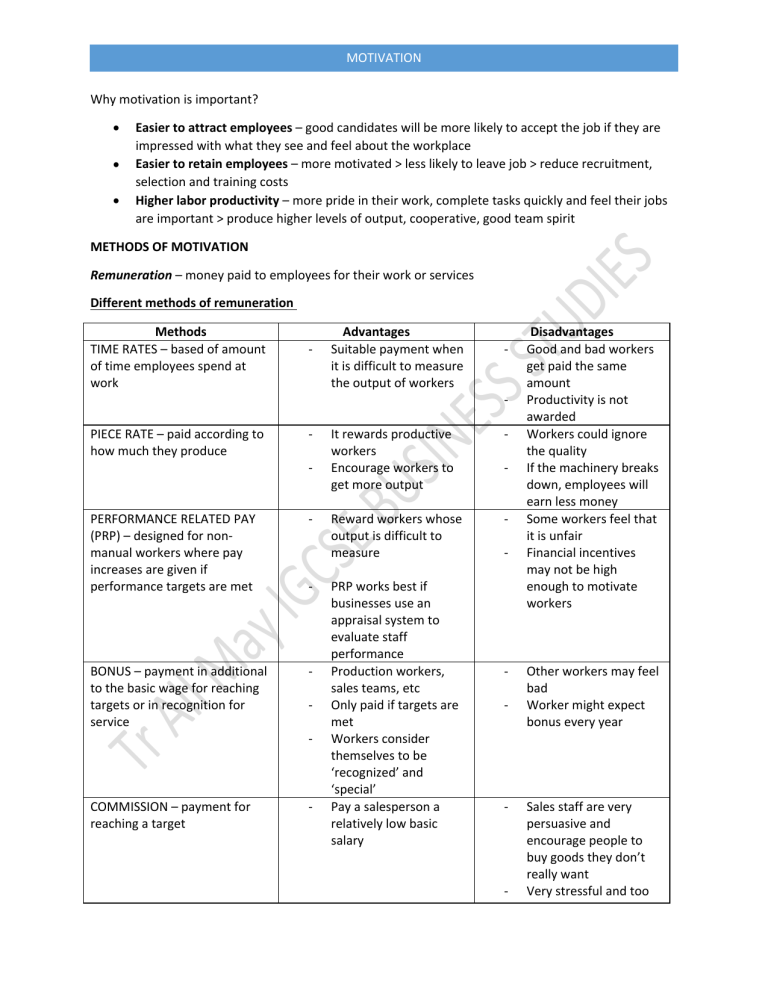
MOTIVATION Why motivation is important? Easier to attract employees – good candidates will be more likely to accept the job if they are impressed with what they see and feel about the workplace Easier to retain employees – more motivated > less likely to leave job > reduce recruitment, selection and training costs Higher labor productivity – more pride in their work, complete tasks quickly and feel their jobs are important > produce higher levels of output, cooperative, good team spirit Remuneration – money paid to employees for their work or services Different methods of remuneration - Advantages Suitable payment when it is difficult to measure the output of workers - - - Ma - Tr All BONUS – payment in additional to the basic wage for reaching targets or in recognition for service COMMISSION – payment for reaching a target - Reward workers whose output is difficult to measure - CS - y IG PERFORMANCE RELATED PAY (PRP) – designed for nonmanual workers where pay increases are given if performance targets are met It rewards productive workers Encourage workers to get more output EB US - INE - PIECE RATE – paid according to how much they produce Disadvantages Good and bad workers get paid the same amount Productivity is not awarded Workers could ignore the quality If the machinery breaks down, employees will earn less money Some workers feel that it is unfair Financial incentives may not be high enough to motivate workers SS Methods TIME RATES – based of amount of time employees spend at work STU D IE S METHODS OF MOTIVATION - PRP works best if businesses use an appraisal system to evaluate staff performance Production workers, sales teams, etc Only paid if targets are met Workers consider themselves to be ‘recognized’ and ‘special’ Pay a salesperson a relatively low basic salary - - - - - Other workers may feel bad Worker might expect bonus every year Sales staff are very persuasive and encourage people to buy goods they don’t really want Very stressful and too MOTIVATION much competition between staffs PROMOTION – employees want to improve their skills, learn new ones and try to get promotion> promotion always comes with higher pay > reward employees for taking on additional responsibilities FRINGE BENEFITS – perks over and above the normal wage or salary Discounts when buying the employer’s product Free accommodation Free private health insurance, etc STU D IE S - NON – FINANCIAL REWARDS SS 1. JOB ROTATION – allow employees to change jobs from time to time - Motivate workers and provide a business with more flexibility - Training costs will rise and benefits of specialization may be lost EB US INE 2. JOB ENRICHMENT – workers should be given tasks that require more responsibility and creativity if a business wants to motivate them - More challenging > more interesting - Take extra task without resources and training > may be displeased Tr All Ma y IG CS 3. AUTONOMY (empowerment) - giving workers the authority to make choices and decisions about the way they work - Feel trusted, more self-confidence, a way of recognizing their achievement - Higher productivity, reduce the numbers of managers and supervisors - Some workers may not be confident


