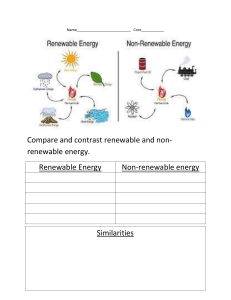
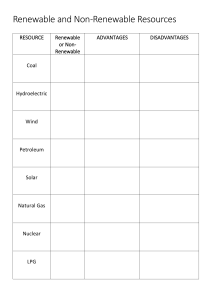
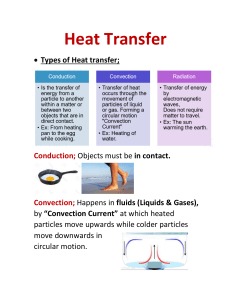
S3 Science Energy Topic Forms of Energy There are 8 main forms of energy o o o o o o o o Heat Light Sound Electrical Potential (gravity or elastic) Kinetic (movement) Chemical Nuclear Energy Changes Energy can be changed from one form into another. It cannot be created or destroyed. E.g. o o o o o Kettle - Electrical to Heat Balloon bursting – Potential to Sound Burning magnesium – Chemical to Light Sun - Nuclear to Light and Heat Drumming – Kinetic to Sound Heat Energy Heat Energy travels in 3 different ways: o o o Conduction Convection Radiation Heat Energy - Conduction Solid Objects The particles vibrate beside each other passing the energy from one particle to the next. Heat Energy - Convection Liquids & Gases The hotter particles rise up. The cooler particles move down. A convection current is made. The top of a room is always warmer than the bottom because of convection (heat rises). Heat Energy - Radiation All hot objects (Solids, liquids & gases) Infrared rays of energy are given out Infrared rays can travel through a vacuum (space) Energy Sources Energy sources can either be renewable or non-renewable. Non-renewable energy sources will run out. Renewable energy sources will not run out. Non-renewable Energy Sources The main non-renewable energy sources are: o o Fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas) Nuclear fuels (uranium and plutonium) We have to conserve them so they last longer before they run out. Renewable Energy Sources The main renewable energy sources are: o o o o Wind Waves Hydroelectric Solar They are better for the environment. Energy Sources Example Draw lines to match the object with its source of energy and tick, if it renewable or non-renewable.