation of the actual number of atoms present in one molecule of a substance. Formula of one molecule of water is H2O. It shows that one molecule of water is made up of 2 atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. Chemical equation The symbolic representation of a chemical rxn is called a chemical equation The description of a chemical reaction is quite long. Therefore it can be written in the form of a chemical equation. Reactants: The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are called reactants. Products: The substances that are formed as a result of a chemical equation are called products. The word equation shows the change of reactants into products through an arrow placed between them. The reactants are in the LHS with a + b/w them The products are in the RHS with a + b/w them. The arrow head points towards the products showing the direction of the equation. Unbalanced chemical equation If the number of atoms on the reactant side and the number of atoms on the products side are not equal then the reaction is said to be an unbalanced equation. Balanced chemical equation According to the law of conservation of mass on a chemical reaction the number of atoms in the reactant side and the product side are same. Therefore a chemical reaction has to be balanced If the number of atoms on the reactant side and the product side are equal then the reaction is said to be a balanced equation. Example : Zn + H2SO4 3Fe + 4H2O ZnSO4 + H2 Fe3O2 + 4H2 Information conveyed by a chemical equation Names and formula of various reactants and products. Relative number of moles of reactants and products. Relative masses of reactants and products. Relative volumes of gaseous reactants and products. Limitations of a chemical equation It does not mention the state of the substances The reaction may or may not be complete It does not reveal the speed of the reaction. It does not give the concentration of the substance. It does not give conditions such as temperature, pressure etc., Making a chemical reaction more informative To make a chemical reaction more informative the physical states are often mentioned along with the formulae. Notations Word l Liquid g Gas s solid aq aqueous Sometimes reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, catalyst etc., are also mentioned above or below the arrow.Example : CO(g) + 2H2O(l) 340 atm CH3OH(l) 6CO2 +12H2O CHLOROPHYLL C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O Exothermic reaction: Reactions in which heat is produced along with the formation of products is called an exothermic reaction. i. ii. Burning of natural gas: CH4 + 2O2 Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 CO + 2H2O 6CO2 + 6H2O Types of chemical reactions Combination reaction A reaction in which 2 or more reactants combine to form a single product is called a chemical reaction. Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to produce calcium hydroxide and a large amount of heat CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 In this calcium oxide reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide Such a reaction in which a single reactant is formed is called combination reaction. i. Burning of coal: C + O2 CO2 ii. Formation of water: 2H2 + O2 2H2O iii. Formation of ammonium chloride NH3 + HCl NH4Cl Decomposition reaction A reaction in which a single reactant breaks down into two or more products is called decomposition reaction. Ferrous sulphate crystals on heating loses water and the colour of the crystals change from light green to white. On further heating it decomposes into ferric oxide and sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide. Ferrous sulphate crystals –(FeSO4, 7H2O) 2FeSO4 HEAT Fe2O3 + SO2 + SO3 Decomposition of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide on heating is an important decomposition reaction used in various industries. Calcium oxide is called quick lime It is used in the manufacture of cement. CaCO3 HEAT CaO + CO2 Lead nitrate powder on heating decomposed into lead oxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen. The emission of brown fumes is nitrogen dioxide. 2Pb(NO3)2 HEAT 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2 The decomposition reaction which is carried out by heating is called thermal decomposition. Electrolysis of water When water taken in an electrolytic cell, is acidified with a small quantity of sulphuric acid and a direct current is passed through it it undergoes decomposition to yield hydrogen and oxygen. Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen gas due to the passage of current. It is also called water splitting. It ideally requires a potential difference of 1.23 volts to split water . The volume of gas in the hydrogen test tube is twice the volume of gas in the oxygen test tube. Black and white photography (photolysis) When silver chloride is exposed to sunlight for some time white silver chloride turns grey in sunlight This is the decomposition of silver chloride by light into silver and chlorine. This is the reason why silver chloride should be stored in air tight containers. 2AgCl SUNLIGHT 2Ag + Cl2 Silver bromide also behaves the same way Endothermic reactions Reactions in which energy is absorbed are called endothermic reactions. If blue crystals of copper nitrate absorb heat it decomposes into black copper oxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen. Displacement reaction A reaction in which a high reactive element displaces the low reactive element is called displacement reaction When iron nail is immersed in copper sulphate solution the iron nail becomes brownish in colour and the blue colour of copper sulphate solution starts fading. In this iron has displaced copper from copper sulphate soln Fe + CuSO4 FeSO4 + Cu Other examples Zinc + copper sulphate gives zinc sulphate + copper Lead + copper chloride gives lead chloride + copper Double displacement reaction Reactions in which exchange of ions take place between the reactants are called double displacement reactions. Na2SO4 + BaCl2 BaSO4 + 2NaCl When sodium sulphate is added to barium chloride it results in the formation of sodium chloride and white precipitate of barium sulphate. When lead nitrate is added to potassium iodide it results in the formation of precipitate of yellow lead iodide and white potassium nitrate. Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI PbI2 + 2KNO3 Precipitation reaction Any reaction that produces a precipitate is called precipitation reaction. Neutralization reaction Neutralization reaction is reaction in which the reactants are an acid and a base and the products are salt and water. In this reaction the positive charge of the hydrogen ions of the acid and the negative charge of the hydroxide ions of the base get neutralised. Oxidation, reduction and redox reactions. Oxidation reaction A reaction in which oxygen is added or hydrogen is removed is called an oxidation reaction. Addition of O2: 2Mg + O2 Removal of H2: 2HI 2MgO H2 + I2 Reduction reaction: A reaction in which hydrogen is added or oxygen is removed is called a reduction reaction. Removal of O2: 2CuO 2Cu + O2 Addition of H2: H2 +2 Cl 2HCl Redox reaction A reaction in which oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously is called a redox reaction. Mg + H2SO4 MgSO4 + H2 Oxidising agent –the substance responsible for oxidation. Reducing agent the substance responsible for reduction. Oxidised substance –substance that gains O2 or loses H2 Reduced substance –substance that gains H2 or loses O2 The effects of oxidation in our day to day life 1. Corrosion Some metals when exposed to moisture, oxygen, acids etc., are tarnished due to the formation the respective metal oxide on their surface. This is called corrosion. Iron articles after some time get coated with a reddish brown powder called rust. The corrosion of iron is called rusting. The problem with iron is that the oxide formed does not firmly stick to the metal surface. This causes the metal surface to flake out This eventually weakens the metals. Copper gets coated with a black colour copper oxide. Silver reacts with sulphide and gets tarnished forming black colour silver sulphide. Effects of corrosion It causes damage to car bodies, railways, bridges and to all objects made of metals. Prevention Painting Alloy making Galvanisation Anodising Electroplating 2. Rancidity When the substance containing oils and fats are exposed to air they get oxidised and become rancid due to which their smell and taste change. This process is called rancidity. Prevention This can be prevented by adding antioxidants to the substances containing fats and oil. Keeping food in air tight containers also prevent rancidity. Chips manufacturers usually flush bags of chips with gas such as nitrogen to prevent the chips from getting oxidised. Formation of calcium carbonate from calcium oxide. Calcium oxide is mixed with water to form calcium hydroxide and a large amount of heat. This calcium hydroxide also known as slaked lime is used for white washing. Calcium hydroxide after been used for white washing slowly reacts with atmospheric CO2 Calcium carbonate is formed as a result after 2 -3 days. This calcium carbonate gives the walls a shiny finish. Chemical formula of marble is CaCO3