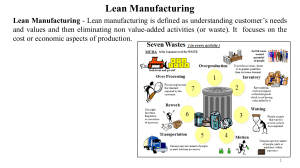
Quiz 2.2 Examine the lean philosophy as it applies to an organisation that you know of. (5 marks) Answer: Lean philosophy, often referred to as Lean thinking or Lean management, is a methodology derived from the Toyota Production System (TPS) and is widely used in various industries to improve efficiency, eliminate waste, and optimize processes. The core idea behind Lean is to create more value for customers with fewer resources by identifying and eliminating activities that do not add value. Here are some key principles of Lean and how they may apply to an organization: 1. Identify Value from the Customer's Perspective: The first step in Lean is to understand what the customer perceives as value. This involves identifying the specific products or services that customers are willing to pay for and focusing efforts on delivering that value. 2. Value Stream Mapping: Value stream mapping is a technique used to visualize the flow of materials and information required to deliver a product or service. By mapping the entire process, organizations can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas where value is not being added. 3. Eliminate Waste: Lean philosophy identifies various types of waste, including overproduction, excess inventory, waiting time, unnecessary transportation, defects, and more. By systematically eliminating these wastes, organizations can streamline their processes and become more efficient. 4. Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Lean encourages a culture of continuous improvement, where employees at all levels of the organization are empowered to identify and implement small, incremental improvements in their work processes. 5. Just-in-Time (JIT) Production: JIT is a key element of Lean that aims to produce and deliver products or services just when they are needed, minimizing inventory costs and reducing waste. 6. Respect for People: Lean emphasizes the importance of respecting and involving employees in the improvement process. Workers are encouraged to share their insights and suggestions to enhance efficiency and quality. 7. Pull System: The pull system in Lean means producing items based on actual customer demand rather than pushing products into the market. This ensures that production is aligned with real demand, reducing overproduction and inventory holding costs. 8. Standardized Work: Lean encourages the establishment of standardized work procedures to ensure consistency, quality, and continuous improvement. When applied effectively, the Lean philosophy can lead to significant improvements in an organization's productivity, quality, and overall performance. However, implementing Lean requires strong leadership commitment, a willingness to change existing practices, and a dedication to fostering a culture of continuous improvement throughout the organization. References: Foster, S.T. and Gardner, J.W., 2022. Managing quality: Integrating the supply chain. John Wiley & Sons. Womack, J. P., Jones, D. T., & Roos, D. (2007). "The Machine That Changed the World: The Story of Lean Production." Free Press.