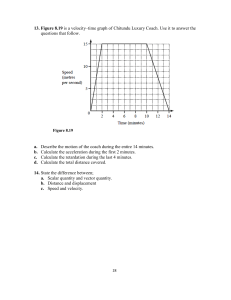
Subject : F4 Physics Chapter / Topic Subtopic : : 2 Force and Motion I 2.1 Linear Motion A. Distance and Displacement B. Speed and Velocity C. Acceleration D. Ticker Timer E. Linear Motion Equations 2.1 Linear Motion A. Distance and Displacement 1. Distance is the total length travelled by an object from one position to another. S.I. unit for distance: ____________ 2. Displacement is the distance between two locations measured along the shortest path connecting them, in a ______________ S.I. unit for displacement: ______________ 3. In Figure below , a stone travelled from point A to B along curve path. 2.5 m A a) B 1.8 m The curve path is the ______________ travelled by the stone. The distance travelled by the stone is ___________________ m. b) The straight line from A to B is the ____________________ of the stone from A. The displacement of the stone is _____________ m to the east of A. 4. Distance has __________________ only but no _________________. Distance is a __________________ quantity. 5. Displacement has ______________ and _________________. Displacement is a ______________ quantity. 6. Compare distance and displacement Distance a) The total length travelled by an object from one position to another. Displacement a) The shortest distance from a reference point. b) A ______________ quantity b) A ______________ quantity c) SI unit: c) SI unit: 1 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 7. Example a) P moves from O to A: O 10 m A P Displacement of P from O = _____________ Distance travelled by P = ______________ b) P moves from O to A and turns back to O. O 15 m P Distance travelled by P = ______________ A Displacement of P from O = _____________ c) P moves from O to A and Q moves from O to B B 30 m O 25 m A Q P Distance travelled by P = ______________ Displacement of P from O = _____________ Distance travelled by Q = ______________ Displacement of Q from O = ____________ d) P moves from O to A and then it turns back and moves to B. B P Distance travelled by P = ______________ O 100 m A 160 m Displacement of P from O = _____________ e) P moves from O, following a circular path of radius of 5 m, and then reaches A. OA is a diameter of the circle O Distance traveled by P = _______________________ Displacement traveled by P = __________________ A ● 2 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I B. Speed and Velocity 1. Speed is the distance travelled per unit time. Speed also defined as the _________________ of change of distance. Average speed, 𝑠 = Total distance travelled, 𝑑 Time taken, 𝑡 S.I. unit for speed: _______________ 2. Velocity is the _________________________________________ Velocity also defined as the rate of change of _________________ Average velocity, 𝑣 = Total displacement travelled, 𝑠 Time taken, 𝑡 S.I. unit for velocity: _____________ 3. Compare speed and velocity Speed 4. Velocity a) The rate of change of distance. Distance, 𝑑 𝑣= Time, 𝑡 a) The rate of change of displacement. Displacement, 𝑠 𝑣= Time, 𝑡 b) A _____________quantity b) A _____________quantity c) SI unit: c) SI unit: Units conversion a) Express 40 m s-1 in km h-1. b) Express 108 km h-1 in m s-1. c) A car is moving with speed of 50 m s-1. What is its speed in km h-1? d) A train is moving with speed of 90 km h-1. What is its speed in m s-1? 3 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 5. Example a) P moves from O to A. the time taken is 5 s. O 10 m A Distance travelled by P = ______________ P Displacement of P from O = _____________ Speed of P = Velocity of P = b) P moves from O to A and turns back to O in 40 s. O 10 m A P Distance travelled by P = ______________ Displacement of P from O = _____________ Speed of P = Velocity of P = c) P takes 50 s to move from O to A and then it turns back and moves to B. B O P 60 m A 90 m Distance travelled by P = ______________ Displacement of P from O = _____________ Speed of P = Velocity of P = d) P moves from O to A, B, C and then back to O. Time taken is 90 seconds. O 60 m 80 m C Distance travelled by P = ______________ Speed of P = A 80 m 60 m B Displacement of P from O = _____________ Velocity of P = 4 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I e) P moves from O to A, B and finally to C. Time taken 1 hour. O 15 km A 16 km P C 3 km B f) Distance travelled by P = ______________ Displacement of P from O = _____________ Speed of P = Velocity of P = P takes 50 s to move from O, following a circular path of radius of 5 m, to A. OA is a diameter. O A Distance travelled by P = ______________ Displacement of P from O = _____________ Speed of P = Velocity of P = 5 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I C. Acceleration 1. An object is moves with acceleration, a) if the velocity increases, then the acceleration is ______________. b) if the velocity decreases, then the acceleration is ______________ and known as _____________________. 2. c) if the velocity uniform in a straight line, then the acceleration is ______________. d) if the ______________ of motion changes, then the object moves with acceleration. Acceleration, a is defined as the __________________________________________. Acceleration, a is defined as the change of velocity in 1 second. Acceleration = Change of velocity Time taken = 𝑎= 𝑣−𝑢 𝑡 S.I. unit for acceleration: ______________ 6 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I Exercise 1. Figure below shows he path of a boy walking from his house to playground. If he takes 10 minutes to reach the playground, calculate Playground 300 m House 400 m 2. a) The distance travelled by the boy to reach the playground b) The displacement of the boy from his house c) The Speed of the boy d) The velocity of the boy Mike runs a constant speed of 5 m s-1. He runs 120 m east, then 80 m west, then 60 m east. Consider east to be positive. a) What distance did he travel? b) What was his displacement? c) How long did it take him? d) What was his average velocity? 7 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 3. Every morning Amirul walks to Ahmad’s house which is situated 80 m to the east of Amirul’s house. They then walk towards their school which is 60 m to the south of Ahmad’s house. a) What is the distance travelled by Amirul and his displacement from his house? b) If the total time taken by Amirul to travel from his house to Ahmad’s house and then to school is 15 minutes, what is his speed and velocity? 4. A runner runs from the starting line and achieves a velocity of 18 m s- 1 in 3 seconds. Calculate his acceleration. 5. A bus accelerated uniformly from a velocity of 10 m s -1 to 25 m s-1 in 5 s. What was the acceleration of the bus? 6. A rocket moving with a constant velocity of 2500 m s--1. As the rate of combustion in the combustion chamber increases, the velocity of the rocket increases to 4000 m s-1 in 2 minutes. What is the acceleration of the rocket? 8 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 7. A train is travelling at 20 m s-1 was brought to rest in a time of 50 s. What is its deceleration? 8. John cycles at a uniform speed of 10 m s-1. He then stops pedaling and finally he and his bicycle come to stop after 8 s. What is his average deceleration? 9. A car speeds up uniformly from rest to a velocity of 20 m s-1 in 4 s. Calculate the acceleration of the car. 10. A car is moving at a velocity of 40 m s-1. The brake is applied and the car slows down uniformly to a velocity of 10 m s-1 in 5 s. Calculate the acceleration of the car. 11. A train is travelling at a velocity of 20 m s-1. The driver brakes the train and it comes to a stop after 10 s. Calculate the acceleration of the train. 9 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I D. Ticker Timer 1. The ticker-timer can be used to determine: a) __________________________________ b) __________________________________ c) __________________________________ d) __________________________________ 2. In the laboratory, a ticker-timer as shown in figure above, with a trolley is used to study the motion of an object for a short time interval. A ticker-timer consists of a small electrical vibrator which vibrates at the frequency of 50 Hz. 3. 1 dot-space or 1 tick is the time interval between two dots. The time taken to make 50 dots on the 1 ticker tape is 1 s. Hence, the time for 1 tick is 50 = ______________ 4. To determine the time interval of motion of the object: Time interval = Number of tick × 0.02 s 10 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 5. Calculate the average velocity shown by the following ticker tape. a) 10 cm Total distance = __________ Total time = __________ ticks × __________ s = __________ s Average velocity = b) Total distance = __________ Total time 7 cm = __________ ticks × __________ s = __________ s Average velocity = 6. Analysing motion on a ticker-timer Ticker Tape and Chart a) Uniform velocity Characteristics The distance of the dots is ______________distributed The object is moving at a ________________________ ______________ acceleration b) Positive acceleration The distance between the dots ___________ uniformly. The velocity of the object is _____________ uniformly. ______________ acceleration c) Negative acceleration The distance between the dots ___________ uniformly. The velocity of the object is _____________ uniformly. ______________ acceleration 11 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 7. Acceleration or deceleration from a ticker tape Acceleration, 𝑎 = Where 8. u = initial velocity n = number of ticks 𝑣−𝑢 (𝑛 − 1)𝑡 v = final velocity t = time of 1 ticks The figure below shows a strip of ticker tape that represents the movement of a trolley in an experiment. The frequency of the ticker-timer is 50 Hz. Direction of motion a) Total Time, t b) Initial velocity, u c) Final velocity, v d) Acceleration, a 12 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I Ticker Tape Chart 1. Analysing motion on a ticker-timer Ticker Tape and Chart Characteristics a) Uniform velocity i) All lengths of tape in chart are of ______________ length. ii) The object is moving at a __________________________. iii) The object is moving at a ______________ acceleration b) Unifrom acceleration i) The length of each strips _____________ with equal length. ii) The object is moving at a __________________________. iii) The object is moving at a ______________ acceleration c) Uniform deceleration i) The length of each strips _____________ with equal length. ii) The object is moving at a __________________________. iii) The object is moving at a ______________ acceleration or __________________________. d) Decreasing accleration i) The length of each strips _____________ with length. ii) The object is moving at a __________________________. iii) The object is moving at a ______________ acceleration or __________________________. e) Increasing acceleration i) The length of each strips _____________ with length. ii) The object is moving at a __________________________. iii) The object is moving at a ______________ acceleration or __________________________. 13 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 2. Acceleration or deceleration from a ticker tape chart Acceleration, 𝑎 = Where 3. u = initial velocity n = number of ticks 𝑣−𝑢 (𝑛 − 1)𝑡 v = final velocity t = total time for 1 ticker tape Figure 2.4 shows a tape chart which is obtained from an experiment to determine the acceleration of an object. Each ticker consists of 5 ticks. If the frequency of the ticker-timer used in the experiment is 50 Hz, what is the a) Total time for 1 ticker tape, t b) Initial velocity, u c) Final velocity, v d) Acceleration, a 14 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 4. Figure 2.5 shows a chart representing the movement of a trolley with uniform acceleration. Determine its acceleration. 15 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I Exercise 1. The following diagram shows a part of a ticker tape which records the motion of a trolley down in inclined runway. The ticker timer is operating at a frequency of 50 Hz. Calculate the acceleration for each motion : (a) Answer Initial velocity, u = Final velocity, v = time taken, t = Acceleration, a = (b) 16 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 2. A trolley is moving down a runway. A strip with six dot-spaces as shown in diagram below is obtained. The ticker timer vibrates at a frequency of 50 Hz. Find the acceleration of the trolley. 3. The ticker tape below shows the motion of a trolley. The ticker timer used can make 50 dots in 1 second. Direction of motion A B 14.5 cm (a) Describe the motion of the trolley from A to B. ______________________________________________________________________ (b) Calculate the time taken for trolley to move from A to B (c) What is the average velocity of the trolley? (d) Calculate the acceleration of the trolley using the first and sixth ticks. 17 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 4. The diagram shows a ticker-tape chart obtained from the motion of a trolley. Each strip contains 5 ticks. Calculate (a) the total distance travelled (b) the average velocity (c) the initial velocity of the trolley (d) the final velocity of the trolley (e) the acceleration of the trolley. 18 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 5. The diagram shows the ticker tape chart of the motion of a trolley. The frequency of the ticker timer using a frequency of 50 Hz. Calculate the acceleration of the trolley. (a) What is the total distance travelled by the trolley? (b) Calculate the average velocity of the trolley. (c) Calculate the initial velocity of the trolley (d) Calculate the final velocity of the trolley (e) Calculate the acceleration of the trolley. 19 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 6. The following tape chart shows the motion of a trolley. Each strip consists of 10 ticks. The strips are made by using a ticker timer which is operating at a frequency of 50 Hz. (a) Describe the motion of the trolley. ____________________________________________________________________________ (b) Calculate : (i) the total distance travelled, (ii) the average velocity , (iii) the initial velocity, (iv) the final velocity, (v) the acceleration. 20 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 7. The following tape chart shows the motion of a trolley traveling up an inclined runway. . Each strip consists of 10 ticks. The strips are made by using a ticker timer which is operating at a frequency of 50 Hz. length / cm 20 ● 16 ● ● 12 8 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● 4 0 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● (a) Describe the motion of the trolley. _________________________________________________________________________________ (b) Calculate : (i) the total distance travelled, (ii) the average velocity , (iii) the initial velocity, (iv) the final velocity, (v) the acceleration. 21 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 8. The following tape chart shows the motion of a glass block traveling up an inclined runway. Each strip consists of 5 ticks. The strips are made by using a ticker timer which is operating at a frequency of 50 Hz. (a) State the type of motion represented by : PQ : ______________________________________________________________________ QR : ______________________________________________________________________ (b) Determine the displacement and average velocity for the motion represented by PR. (i) displacement (ii) average velocity. (c) Determine the acceleration for the motion 22 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I E. Linear Motion Equations The following symbols are used in the equations of motion: Quantity Symbol S.I. Unit Displacement Initial velocity Final velocity Acceleration Time Motion with uniform acceleration 1. Summary of equation of motion 1 2 3 4 2. The equation of an object with uniform acceleration, a, are as follows: Displacement, s is given by: s = Average velocity × time Hence, And also From ② rearrange Insert into ① 1 𝑠 = (𝑢 + 𝑣) × 𝑡 2 𝑎= 𝑣−𝑢 𝑡 Insert into ① ━━ ② 𝑣 = 𝑢 + 𝑎𝑡 𝑠= 1 (𝑢 + 𝑢 + 𝑎𝑡) × 𝑡 2 1 𝑠 = 𝑢𝑡 + 𝑎𝑡 2 2 From② rearrange ━━ ① 𝑡= 𝑣−𝑢 𝑎 𝑠= 1 (𝑣 − 𝑢) (𝑢 + 𝑣) × 2 𝑡 𝑠= 𝑣 2 − 𝑢2 2𝑎 𝑣 2 = 𝑢2 + 2𝑎𝑠 ━━ ③ ━━ ④ 23 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I Exercise 1. A car slows down with a deceleration 2.0 m s-2. If the initial velocity of the car is 20 m s-1, How far to take the car to stop? 2. A car is moving with velocity of 35 m s-1. It starts to decelerate and its velocity decreases to 15 m s-1 after 10 s. Calculate the average velocity of the car. 3. A boy starts from rest and moves with uniform acceleration until he reaches a velocity of 30 m s-1 in 5 second. What is the distance travelled by the boy? 4. You enter an expressway from an onramp going 15.6 m s-1. If you need to speed up to 30 m s-1 to join the speed of other vehicles then how long will that take if you accelerate at 4.9 m s-2. 5. A car takes 8 s to increase its velocity from 10 m s-1 to 30 m s-1. What is its average acceleration? 24 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 6. A particle is moving with velocity 15 ms-1.It is accelerating with the rate of 2 ms-2. What is the final velocity of the particle after 6 s? 7. A truck travelling at 25 m s-1 puts its brakes on for 4 s. This produces a deceleration of 2 m s-2. What does the tuck’s velocity drop to? 8. A car travelling with velocity of 10 m s-1 and acceleration uniformly at a rate of 3 m s-2 for 20 s. Calculate the displacement of the car while it is accelerating. 9. A bullet is fired towards a nearby tree with a speed of 200 m s-1. The bullet is shot at a depth of 5 cm. Find the average deceleration of the bullet inside the tree. What is the time taken for the bullet to stop after hitting the tree? 25 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I 10. Salina is driving her car at a velocity of 10 m s-1. On seeing an obstacle in front, she applies the brakes to stop her car. If the deceleration of the car is 2 m s-2, what is the distance her car travels before it comes to a halt? 11. A cyclist riding at a velocity of 4 m s-1 braked with a uniform deceleration and stopped in 3.6 m. How long did he take to stop? 12. A long jumper was running at a velocity of 5 m s-1towards the long jump pit. He needed to achieve a velocity 10 m s-1after covering a distance of 4.5 m before lifting himself off the ground from the jumping board. a) Calculate the required acceleration for him to do so. b) Calculate the time taken for him to cover the horizontal distance of 4.5 m. 26 https://www.facebook.com/PlazPhysics/ F4 Chap 2 Force and Motion I