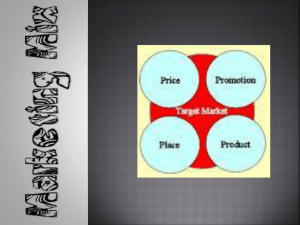
MARKETING REVIEWER Distribution – process of moving the product Channel of Distribution 1. 2. 3. 4. Manufacturer – point of origin Wholesalers – Retailers – Consumers – point of consumption Intermediaries - Wholesalers Retailers Middle man Agents Brokers “THERE WILL ALWAYS BE A NEED FOR SOME SELLING. BUT THE AIM OF MARKETING IS TO MAKE SELLING SUPERFLUOUS. THE AIM OF MARKETING IS KNOW AND UNDERSTAND THE CUSTOMER SO WELL THAT THE PRODUCT OR SERVICE FITS HIM AND SELLS ITSELF. IDEALLY, MARKETING SHOULD RESULT IN A CUSTOMER WHO IS WILLING TO BUY. ALL THAT SHOULD BE NEED IS TO MAKE PRODUCT OR SERVICE AVAILABLE” - PETER DRUCKER Marketing – managing profitable customers relationships - Attracting new customers , retaining and growing of current customers Marketing is NOT synonymous with “ sales or advertising” Selling is only the tip of iceberg Marketing (Philip Kotler) – marketing is a social and managerial process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others. Marketing management – the art and science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them. Creating, delivering and communicating superior customer value is key. a. Customer Management – marketers select customers that can be served well and profitably. b. Demand Management – marketers must deal with different demand states ranging from no demand to too much demand. Market – In marketing ( buyers only). In economics, it’s the buyers and sellers. Target Market – homogenous group which has similar likes and common interests Customers – people who buy the products Consumers – people who uses the products Client – they arrange the time and location Clientele – group of clients Demand – needs and wants of customers Prospects – potential customers Things that can be marketed : Goods, services, experiences, events, persons, places, properties, orgnizations, informtions, ideas A marketer is someone who seeks a responseattention, a purchase, a vote, a donation – from another party called prospect If two parties are seeking to sell something to each other, we call them both marketers 2 interacting components of marketing – company and market 2 components of market – customer and competion The strategic 3C’s concept – can provide a standard for judging marketing effectiveness. The output of these 3C’s is collectively called Key Results Area 1. Customer – sales ( better than before) of product and service 2. Competition - market share ( better than others) – standing in the market 3. Company -profit ( better than expected) – serve as the reason to make your standing go up 4 U’s of marketing 1. New User – who uses the product or services 2. Extended User – who can still use the product or service 3. New Usage – for what purpose is the product or service used? 4. More Usage – when and in what occasions is the product or service used? Core marketing concept a. Needs – are the basic reason or the minimum requirements consumers look for in a product or service. They are called the qualifying or “gatekeeper” dimension in a purchase. (physical, social and individual) b. Wants – are determining dimensions among many choices. They are the motivating attribute. c. Expectations – are values or intangibles associated with a product or service. They are actually part of wants. Marketers don’t create the needs and wants of customers because they are already existing, they are the one telling that they need this product of that there product exists. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs - Self-actualization ( self-fulfillment) Self-esteem Love and belonging - Safety needs ( security) Physiological needs ( basic needs) Features – product attributes Advantages – positive Benefits – what’s in the product Approaches of Marketing 1. traditional marketing – without the use of social media. Examples are mass media, television,radio, e-mails, print medias 2. contemporary marketing – modern marketing strategies. Examples are social media apps, shoppe, influencers Goals of Marketing Awareness – informing the customers about the product or service Trial – encourage the customer to buy the product ( free tastes, testers) Availability – accessibility – distribution Repeat Purchase – buying product again ( loyal customers) Marketing Orientation a. production concept – internal capabilities, producing in lower price (manpower, machine, money, equipments) b. product concept – innovation, quality of the product, features - KAIZEN c. selling concept – aggressive sales technique, salespersons at sales method. In short to make profit d. marketing concept – company plus customer. Focus not only on customers but they also focus on profits e. societal-marketing concept – company plus customer plus the society Marketing Mix ( 4 P’s) 1. product – to satisfy the needs and wants of the target market (satisfaction). The good or service the company provides. 2. price – to make the product affordable to the target market and reflect the value of benefits provided (amount) 3. place – to make the product conveniently available to the target market ( distribution). Refers to where the product is purchased. 4. promotion –to build and improve consume demand ( advertising to effectively persuade) Promotions Mix a. advertising – to effectively inform, persuade and remind the target market b. public relations – to offer a positive image of the company and the brand (influence perception of public, disseminating information) c. sales promotion – to convince customers to buy immediately(discount) d. selling – to get the customer to buy YOU DON’T TRY TO SERVE EVERYBODY - #1 RULE OF MARKETING 3 people with local businesses 1. Richard V. Sanz 2. Jose Magsaysay Jr. 3. Edgar Injap Sia