Enzyme Catalysis: AP Biology Study Guide & Experiment Controls
advertisement

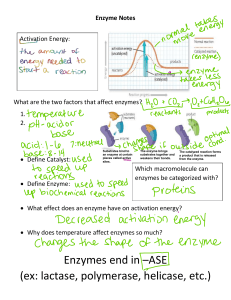
AP Daily 3.2 Video One - Enzyme Catalysis 1. Why do enzymes usually facilitate only one type of reaction? Enzymes usually facilitate only one type of reaction because they have specific active sites that are complementary to the shape and chemical properties of their substrates, allowing them to bind and catalyze specific reactions effectively. 2. What is activation energy? Activation energy is the energy required to start a chemical reaction. It’s the energy barrier that reactants must overcome to transform into products. 3. How do enzymes affect activation energy, and how does this affect the rate of reaction? Enzymes lower the activation energy required for a chemical reaction, making it easier for the reaction to occur. This affects the rate of the reaction by increasing the speed at which it takes place. 4. A big part of your success on the AP exam will be determined by your ability to identify the components of an experiment. Pause the video at 2:45, and identify what would be the best control of this experiment. Place a catalase-soaked disk in a beaker of water. AP DAILY 3.2 VIDEO TWO - ENZYME CATALYSIS 1. Describe three differences between the control group and the experimental group. The control group produces data in standard conditions, whereas the experimental group generates data in altered conditions. The experimental outcomes are then compared to those of the control group, serving as a reference point. Lastly, the control group gathers data in untreated conditions, while the experimental group collects data under treated conditions. 2. How is a negative control different from a positive control? A negative control is used to determine what happens when the variable being tested is absent or has no effect, typically resulting in no significant change. A positive control is used to show the expected outcome when the variable being tested has a known effect, ideally resulting in a known and measurable change. 3. What are controlled variables (aka constants) and why are they useful? Controlled variables, also known as constants, are factors in an experiment kept the same to ensure that observed effects are due to the manipulated variable, enhancing the reliability and validity of the experiment’s results. 4. In the peroxidase experiment in the video, what is the control group? Justify the use of it as a control group. Is it an example of a negative or positive control? Control group = 37 degrees Celsius This test represents the normal temperature for human cells. Positive control. 5. In the polyphenol oxidase experiment in the video, what is a possible control group? Justify the use of it as a control group. Control Treatment: Reaction without enzyme Justification: Confirms enzyme is necessary