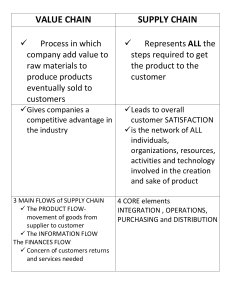
PROCUREMENT/ PURCHASING Learning Outcomes 1. Describe the role of procurement in the supply chain 2. Identify the differences between traditional purchasing and contemporary purchasing. 3. Identify and define the four stages of purchasing sophistication Learning Outcomes 4. Describe the critical success factors (CSFs) needed in the purchasing function 5. Identify the key functions of purchasing 6. Construct a vendor rating system when making an important purchase. ROLE OF PROCUREMENT IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN What is Procurement? It is the business functions of procurement planning, purchasing, inventory control, traffic, receiving, incoming inspection, and salvage operations BUYER An individual whose functions may include supplier selection, negotiation, order placement, supplier follow-up, measurement and control of supplier performance, value analysis, and evaluation of new materials and processes. In some companies, the supplier scheduler handles the functions of order placement and supplier follow-up PRODUCT Any good or service produced for sale, barter, or internal use TRADITIONAL PURCHASING VERSUS CONTEMPORARY PURCHASING TRADITIONAL • buyers were to send a request for quotation (RFQ) to two or three potential suppliers • they decided to whom they would award the order, usually based on the lowest quoted cost, assuming the delivery time and product quality were acceptable TRADITIONAL The traditional purchasing function was concerned primarily with the buying process in which they placed the orders and followed up to assure delivery of those orders • To evaluate vendors many companies have resorted to using vendor rating systems that cover a number of both tangible and intangible factors Table 1 CONTEMPORARY PURCHASING Companies recognize that purchasing should be involved in both tactical and strategic decisions The contemporary approach requires the buying organization to become partners with its suppliers CONTEMPORARY PURCHASING Purchasing organizations are expected to participate, often as part of a cross-functional team, in decisions concerning strategic sourcing. CONTEMPORARY PURCHASING These decisions include: • Supplier evaluation • Supplier selection for long-term relationships • Contract structuring and negotiation • Supplier relationship management (SRM) • Supply chain coordination and collaboration CONTEMPORARY PURCHASING Contemporary purchasing is more oriented to building long-term relationships with fewer, but more dependable suppliers. CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING 1. Functionality The first CSF for purchasing was to obtain goods or services that satisfied the needs of the users CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING 2. Availability Purchasing has always had the primary responsibility to make goods or services available when needed by the production line, by the retail store when having a sale. CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING 3. Cost Close behind availability was the requirement to buy goods and services at the lowest possible cost. CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING 4. Quality Obtaining a good quality of purchased goods and services has always been an implicit responsibility of purchasing. CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING 5. Match Inflow with Outflow Just as matching the product amounts and mix produced with the amounts sold required collaboration between the production and marketing departments, matching inflows with outflows required collaboration between production and purchasing as well. CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING 6. Reduce Variances in Delivery • It is necessary for purchasing departments to monitor the performance of their suppliers and encourage them to be more consistent in their performance. • If they did not improve, suppliers faced the prospect of reduced business, or even elimination as a supplier. CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING 7. Increase Supplier Dependability • The attention to supplier delivery performance opened the opportunity and need to evaluate suppliers on other tangible criteria as well, such as lead times and quality of merchandise, and even to explore such intangible services such as the supplier’s help in suggesting ways to improve the buyer–seller relationship CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING 8. Reduce the Bullwhip Effect • The bullwhip effect is an extreme change in the supply position upstream in a supply chain, generated by a small change in demand downstream in the supply chain CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING 9. Become an Intercompany Facilitator • They generally had the most information about suppliers and could expand their information base to include information desired by other functions in the buying organization. CRITICAL FACTORS FOR PURCHASING 10. Find Sustainable Suppliers • The reputation of a firm is closely linked to the social, environmental, and ethical profiles of an organization’s spending. • Purchasing departments must add finding responsible suppliers to their list of operating objectives. PURCHASING PROCESS, SUPPLIER EVALUATION, AND BUILDING SUPPLIER RELATIONSHIPS Purchasing Process These activities include: 1. determining the order quantity 2. timing the order placement 3. monitoring the orders for on-time delivery 4. assessing the accuracy of the order 5. checking the quality of the product 6. approving the supplier invoice for payment 7. and reconciling problems that occur during the process. 1. purchaser receives the request 5. orders are received 2. purchaser selects a supplier PURCHASING CYCLE 4. orders are monitored 3. purchaser places the order with a vendor Figure 1. Purchasing Cycle Figure 2. Purchase Order Process Flow Supplier Evaluation The evaluation should include tangible and less tangible measures • Tangible measures - product quality and on-time delivery • Less tangible measures - supplier cooperativeness and trust. Supplier Relationship Management “a comprehensive approach to managing an enterprise’s interactions with the organizations that supply the goods and services the enterprise uses. Supply Chain Coordination/Collaboration All of the activities mentioned should lead to an effective level of supply chain coordination and eventually to collaboration among supply chain participants. Thank You