Big Data & Analytics: Exploiting Data for Competitive Advantage
advertisement

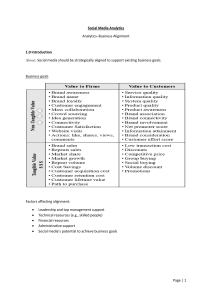
Big data-> large volume and variety Data new source of value, data today enables growth, data can be extracted, processed and transferred. Metaphor of oil-> data are like a commodity (how can I extract value from data?) How companies can exploit BIG DATA? Data analytics: the use of data and related business insights developed through applied analytical disciplines (for example, statistical, contextual, quantitative, predictive, cognitive, and other models) to drive fact-based planning, decisions, execution, management, measurement, and learning. 3 main benefits from data analytics: 1. Cost reduction -> identification of more efficient way of making business 2. Improved decision-making processes 3. New products and services Analysis on data-> more precise analysis of the context and the individual How can we apply data to segmentation? -> loyalty programs (you have data on what each person will purchase in relation to its fidelity card) RFM (recency, frequency and monetary value) Recency: last time I performed a specific purchase action Frequency: how frequent I purchase some products/brand Monetary value: I purchase in box (amount that would be paid in cash) Data allow you to make decisions based on these 3 dimensions-> I can segment users based on these dimensions We can use data to better refined customer journey-> set of interactions that a user has with the company Companies don’t have a unified vision of the customer, they have different set of data and often they don’t communicate If I introduce a new product with a specific price and I observe how this product could affect sales of other products (cannibalization) Data has enabler of decision related to shelf-placement (what product should I place near another) We can use data to support our managerial decision, to make better context analysis, using for segmentation and positioning Example: Walmart Walmart performs analysis of real- time data. These analyses enable Walmart to deliver information to business partners fast, so they can take action proactively and cut down the turnaround time. In Walmart data analysis system has led to a reduction in the time it takes from a problem being spotted in data to a solution being proposed, from an average of 2-3 weeks down to around 20 minutes. Data analytics and value creation Descriptive analytics: analyzing a phenomenon that it’s occurred -> only describing The value is in terms of potential knowledge of what happened Diagnostic analytics: why a specific phenomenon occurred? I make a sensitivity analysis, what if I would increase the price? Predictive analytics: what will happen in the future (forecast)-> best/worst case scenarios Prescriptive analytics: Managerial actions (how can I make it happen?)-> the value and the complexity increases It’s vital to extract managerial implications from data Data analytics and competitive advantage Data -> ability to design and control digital network An advantage is in terms of knowledge (example: car sharing has the knowledge of movement of users in specific area) We are moving from an era of core competences to and era in which the data and analytics will constitute the key success of a Company Data is related to network effect-> the more individuals interact with my platform, the more value I ca extract In digital operating models, the learning effect and the network effect amplify the impact of number of users on value creation, providing the opportunity to overwhelm traditional organizations. Network effects->potential amplification of the value I provide to my users as the number of the latest increases (example TripAdvisor) Data will enable another lever to use for competitive advantage BIOMETRIC DATA BI INTELLIGENCE FORECAST (31 Dec 2013): Google Glass Will Become A Mainstream Product and Sell Millions By 2016 In 15 January 2015-> google ended sales of google glass Also, 3D televisions failed Zalando seemed to not be successful at the beginning-> instead it wasn’t like that We assume that consumers are able to verbalise their needs and marketers are able to ask the right questions to customers The validity of self-reports can be severely compromised by a number of shortcomings: - Respondents have imperfect memory - The mere act of asking a question is known to change respondents’ behaviour - Highly sensitive questions are subject to misinterpretation or outright deception. We try to solve all these issues by issuing a set of tools that related to neuromarketing Neuromarketing refers to the application of tools and theories from neuroscience to better understand consumer decision-making and related processes We have a neuron physiological phase related to a psychological phase The umbrella term of ‘neuromarketing’ additionally encompasses other psychophysiological techniques concerned with data other than brain activity: biometrics (thus, bio marketing) Biometrics: they study also peripheral neuro system Impulse purchases are related to emotional stages What can biosciences do for marketing? You measure how your brain responds to certain questions Neuromarketing and bio marketing are growing rapidly as they provide researchers with a chance to observe consumer responses toward a certain product or service without interfering. You have measurement in real time and overtime These techniques can be used to: 1. Detect consumers’ visceral reactions to marketing stimuli -> Neuroscience techniques can provide information about implicit processes that are typically difficult to verbalize and devoid of self- reports biases. Examples includes situations in which the decision maker is unaware of or unable to articulate why he or she exhibits a specific behavior. 2. Improving predictions of consumer behavior -> Incorporating neural measures into decision-making models can improve predictions of marketing-relevant behavior Example: Predicting impulse buying (individual is highly involved) 3. Consumer insight generation and validation BIOMARKETING Toolbox->neuroscientist can use: 1. Physiological layer Cortical and subcortical neural activity Sympathetic and parasympathetic system (cardiac, respiratory, muscular, skin temperature, hormonal, pupil dilatation, genetics, electrodermal activity) 2. Behavioural layer (observable behavioural) Ocular activity, facial expressions, body gestures, vocal spectrum, interface interactions 3. Cognitive layer (self-reports and interviews)-> rationalization of a behaviour Biomarketing is used to complete other researched methods 1.Detect physiological responses in the cortical system-> FMRI (works on the metabolic and blood oxygenation) – functional magnetic resonance imagining (high precision, not affordable – too expensive) EEG (works on the electrical responses from the cortical system)-electroencephalogram It only works on the external part of the brain We can detect where attention, memorisation, engagement and pleasure occur in real time Mobility of the individual is quite limited in MEG, NIRS and CT 2.Eye tracker Key points in using biomarketing techniques: - Integrating tools lead to a deeper understanding of consumer experience - Traditional marketing methods (survey, focus group, interview) should be still used as they provide complementary information on consumer evaluations and intentions - Neuromarketing and biomarketing studies require a expert in different fields (marketing, medicine, design...) with different background to be conducted and to interpret results to extract actionable managerial insights Application fields Evaluation of new products in terms of usability, effectiveness and required cognitive effort with the purpose of increasing probabilities of success and fastening the process of adoption. Understanding the user experience Testing the usability Effectiveness of labels Emotional impact of packaging Segment the audience also taking into consideration biometrics data Work also on the packaging Support price definition for new products and price promotions for established products Testing price modulation Understanding reactions to price promotion Understanding reactions to promotion display Evaluate both physical and virtual stores, in terms of retail experience, touchpoints, interactive tools experience, layout Effectiveness of shelf display Point-of-sale layout Effectiveness of visual merchandising Attractiveness of website display Neuromarketing can help communication activities both in the ex-ante planning phase and in the phase of ex-post evaluation of communication campaign effectiveness. Understanding the impact of an advertisement content in terms of aroused emotions, memorability, ability to gain attention. Appraising the level of sensibility of different targets towards the content and the causes of its effectiveness or ineffectiveness. Product placement: understanding if it is perceived by the target and in which measure it causes an answer towards the brand. Understanding the right context in which place the advertising campaign