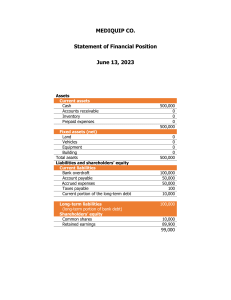
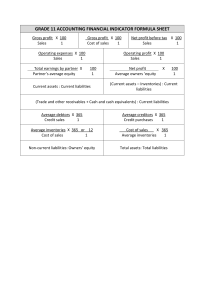
GRADE 10 LESSON 111 ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS WORKSHEET 1 It is important for a business to measure its performance A business has to assess whether they have been successful or not and to determine the areas in which they can approve. A business has to answer the following questions: ● How profitable is the business? ● How well does the business control its expenses? ● Should the owner be satisfied with the profit earned taking into account the amount he invested in the business? ● Can the business pay off all its debts? ● Can the business pay off its debts without any problem in the short term? ● Did the business handle its working capital effectively? It is essential for the owner to analyse the financial statements. The aim of analysis and interpreting the financial statements of a business is to determine the following: Profitability How profitable is the business? How well does it control its expenses? Return Does the owner earn a good return on the capital he has invested in the business? Solvency Can the business pay off all its debts? Liquidity Can the business pay off its short-term debts (current liabilities) without any problems in the short term? These current liabilities can be paid only from current assets that can be converted to cash. 1 111 Accounting Grade 10 WORKSHEET 2 How do we calculate these ratios? PROFIBILITY RATIO’S (from the Income Statement) Percentage gross profit on sales Gross profit x 100 Turnover =% Percentage gross profit on cost of sales (also the mark-up percentage) Gross profit Cost of sales =% Percentage net profit on sales Net profit Turnover Percentage operating expenses on sales Percentage operating profit on sales x x 100 1 100 1 =% Operating expenses Turnover Operating profit Turnover x x 100 1 100 1 =% =% LIQUIDITY RATIO’S (from the Balance sheet) Current assets : Current liabilities Current ratio = x:1 Current assets - inventories : Current liabilities Acid-test ratio = x:1 SOLVENCY RATIO (from the Balance sheet) Total assets : Total liabilities Solvency ratio =x:1 RETURN ON INVESTMENT (from Income statement and Balance sheet) Return on owner’s equity net profit owner’s equity x 100 1 =% 2 111 Accounting Grade 10 Where do we get our information from? INCOME STATEMENT Notes R 399 480 Sale Cost of sales (200 000) Gross profit 199 480 Other operating income 341 988 Rent income 332 260 Discount received 9 728 Gross operating income 541 468 (165 140) Operating expenses Stationery 6 860 Telephone 25 780 Water and electricity 22 100 Salaries 67 400 Depreciation 43 000 Operating profit 376 328 Interest income 100 Operating profit before interest expense 376 428 Interest expense (52 200) Net profit for the year 324 228 BALANCE SHEET ASSETS NON-CURRENT ASSETS Tangible assets Financial assets Fixed deposit CURRENT ASSETS 922 000 3 912 000 10 000 240 800 3 111 Accounting Grade 10 Inventories 4 200 200 Trade and other debtors Cash and cash equivalents 5 6 40 000 600 TOTAL ASSETS EQUITY AND LIABILITIES Equity 1 162 800 7 904 300 NON-CURRENT LIABILITIES 200 000 Loan 200 000 CURRENT LIABILITIES 58 500 Trade and other creditors Bank overdraft TOTAL EQUITY AND LIABILITIES 8 40 500 18 000 1 162 800 4 111 Accounting Grade 10 CHALKBOARD SUMMARY / TRANSPARENCY ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Profitability Liquidity Gross profit on sales Current ratio Gross profit on cost of sales Acid-test ratio Solvency Return Net profit on sales Operating expenses on sales Operating profit on sales 5 111 Accounting Grade 10