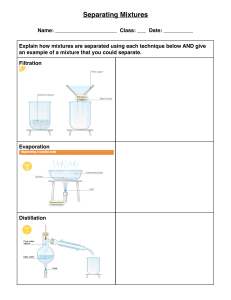
Title: Describing the Appearance and Uses of Uniform and Non-Uniform Mixtures Introduction: In this workbook, we will be exploring the different types of mixtures, specifically uniform and nonuniform mixtures. Mixtures are a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. Uniform mixtures are also called homogeneous mixtures, where the substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. Non-uniform mixtures are also called heterogeneous mixtures, where the substances are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture. Chapter 1: Uniform Mixtures In this chapter, we will explore uniform mixtures, their appearance, and their uses. Activity 1: Classifying Mixtures In this activity, students will be provided with various mixtures and asked to classify them as either uniform or non-uniform. Activity 2: Identifying Uniform Mixtures In this activity, students will be shown various uniform mixtures and asked to identify the substances in the mixture. Activity 3: Uses of Uniform Mixtures In this activity, students will be asked to research and list down the different uses of uniform mixtures in their daily lives. Chapter 2: Non-Uniform Mixtures In this chapter, we will explore non-uniform mixtures, their appearance, and uses. Activity 1: Classifying Mixtures In this activity, students will be provided with various mixtures and asked to classify them as either uniform or non-uniform. Activity 2: Identifying Non-Uniform Mixtures In this activity, students will be shown various non-uniform mixtures and asked to identify the substances in the mixture. Activity 3: Uses of Non-Uniform Mixtures In this activity, students will be asked to research and list down the different uses of non-uniform mixtures in their daily lives. Chapter 3: Mixtures in Everyday Life In this chapter, we will explore the various mixtures that we encounter in our daily lives. Activity 1: Identifying Mixtures In this activity, students will be given various substances and asked to identify whether they are pure substances or mixtures. Activity 2: Mixtures in Food In this activity, students will be asked to research and list down the different mixtures that we find in our food. Activity 3: Mixtures in Cleaning Products In this activity, students will be asked to research and list down the different mixtures that we find in cleaning products. Conclusion: By the end of this workbook, students will have a better understanding of uniform and non-uniform mixtures, their appearance, and their uses. They will also be able to identify various mixtures in their daily lives and understand their importance. Title: Understanding Uniform and Non-Uniform Mixtures Lesson Objective: Students will be able to describe the appearance and uses of uniform and non-uniform mixtures. Introduction: Have you ever mixed water and sugar together to make lemonade? What about sand and gravel to make concrete? These are examples of mixtures, which occur when two or more substances are combined together. In this lesson, we will learn about two types of mixtures: uniform and non-uniform. Part 1: Uniform Mixtures Uniform mixtures, also known as homogeneous mixtures, are mixtures where the substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. The appearance of a uniform mixture is the same throughout. Examples of uniform mixtures include salt water, air, and brass. Activity: To demonstrate the appearance of a uniform mixture, we will mix food coloring and water together. The resulting mixture will be the same color throughout. Discussion: Why do you think uniform mixtures are useful? What are some real-world examples of uniform mixtures? Part 2: Non-Uniform Mixtures Non-uniform mixtures, also known as heterogeneous mixtures, are mixtures where the substances are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture. The appearance of a non-uniform mixture can vary depending on where you look. Examples of non-uniform mixtures include soil, salad dressing, and cereal in milk. Activity: To demonstrate the appearance of a non-uniform mixture, we will mix oil and water together. The resulting mixture will have two distinct layers, with the oil floating on top of the water. Discussion: Why do you think non-uniform mixtures are useful? What are some real-world examples of non-uniform mixtures? Part 3: Uses of Uniform and Non-Uniform Mixtures Both uniform and non-uniform mixtures have practical applications. For example, uniform mixtures are often used in the production of medicines, where it is important that the active ingredients are evenly distributed throughout the final product. Non-uniform mixtures are useful in many ways, such as in the production of concrete or asphalt, where different sized particles are needed to create a strong material. Activity: Divide students into small groups and have them research and present real-world examples of both uniform and non-uniform mixtures. Conclusion: In this lesson, we learned about uniform and non-uniform mixtures. We discovered that uniform mixtures have an even appearance throughout and non-uniform mixtures have an appearance that varies depending on where you look. We also learned that both types of mixtures have practical applications in everyday life. Module 1 Title: Uniform and Non-Uniform Mixtures Grade Level: Sixth Grade Duration: 2-3 class periods Overview: In this module, students will learn about uniform and non-uniform mixtures. They will explore the appearance and uses of different types of mixtures through hands-on activities. Learning Objectives: Define uniform and non-uniform mixtures. Identify examples of uniform and non-uniform mixtures. Describe the appearance and properties of uniform and non-uniform mixtures. Explain the uses of uniform and non-uniform mixtures. Demonstrate an understanding of the concepts through hands-on activities. Materials Needed: Water Salt Sugar Sand Coffee filter Plastic cups Spoons Measuring cups Marker Straws Activities: Activity 1: Sorting Mixtures Divide students into groups of three or four. Give each group a mixture of salt, sugar, and sand. Instruct students to separate the mixture into its individual components using only spoons and plastic cups. Once students have separated the mixture, ask them to describe the appearance and properties of each component. Activity 2: Filtration Show students a mixture of water and sand. Instruct them to use a coffee filter to separate the sand from the water. Once the sand is separated, ask students to describe the appearance and properties of both the sand and water. Activity 3: Making a Non-Uniform Mixture Show students a mixture of water and salt. Instruct them to add more salt to the mixture until it becomes a non-uniform mixture. Ask students to describe the appearance and properties of the non-uniform mixture. Discuss the uses of non-uniform mixtures, such as in cooking. Activity 4: Making a Uniform Mixture Show students a mixture of water and sugar. Instruct them to add more sugar to the mixture until it becomes a uniform mixture. Ask students to describe the appearance and properties of the uniform mixture. Discuss the uses of uniform mixtures, such as in making drinks. Assessment: Have students write a paragraph describing the difference between uniform and non-uniform mixtures. Ask students to identify and describe three examples of uniform and non-uniform mixtures they encounter in their daily lives. Extensions: Have students research other examples of uniform and non-uniform mixtures and present their findings to the class. Ask students to create a uniform mixture and a non-uniform mixture using different materials and share their creations with the class. Module 2 Title: Separating Mixtures for Community Benefits Grade Level: Sixth Grade Duration: 2 weeks Overview: In this module, students will learn about the process of separating mixtures and how it benefits their community. They will explore different methods of separating mixtures and understand the importance of separating mixtures to obtain pure substances that can be used in various industries. They will also learn how separating mixtures helps reduce waste and pollution in the community. Objectives: Students will be able to define the term "mixture" and identify common mixtures in their community. Students will understand the different methods of separating mixtures, including filtration, evaporation, and distillation. Students will understand the importance of separating mixtures in obtaining pure substances for use in various industries. Students will understand how separating mixtures helps reduce waste and pollution in the community. Students will be able to apply their knowledge of separating mixtures to solve real-world problems in their community. Activities: Introduction to Mixtures (1 day) Discuss with students the concept of mixtures and provide examples of common mixtures found in their community. Ask students to identify the different components of a mixture and discuss the challenges of separating them. Separation Methods (3 days) Introduce students to different methods of separating mixtures, including filtration, evaporation, and distillation. Conduct hands-on experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of each method. Allow students to work in small groups to separate a mixture of their choice using one of the methods discussed. Benefits of Separating Mixtures (3 days) Discuss with students how separating mixtures helps obtain pure substances for use in various industries. Provide examples of how separating mixtures is used in different industries, such as food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. Discuss how separating mixtures helps reduce waste and pollution in the community. Real-World Applications (3 days) Ask students to identify a real-world problem in their community that can be solved by separating mixtures. Allow students to work in small groups to design and implement a solution to the identified problem. Have students present their solutions to the class and discuss the effectiveness of their methods. Conclusion (1 day) Review the concepts learned throughout the module. Ask students to reflect on how their understanding of separating mixtures can be applied in their daily lives. Assessment: Participation in class discussions and activities Completion of hands-on experiments and group projects Written reflection on the benefits of separating mixtures in the community and its applications in realworld problems. Resources: Textbook or online resources on separating mixtures Laboratory materials for conducting experiments Community resources for identifying real-world problems Module 3 Title: Techniques in Separating Mixtures Grade Level: Sixth Grade Introduction: Mixtures are a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. They can be separated into their individual components using various techniques. In this module, we will explore different techniques used for separating mixtures and conduct activities to understand each method. Lesson 1: Decantation Decantation is a technique used to separate a mixture of two immiscible liquids. In this technique, the mixture is left to stand undisturbed until the heavier substance settles down. The liquid on top is then carefully poured out without disturbing the sediment. Activity: Students will be given a mixture of oil and water and will be asked to separate them using decantation. Lesson 2: Evaporation Evaporation is the process of converting a liquid into a gas by heating it. This technique is used to separate a mixture of a solid and a liquid. The liquid is heated until it evaporates, leaving the solid behind. Activity: Students will be given a mixture of salt and water and will be asked to separate them using evaporation. Lesson 3: Filtration Filtration is a technique used to separate a solid from a liquid by passing the mixture through a filter paper. The solid particles are trapped in the filter paper, while the liquid passes through. Activity: Students will be given a mixture of sand and water and will be asked to separate them using filtration. Lesson 4: Sieving Sieving is a technique used to separate a mixture of solids with different particle sizes. The mixture is passed through a sieve, which separates the particles based on their size. Activity: Students will be given a mixture of rice and sand and will be asked to separate them using sieving. Lesson 5: Using a Magnet Using a magnet is a technique used to separate a mixture of magnetic and non-magnetic substances. The magnet attracts the magnetic particles, leaving the non-magnetic particles behind. Activity: Students will be given a mixture of iron filings and sand and will be asked to separate them using a magnet. Conclusion: In conclusion, mixtures can be separated into their individual components using various techniques. Students can learn about these techniques and apply them in their everyday life. By conducting these activities, students can gain a deeper understanding of the physical properties of matter and the ways in which mixtures can be separated.