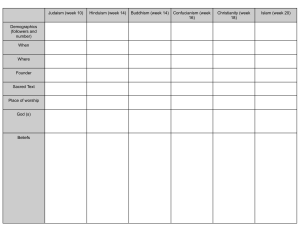
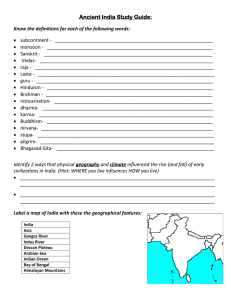
Which ancient Indian religion or philosophy is known for its focus on non-violence, truth, and self-discipline? A. Hinduism B. Buddhism C. Jainism D. Zoroastrianism The "Four Noble Truths" and the "Eightfold Path" are central teachings in which religion that originated in India? A. Hinduism B. Buddhism C. Jainism D. Sikhism What ancient Indian scripture contains a collection of hymns, prayers, and rituals and is one of the oldest sacred texts in the world? A. Bhagavad Gita B. Upanishads C. Vedas D. Mahabharata The caste system, a social hierarchy with distinct social classes, played a significant role in the social structure of ancient India. Which term refers to the lowest caste in the system? A. Brahmins B. Kshatriyas C. Vaishyas D. Dalits (Untouchables) Who is the founder of Buddhism, and what is his title? A. Siddhartha Gautama, the Buddha B. Mahavira, the Enlightened One C. Guru Nanak, the Prophet D. Ashoka, the Great Section II: Short Answer Explain the concept of "dharma" in ancient Indian religions and its significance. Describe the Maurya Empire, including its most famous ruler and his contributions. How did the Silk Road facilitate cultural and economic exchanges between India and other regions? Section III: Essay Analyze the impact of Ashoka's rule on the Maurya Empire and its lasting influence on India. Compare and contrast the beliefs and practices of Hinduism and Buddhism, focusing on key similarities and differences. Answers Section I: Multiple Choice C. Jainism B. Buddhism C. Vedas D. Dalits (Untouchables) A. Siddhartha Gautama, the Buddha Section II: Short Answer "Dharma" refers to the moral and ethical duties and responsibilities that individuals must follow in their lives according to their caste, age, gender, and occupation. It was seen as a guide to living a righteous and virtuous life. Significantly, "dharma" was a core concept in both Hinduism and Buddhism. The Maurya Empire was one of the largest and most powerful ancient Indian empires. Its most famous ruler, Ashoka, contributed to the spread of Buddhism through his support and promotion of the religion. His edicts, inscribed on pillars and rocks, promoted moral principles and social justice. The Silk Road facilitated cultural and economic exchanges between India and other regions by allowing the trade of goods, technologies, art, and ideas. It was a network of trade routes connecting India to Central Asia, the Middle East, and China, promoting cultural diffusion. Section III: Essay Ashoka's rule had a profound impact on the Maurya Empire and its lasting influence on India. His embrace of Buddhism and promotion of non-violence and moral values through his edicts contributed to the spread of Buddhism in India. His support for a more just and compassionate society left a lasting impact on India's social and moral values. Hinduism and Buddhism share the concepts of karma and reincarnation. Both believe in the cycle of life, death, and rebirth. However, they differ in their views on the self (atman in Hinduism and anatta in Buddhism), the role of deities, and the ultimate goal (moksha in Hinduism and Nirvana in Buddhism). While Hinduism includes a wide variety of gods and goddesses, Buddhism rejects the idea of a personal creator god. Hinduism relies on rituals and the caste system, whereas Buddhism emphasizes meditation and the Middle Path to attain enlightenment.