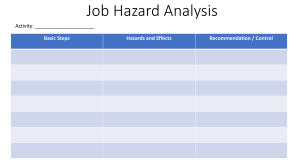
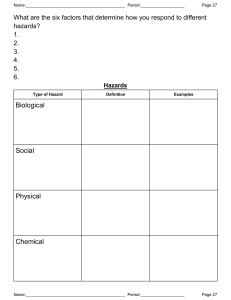
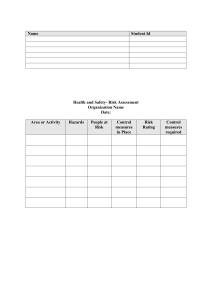
DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AND MANAGEMENT MODULE 1 by Benjamin Pelayo Jr. NSTP Facilitator Katipunang Luntian DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AND MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS WHAT IS DISASTER? Disasters are emergencies that cannot be handled by those affected without outside assistance. A serious disruption of the functioning of a community or a society involving widespread human, material, economic or environmental losses and impacts, which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources (UNISDR, 2009) They may be caused by natural or man-made events wherein communities experience severe danger and incur loss of lives and properties causing disruption of their social structure and to all or some of the affected communities’ essential functions. WHAT IS HAZARD? HAZARD is an event or occurrence that has the potential to cause harm to life and damage property and the environment. WHAT IS VULNERABILITY? VULNERABILITY comprises conditions determined by physical, social, economic, and environmental factors or processes, which increase the susceptibility of a community, school, or certain area in a locality to the impact of hazards. WHAT IS RISK? RISK is the probability of harmful consequences, or expected loss of lives, people injured, livelihoods, disruption of economic activities and damages to the environment as a result of interactions between natural or human induced hazards and vulnerable / capable conditions. WHAT ARE CAPACITIES? CAPACITIES are those positive resources and abilities which are helpful to individuals, families and community in Mitigating, preparing for, responding to and recovering from the hazard impact. Hazard x Vulnerability Risk = ------------------------------------Capacities Last year, the World Risk Index 2022 put the Philippines at the number one spot for the most-disaster-prone country in the world. The WRI report gave the country an index score of 46.86, the highest among the top ten most-disaster-prone countries worldwide because of high risk, exposure, and vulnerability (Dela Pena, 2023). The top ten most disasters prone countries are the following, in second place is India with an index score of 42.31, followed by Indonesia with 42.31, Colombia with 38.37, Mexico with 37.55, Myanmar with 35.49, Mozambique with 34.37, China with 28.70, Bangladesh with 27.90, and Pakistan with 26.75. NATURAL HAZARDS Hydro-Meteorological Phenomena and Hazard Cyclone/Typhoon/Tornado Thunderstorm Flood Storm Surge Landslide Global warming Extreme Climatic Vulnerabilities Heat Waves Geological Phenomena and Hazards Earthquakes Tsunami Volcanic Eruption Astronomical Hazards HUMAN-INDUCED HAZARDS Technological Hazards Structure collapse Socio-Economic, political, Security Hazards Fire Bomb threats Vehicular related accident Kidnapping threats Chemical spill Hostage taking Electrical blackout Civil disorder Food poisoning Environmental Hazards Red tide Water pollution WHAT CAN WE DO WITH THE POSSIBLE RISK? There is a need to understand and to put into life the concepts, principles, and practical application of disaster risk reduction and management. CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK OF DRRM The Conceptual Framework of elements of Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) considered with the possibilities to minimize vulnerabilities and disaster risks throughout a society, to avoid through PREVENTION or to limit through MITIGATION and PREPAREDNESS the adverse impacts of hazards, within the broader context of sustainable development. CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK OF DRRM CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK OF DRRM WHAT IS PREVENTION? These are activities to provide outright avoidance of the adverse impact of hazards and means to minimize related environmental, technological and biological disasters. WHAT IS MITIGATION? These are both Structural and non-structural measures undertaken to limit the adverse impact of natural degradation and technological hazards. hazards, environmental WHAT IS PREPAREDNESS? These are activities and measures taken in advance to ensure effective response to the impact of hazards, including the issuance of timely and effective early warnings and the temporary evacuation of people and property from threatened locations. WHAT IS MITIGATION? WHAT IS PREPAREDNESS? WHAT IS PREPAREDNESS? WHAT IS PREPAREDNESS? WHAT IS PREPAREDNESS? WHAT IS R.A. 10121? WHAT IS R.A. 10121? R.A. 10121 is an act strengthening the Philippine Disaster Risk Reduction and Management system, providing for the national disaster risk reduction risk and reduction framework and institutionalizing the national disaster risk reduction and management plan, appropriating funds therefore and for other purposes. This act shall be known as the “Philippine Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Act of 2010 WHY THERE IS A NEED FOR DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AND MANAGEMENT The Systematic Process of using administrative decisions, organizations, operational skills and capacities to implement policies, strategies and coping capacities of the society and communities to lessen the impacts of natural hazards and related environmental and technological disasters; includes structural and non-structural measures is the primary reason why there is a need for disaster risk reduction and management system. ELEMENTS OF DISASTER RISK MANAGEMENT Risk Reduction Risk can be reduced and measures can be employed to ensure that hazards will not result in disasters if people reduce the weaknesses and vulnerabilities to existing hazards in the location. The concept and practice of reducing disaster risks through systematic efforts to analyze and manage the causal factors of disasters, including through reduced exposure to hazards, lessened vulnerability of people and property, wise management of land and the environment, and improved preparedness for adverse events. Risk Management It is needed for disaster prevention to ensure sustainable development so that people can lead a good, healthy, and happy life without creating damage to the environment. The systematic process of using administrative directives, organizations, and operational skills and capacities to implement strategies, policies and improved coping capacities in order to lessen the adverse impacts of hazards and the possibility of disaster. THANK YOU AND KEEP SAFE!!! DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AND MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS MODULE 1 by Benjamin Pelayo Jr. NSTP Facilitator Katipunang Luntian