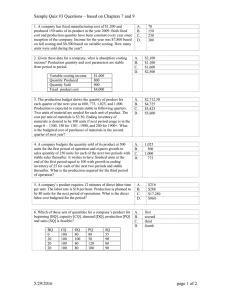
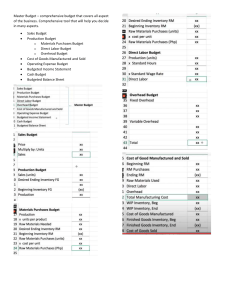
Taccaban, Karen Joy R. Section 2 Managerial Accounting Mid -term Examination Answer the following questions: 1. Peter and Senen Co. sell the same product in a competitive industry. Thus, the selling price of the product for each company is the same. Other data about the two companies are as follows: Peter Senen Fixed Costs P50,000 P70,000 Contribution margin ratio 40% 52% What are the companies’ break event points? PETER = 50,000/40% =P125,000 SENEN = 70,000/52% =P134,615 Data for questions No. 2 through 13 Ethel Corp. produces and sells a single product. The selling price is P25a and the variable cost is P15 per unit. The corporation’s fixed costs is P100,000 per month. Average monthly sales are 11,000 units. 2. What is the corporation’s contribution margin per unit and as a percent of sales (CMR)? Sales- VC=CM 25-15 =10 per unit; 40% 3. What is the corporation’s break- even point? Be units = 100,000/10= 10,000 or Be sales = 100,000/40%= 250,000 4. If the corporation desires to earn profit of P20, 000 before tax, it must generate sales of how much? =(100,000+20,000)/10 = 12,000 units* 25/unit = P300,000 5. If the corporation pays corporate income tax at the rate of 30%, and it desires to earn after-tax profit of P21, 000, it must generate sales of how much? =P325,000 6. How much sales in pesos must be generated to earn profit that is 8% of such sales? =P312,500 7. How many units must be sold to earn profit of P2 per unit? = 12,500 units Taccaban, Karen Joy R. Section 2 8. With average monthly sales of 11,000 units, what is the corporation’s margin of safety? = (11,000*25)-250,000 =275,000-250,000 =25,000 9. What is the Corporation Margin of safety ratio and the break-even sales ratio? Margin of safety ratio=25,000/275,000=9.1% Be sales ratio= 250,000/275,000= 90.91% 10. At the present average monthly sales level of 11,000 units, the corporation’s operating leverage factor is what? DOL= 110,000/10,000 = 11 Sales VC CM FC OE 275,000 165,00 110,00 (100,000) 10,000 11. If fixed costs will increase by P20, 000, the Break-even point in units will increase (decrease) by how much? @100,000FC= 100,000/10 =10,000 units @120,000 FC= 120,000/10 = 12,000 units 12,000-10,000= 2,000 units increase 12. If variable costs per unit will go up by P5, the peso breakeven sales will increase (decrease) to? Be sales= 100,000/20% = 500,000 VC @15= 100,000/40% = 250,000 500,000-250,000= P250,000 increase 13. If selling price will increase to P30, the break -even point in units will increase (decrease) by how much? 13. Be units= 100,000/15 = 6,666.66 or 66,667 units 10,000-6,667= 3,333 decrease in units 14. If sales increase from P800,000 to P900,000, and if the degree of operating leverage is 5, one could expect profit to increase by how many percent? 14. Percentage change in OI= 5*12.5% = 62.5% % of change in sales=900,000/800,000 = 12.5% Taccaban, Karen Joy R. Section 2 15. A company has an operating leverage factor of 4. When its sales increased to P500,000, its profit before tax increased by 100%.Its variable cost ratio is 40%. How much is the company’s fixed costs? 15. =P350,000 Data for questions No. 16 through 24 JYD Corporation uses an absorption costing system for internal reporting purposes. At present, however, it is considering to use the variable costing system. Following are some data regarding JYD Corporation’s budgeted and actual operations for the calendar year 2018. Costs Materials Labor Variable Factory Overhead Fixed Factory Overhead Variable Selling Expenses Fixed Selling Expenses Variable Administrative Expenses Fixed Administrative Expenses Total Budgeted P25,200 18,480 8,400 10,640 16,800 14,700 4,200 6,300 P104,720 Actual P23,400 17,160 7,800 10,000 15,000 14,700 3,750 6,375 P98,185 Finished goods inventory beginning Production Sales Budgeted (Units) 280 1,120 1,120 Actual (Units) 280 1,040 1,000 The budgeted costs were computed based on the budgeted production and sales of 1,120 units, the company’s normal capacity level. The Corporation uses a predetermined factory overhead rate for applying manufacturing overhead costs to its product. The denominator level used in developing the predetermined rate is the firm’s normal capacity. Any over or under applied factory overhead cost is closed to cost of goods sold at the end of the year. There is no work in process inventories at either the beginning or end of the year. The actual selling price was the same as the amount planned, P130 per unit. The previous year’s planned per unit manufacturing costs were the same as the current planned unit manufacturing cost. The beginning inventory of finished goods for absorption costing purposes was valued at such per- unit manufacturing cost. Taccaban, Karen Joy R. Section 2 16. What is the standard product costs per unit under Absorption Costing and Variable Costing? DM DL VMOH FMOH Product cost Absorption 22.5 16.5. 7.5 9.5 56 Variable 22.5 16.5 7.5 46.5 17. What are the manufacturing cost variances for Variable Manufacturing Cost and Fixed Manufacturing cost? Budgeted Variable Cost= 25,200+18,480+8,400 = 52,080 Budgeted Fixed cost= 10,640 actual variable cost= 10,000 Actual Variable Cost= 23,400+ 17,160+7,800 = 48,360 VOH= 52,080-48,360= 3,720 FMOH= 10,640- 10,000= 640 18. What is the Corporation’s operating income (loss) under both the absorption and variable costing methods? ABSORPTION Sales(1000x130) Variable Manufacturing cost(46.5x1,000) Fixed Manufacturing cost(9.62x1000) Variable Non-Manufacturing cost expense(15,000+3,750) Fixed Non-Manufacturing cost expense(14,700+6,375) Operating Income VARIABLE Sales(1000x130) Variable Manufacturing cost(46.5x1,000) Fixed Manufacturing cost Variable Non-Manufacturing cost expense(15,000+3,750) Fixed Non-Manufacturing cost expense(14,700+6,375) Operating Income 130,000 46,500 9,620 18,750 21,075 (95,945) 34,055 130,000 46,500 10,000 18,750 21,075 (96,325) 33,675 19. What were the values of the company’s actual ending finished goods inventory under the absorption and variable costing methods? ABSORPTION Ending FG Inventory= 40x56 or 56.12 = 2,240 or 2,245 VARIABLE Ending FG Inventory= 40x46.5 = 1,860 20. What were the Corporation’s total fixed costs expensed this year on both absorption and variable costing methods? ABSORPTION Total FC Expensed= (9.62x1,000)+ 21,075 = 30, 695 VARIABLE Total FC Expensed = 10,000+21,075 = 31,075 Taccaban, Karen Joy R. Section 2 21. What was the Corporation’s actual manufacturing contribution margin for the year calculated on the variable costing basis? Sales DM DL VMOH 130,000=. 1,000X 130 (22,500)= 1,000X22.5 (16,500)= 1000X16.5 (7500)= 1000X7.5 83,500 22. What was the Corporation’s actual contribution margin for the year calculated on the variable costing method? Actual CM under Variable Costing =83,500- 18,750 = 64,750 23. What were the total variable costs expensed currently by the corporation under the absorption and variable costing bases? ABSORPTION Total VC= (46.5x1,000)+ 18,750 = 62,250 VARIABLE Total VC = 46.5x1,000)+ 18,750 = 62,250 24. The difference between the Corporations’ operating income calculated on the absorption costing basis and that on the variable costing basis was how much? Absorption Variable P34,055 P33,675 P 380 Data for Questions 25 through 35 Petesy Corporation is preparing its Master Budget for 2019. Budget information is as follows: 2019 2020 Sales Production CostOperating Expenses 1st Quarter P280,000 P192,000 2nd Quarter 320,000 200,000 3rd Quarter 360,000 224,000 4th Quarter 352,000 200,000 1st Quarter 320,000 224,000 The budgeted Finished Goods Inventories are: 2018 March 31 P56,000 P64,000 68,000 72,000 76,000 72,000 Taccaban, Karen Joy R. Section 2 June 30 52,000 September 30 60,000 December 31 48,000 The company uses the JIT system on its purchase of materials. It buys materials on cash basis. Included in the production cost each quarter is P44, 000 in depreciation. The operating expenses include depreciation of P12,000 per quarter. All production costs and operating expenses, with the exemption of depreciation are to be paid during the quarter of incurrence. Collections on sales are planned at 60% during the quarter of sales, the balance during the quarter following the sale. Dividends of P20,000 is to be paid in June and again in December if covered by sufficient profits. No dividends will be paid if the net profit is less than P120,000.Income Tax is equal to 32 of the quarter’s income before tax and is paid in the following quarter. The Statement of Financial Position as of December 31, 2018 is as follows: Petesy Corporation Statement of Financial Position December 31, 2018 Assets Equities Cash P76,000 Income tax payable P 12,000 Accounts Receivable 120,000 Inventory 44,000 Share Capital 640,000 Plant and Equipment 580,000 Retained Earnings 168,000 Total 820,000 Total P820,000 25. How much was the actual sales during the last quarter of 2018? AR at the end of 2018 Bal. Received in the following quarter Sale last quarter of 2018 120,000 40% 300,000 26. What is the total budgeted cost of goods sold for the year 2019? 192,000+ 200,000+240,000+220,000= P816,000 27. How much dividends will be paid in 2019? P0 or none 28. What is the total budgeted cash disbursements for production costs and operating expenses for the year 2019? 200,000+212,000+240,000+220,000= P872,000 29. What is the budgeted cash balance on December 31, 2019?P455,200 30. What is the expected balance of accounts receivable as of December 31, 2019? Expected Cash Balance 1st Qtr 2nd Qtr. 3rd Qtr 4th Qtr Full Year Taccaban, Karen Joy R. Opening Balance Sales Receieved from Current Qtr. Sale Received from Previous Qtr. Sale Total Received Accounts Receivable Accounts Receivable, End Section 2 120,00 112,000 0 280,00 320,000 0 168,00 192,000 0 120,00 112,000 0 288,00 314,000 0 112,00 128,000 0 P140, 800 128,000 144,000 120,000 360,000 352,000 1,312,000 216,000 211,200 787,200 128,000 144,000 504,000 344,000 355,200 1,291,200 144,000 140,800 140,800 31. What is the budgeted balance of raw materials inventory as of December 31, 2019? Raw Materials = 0 Finished Goods = P48,000 32. What is the expected balance of Income tax payable as of December 31, 2019? P20,480 33. What is the budgeted balance of Retained Earnings as of December 31, 2019? Budgeted Balance of Retained Earnings Opening Balance 168,000 During the year 109,600 P277,600 34. What is the expected balance of the plant and equipment account as of December 31, 2019? Balance of Plant and Equipment Opening Balance During the year 580,000 (224,000) P356,000 35. If a budgeted statement of financial position as at December 31, 2019 is to be prepared, total assets will be how much? Petesy Corporation Statement of Financial Position December 31, 2019 Assets Cash Accounts Receivable. Amount 393,280 140,800 Liabilities Income tax Payable Share Capital. Amount 20,480 640,000 Taccaban, Karen Joy R. Inventory. Plant and equipment. Total Section 2 48,000 356,000 938,080 Retained Earnings 277,600 938,080 Data for Questions 36 through 38 The accountant of JYD Corporation prepared the following cost analysis report on direct labor costs for the jobs completed during the previous months: Job Actual Hrs. at Actual RatesActual Hrs. at Standard Rates Standard Hrs. at Standard Rates 105 P2,270 P2,590 P2,170 110 10,740 10,970 10,500 117 4,730 4,900 4,620 120 13,850 13,600 13,480 Total P31,590 P32,060 P30,770 36. What is the total direct labor variance for the jobs completed? Job 105 110 117 120 Total Actual Hrs. at Actual Rates P2,270 10,740 4,730 13,850 P31,590 Standard Hrs. at Standard Rates P2,170 10,500 4,620 13,480 P30,770 31,590- 30,770 = 820 unfavorable or -820 37. What is the labor rate variance? 32,060-31,590= 470 Unfavorable 38. What is the labor efficiency variance? 30,770 – 32, 060 = -1,290 or 1,290 unfavorable Data for Questions 39 through The following information pertains to Peter Senen Company’s production on a one unit of Product A: Quantity Price Cost per Unit Materials-standard 7.5 kgs P0.30/kg P2.25/unit Labor –standard .6 hr. 10.00/hr. 6.00/unit During the period, the company produced 15,000 units of Product A. It purchased 140,000 kgs. of materials at P0.25 per kilo. It incurred direct labor cost of P90,780 at P10.20 per labor hour used. At the end of the period, the company’s inventory of materials increased by 25,000 kgs. The company recognizes the material price variance when materials are purchased. 39. How much was the company’s material price variance? = (Standard rate- Actual rate)x Actual material purchased = (0.30 – 0.25)x 140,000 = 0.05x 140,000 = 7000 favorable Taccaban, Karen Joy R. Section 2 40. What was the company’s materials quantity variance? Standard Quantity= 7.5 x 15,000 = 112, 500kg Actual Quantity= 140,000 – 25,000 = 115,000kg Material Quantity Variance= (112,500 – 115,000) x 0.30 = -2500 x 0.30 = -750 or 750 unfavorable End of the Examination. Good Luck!