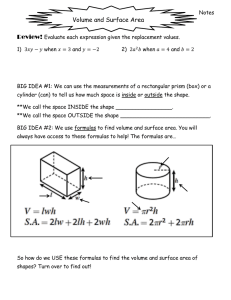
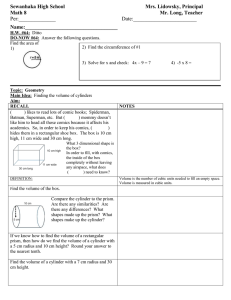
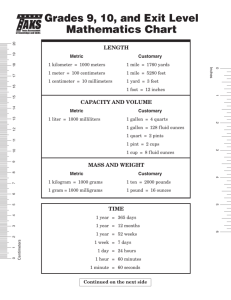
Mean Absolute Deviation Simple Interest Compound Interest Formula: I=Prt Formula: A = P(1+r)t P = ____________ P = ____________ r = ____________ r = _____________ t = ____________ t = _____________ To convert rate from % to decimal, divide the % by 100 Time has to be in years. If given months, divide by 12. Solving 1-Step Equations and Inequalities Work Space Solving Multi-Step Equations and Inequalities Work Space 1. 2. 3. Distributive Property Combine like terms on the same side of the equation Get the variable by itself using inverse operations a. If you divide by a negative while solving an inequality, flip the sign Solving Equations using Algebra Tiles Work Space 1. 2. 3. Distributive Property Combine like terms on the same side of the equation Get the variable by itself using inverse operations a. If you divide by a negative while solving an inequality, flip the sign Direct Variation y = kx X Y Work Space k = (y ÷ x) Slope of a Line Calculate from two points: Point 1 (____,____) Point 2 (____,____) x1 = ____ y1 =____ x2 =____ y2 =____ Work Space: Find slope using a graph: Slope-Intercept form from two points Slope Intercept Form: y=mx+b Points: (___,___) (___,___) Step 1: Determine m using the slope formula Y2 = ___ Y1 = ___ X2 = ___ X1 = ___ Step 2: plug two coordinates in the slope-intercept formula to determine b Step 3: Plug in the slope and y-intercept to write your new formula Y = ____ X = ____ m = ____ m = ______ b = ______ __ = __ (__) + b y = ___x + ___ Reflection Pre-Image Image (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) Basic Reflection rules: Across x-axis (x,y) -> (x,-y) Across y-axis (x,y) -> (-x,y) Across y = x (x,y) -> (y, x) Across y = -x (x,y) -> (-y,-x) Dilation: Scale Factor (k) = ______ Pre-Image Image (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) Work Space: Translation: Rules = (x + ____ , y + ____) Pre-Image Image (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) Work Space: Pre-Image Image (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) (____,____) Rotation Rules CC (90) C (270) (-y, x) CC (180) C (180) (-x, -y) CC (270) C (90) (y, -x) CC (360) C (360) (x,y) Rotation Rotation Rules Clockwise Counterclockwise Reflection Rules Rules 270 (-y,x) x-axis (x, -y) y-axis (-x, y) y=x (y,x) y = -x (-y, -x) 90 180 (-x,-y) 180 90 (y,-x) 270 360 (x,y) 360 Pythagorean Theorem a2 + b2 = c2 √c2 - a2 = b √c2 - b2 = a a = _____________ b = _____________ c = _____________ Work Space Find missing angle measurement triangle a + b + c = 180° 180° - a - b = c a =__________ b =__________ c =__________ Work Space Finding Exterior Angle 2 Strategies to find measure of an exterior angle. 1) 2) Subtract the linear pair from 180 Add the two other interior angles that do not form a linear pair with the exterior angle Work Space Parallel lines cut by a Transversal Work Space Corresponding = angles are equal Supplementary = angles add up to 180 Interior Angle Measurements Shape Shape Model Angle Sum Equals Triangle 180 Square/Rectangle 360 Pentagon 540 Hexagon 720 Heptagon 900 Octagon 1080 Non-Polygons Circles Ovals Any shape with a curve Area Formulas A = ½ bh b =_____ h =_____ Work Space A = bh b =_____ h =_____ Work Space A = ½ (b1 + b2)h b1 =_____ h =_____ b2 =_____ Work Space A = ℼr2 r =____ r = diameter/2 Work Space Circumference C = 2ℼr r =______ C =ℼd d =_____ Work Space Volume Formulas - All B = Area of the Base V = Bh h =____ B (rect./squ.) = bh B (triangle) = ½ bh V = Bh h =_____ B = ℼr2 V = ⅓ Bh B (square) = bh B (triangle) = ½ bh V = ⅓ Bh B = ℼr2 V = 4/3ℼr3 h (of prism)=____ b =____ h =____ h (cylinder)=____ b =____ r =____ h (pyramid) =____ b =____ h =____ h =_____ r =_____ r =_____ Volume Formula: Prism or Cylinder V = Bh h (of prism) =____ B (rectangle/square.) = bh B (triangle) = ½ bh V = Bh h =_____ B = ℼr2 h (of prism)=____ b =____ h =____ h (cylinder)=____ b =____ r =____ Volume Formula: Pyramid or Cone V = ⅓ Bh B (square) = bh V = ⅓ Bh B (triangle) = ½ bh V = ⅓ Bh B = ℼr2 h (pyramid) =____ b =____ h =____ h (pyramid) =____ b =____ h =____ h =_____ r =_____ Volume Formula: Sphere V = 4/3ℼr3 r =_____ Volume Formulas Fill in the Blanks Cylinder: 3.14 x ___2 x___ Cone: ⅓ x 3.14 x ___2 x___ Sphere: 4/3 x 3.14 x ___3 Rectangular Prism and Cubes: ___ x ___ x ___ Triangular Prism: (½ ___ x ___) x ___ Surface Area Formulas Lateral (Prism) Total (Prism) Lateral (Cylinder) Total (Cylinder) S = Ph S = Ph + 2B S = 2ℼrh S = 2ℼrh + 2ℼr2 P =_____ h =_____ P =_____ h =_____ B =_____ r =_____ h =_____ r =_____ h =_____ P = perimeter of base h = height of the Prism or Cylinder B = Area of the Base Surface Area Formulas: Prism Lateral (Prism) Total (Prism) S = Ph S = Ph + 2B P =_____ h =_____ P =_____ h =_____ B =_____ P = perimeter of base h = height of the Prism or Cylinder B = Area of the Base Surface Area Formulas: Cylinder Lateral (Cylinder) Total (Cylinder) S = 2ℼrh S = 2ℼrh + 2ℼr2 r =_____ h =_____ r =_____ h =_____ Length Conversions Customary Metric 1 mile = 1,760 yards 1 yard = 3 feet 1 foot = 12 inches 1 kilometer = 1,000 meters 1 meter = 100 centimeters 1 centimeter = 10 millimeters mile (mi) yard (yd) feet (ft) inches (in.) kilometer (km) meter (m) centimeter (cm) millimeter (mm) Work Space Volume and Capacity Conversions Customary 1 gallon = 4 quarts 1 quart = 2 pints 1 pint = 2 cups 1 cup = 8 fluid ounces gallon (gal) quarts (qt) pints (pt) cups (c) fluid ounces (fl oz) Metric 1 liter = 1,000 milliliters liter = L milliliter = mL Work Space Weight and Mass Conversions Customary Metric 1 ton = 2,000 pounds 1 pound = 16 ounces 1 kilogram = 1,000 grams 1 gram = 1,000 milligrams ton (T) pounds (lb) ounces (oz) kilogram (kg) gram (g) milligram (mg) Work Space Adding and Subtracting Fractions Step 1: Original Problem Step 2: Find LCM of denominators Step 3: Convert to equivalent fractions Step 4: Rewrite problem and solve Simplify if needed Comparing Fractions: Butterfly Method Comparing Rational Numbers Adding Positive and Negatives Work Space Multiplying Integers Work Space Data Mean: Average Mode: The number that is repeated the most Range: Subtract the largest number and the smallest number Work Space Data Set: ____________________________________ Least to Greatest: Median: List the numbers from least to greatest, median is the middle number ____________________________________ Graphing Data Data: