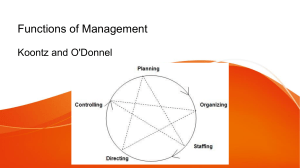
CHAPTER 12: Managerial Function of LEADING Reporter: RINALENE S. CARDENAS Functions of Management by various authors Fayol 1916 Terry 1956 1. Planning 2. Organizing 3. Commanding 4. Coordinating 5. Controlling 1. Planning 2. Organizing 3. Actuating 4. Controlling rev. 1968 Source: Principles of Management Nature of management (peoi.org) Koontz & O’Donnel 1959 Newman & Summer 1961 1. Planning 2. Organizing 3. Staffing 4. Directing 5. Controlling 1. Planning 2. Organizing 3. Leading 4. Controlling Discussion Objectives: 1 Define Leading 2 Define Leadership 3 Identify the Nature and Characteristics of a Good Leader 1 LEADING is a management function that involves inspiring and influencing people in the organization to achieve a common goal. Source: ORGANIZATION AND MANAGEMENT by Cabrera, Altarejos, & Benjamin is influencing people so that they will contribute to organization and group goals. Source: Management: Science, Theory, & Practice by Weihrich Inspire vs Influence Inspire passive and doesn’t have intent to act MOTIVATION Influence active and intentional that has direct effect ACTION LEADING COMMANDING by Henry Fayol “the optimum return from all employees of a unit in the interest of the whole concern.” Source: Management Theory of Henri Fayol: Summary, Examples | NanoGlobals DIRECTING by Koontz & O’donnel “is the interpersonal aspect of managing by which subordinates are led to understand and contribute effectively and efficiently to the attainment of enterprise objectives.” Source: Directing in Management: Meaning, Nature, Concept, Principles, Techniques (preservearticles.com ) DIRECTING by Earnest Dale “concerns the total manner in which a manager influences the subordinates. It is the final action of a manager in getting others to act after all preparations have been done.” Source: Principles of Management(uou.ac.in) ACTUATING by George R Terry ‘‘a fundamental statement providing a guide to action.’’ Source: The evolution of management thought by Wren and Bedian (wikiquote.org) Elements / Sub-functions of Leading 1 Motivation Chapters 10-11 2 Leadership Chapter 12 3 Communication 4 Supervision Chapter 14 Chapter 15 2 LEADERSHIP is the ability of a manager to induce subordinates to work with confidence and zeal. -Koontz and O’Donnell Source: Leadership: Meaning, Characteristics and Functions (yourarticlelibrary.com) is a relationship in which one person influences others to work together willingly on related tasks to attain what the leader desires. -G.R. Terry Source: What is Leadership? - Definition, Concept, Importance & Leadership Skills (economicsdiscussion.net) Importance of Leadership 1 Initiates Action action is initiated when the managers provide direction to their subordinates for carrying out the task 2 Employee Retention builds up morale and motivates the employees with economic and non-economic reward 3 Improved Productivity institutes an effective and efficient working environment through supervision and communication with proper coordination . Leaders are made, not born. Leadership is a skill that can be developed. Good leaders are molded through experience, continued study, and adaptation. 3 NATURE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF A GOOD LEADER Personal inherent, moral, and ethical qualities that distinguish great leaders from the rest of us. Nature and Characteristics of a Good Leader 1 Personality 5 Integrity 2 Drive 6 Leadership motivation 3 Emotional intelligence 7 Knowledge of the business 4 Self-concept 8 Cognitive and practical intelligence Source: Organizational Behavior 5th Edition by McShane and Glinow Nature and Characteristics of a Good Leader 1 . Personality Possessing higher levels of extroversion and conscientiousness. Robbins and Coulter’s Big Five Personality Characteristics Source: ORGANIZATION AND MANAGEMENT by Cabrera, Altarejos, & Benjamin Nature and Characteristics of a Good Leader 2. Drive The leader’s inner motivation to pursue goals. “if you have to choose between someone with a staggering IQ and someone with a lower IQ who is absolutely determined to succeed, you’ll always do better with the second person.” - Larry Bossidy 3. Emotional intelligence The leader’s ability to monitor his or her own and others’ emotions, and use the information to guide the leader’s actions. Nature and Characteristics of a Good Leader 4. Self-concept The leader’s self-beliefs and positive self-evaluation about his or her own leadership skills and ability to achieve objectives. 5. Integrity The leader’s truthfulness and tendency to translate words into deeds. “Practice what you preach.’’ Nature and Characteristics of a Good Leader 6. Leadership Motivation The leader’s need for socialized power to accomplish team or organizational goals. 7. Business Knowledge The leader’s tacit and explicit knowledge about the company’s environment, enabling the leader to make more intuitive decisions. Nature and Characteristics of a Good Leader 8. Cognitive and Practical Intelligence The leader’s above-average cognitive ability to process information and ability to solve real-world problems by adapting to, shaping, or selecting appropriate environments. Cognitive Skills Practical Skills Logic and reasoning Abstract thinking Brainstorming Communicative skills Information seeking Collaboration skills Decision-making Flexibility Thank you! CREDITS: This presentation template was created by Slidesgo, including icons by Flaticon, infographics & images by Freepik