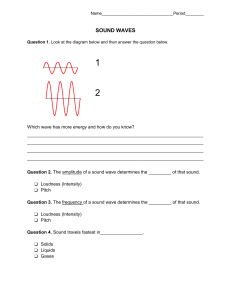
Sound and space Loudness and amplitude Loudness of a sound is a way to describe how quiet or loud the sound appears. Loudness depends on two variables; 1) How much the object is vibrating? 2) How far away the vibrating object is? The greater the distance of each vibration in the object, the greater the distance that particles in air will be pushed. The maximum distance that particles move, either forward or backward in a sound wave, is called as amplitude. As the amplitude of a sound wave increases, the loudness of the sound increases. Quieter sound has a smaller amplitude. Louder sound has a larger amplitude. Pitch and Frequency. Pitch of a sound of a sound is how high or low the sound appears on a musical note. The number of vibrations in each second is called frequency. The frequency of a sound determines its pitch. Faster the vibration, higher the pitch of the sound. A wave with a higher frequency will have more waves in the same time. Higher frequency has higher pitch. Lower frequency has lower pitch. If the amplitude of higher and lower pitch are the same, that means the loudness of both sounds are the same. Interference of sound Interference is what happens when two or more waves meet each other. The effect that is produced when the waves meet each other is called interference. Interference is easiest to detect when the waves have the same frequency and the same amplitude. Waves will reinforce when they meet with peaks together and with the troughs together. 1. Reinforcement / Constructive Interference 2. Cancelation/ Destructive Interference Constructive wave interference The wave interference is said to be a constructive wave interference if the crest of a wave meets the crest of another wave of the same frequency at the same point. or Constructive wave interference is a wave interference which occurs when in phase waves meets with each other and forms a new wave with greater amplitude. Destructive wave interference The wave interference is said to be a destructive wave interference if the crest of a wave meets the trough of another wave of the same frequency. or Destructive wave interference is a wave interference which occurs when out of phase waves meets with each other and forms a new wave with lower amplitude or zero amplitude. Formation of moon Q. How does moon form? The most accepted theory for the formation of the moon today is the giant-impact theory. It proposes that the Moon formed during a collision between the Earth and another small planet, about the size of Mars. The debris from this impact collected in an orbit around Earth to form the Moon. The colliding body is called Theia. Collision theory; One of the theories for the formation of the Moon A newly formed planet, about the same size as Mars, collided with the newly formed Earth. The collision would have caused rocks and dust to break away from the both the planets. The Moon formed when the rocks and the dust was pulled together by gravity. Evidence that supports the collision theory - The Moon is less dense than Earth. - The Moon has small iron core, similar to the Earth. - The composition of rocks on the Earth and the Moon are the same. Evidence that contradicts the collision theory - The surface of Earth does not appear to ever have been molten. A collision that formed Moon would have caused the surface of the Earth to melt. The surface would have later solidified. Nebulae Nebulae are could of dust and gas in space. The gases found in nebulae are mostly hydrogen and a smaller quantity of helium. Stellar nurseries. A stellar nursey is an area in space where starts are formed. When the mass of the dust and the gas collects together and becomes larger, the force f gravity pulling inward increases. The pressure inside the new star also gets large. The pressure can cause atoms to react with each other, causing the new star to give out heat and light. Tectonics Q. what are Tectonic plates? Ans- Tectonic plates are the gigantic pieces of the Earth crust and upper most mantle. The outermost layer of the Earth is called the crust and it is broken into large pieces called tectonic plates. They are made up of oceanic crust and continental crust. Earthquakes occur around mid-ocean ridges and the large faults which mark the edges of the plates. Evidences of Tectonic Plates: 1. Jigsaw appearance of continental coasts 2. Fossil record 3. Alignment of magnetic materials in the Earth’s crust 4. Position of volcanoes