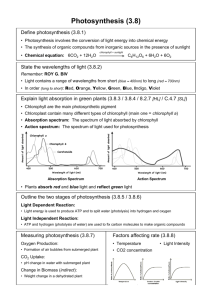
U1: Photosynthesis is the production of carbon compounds in cells using light energy Requires a photosynthetic pigment (chlorophyll) and can only occur in certain organisms (plants, certain bacteria). U2: Visible light has a range of wavelengths with violet the shortest wavelength and red the longest Range of visible light wavelengths: 400 to 700 nm. U3: Chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light most effectively and reflects green light more than other colours When chlorophyll absorbs light, it releases electrons which are used to synthesise ATP (chemical energy). Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet U4: Oxygen is produced in photosynthesis from the photolysis of water Step 1: Light Dependent Reactions ● Light is absorbed by chlorophyll -> ATP (chemical energy) ● Photolysis: photo - light; lysis - disintegration. − + 𝐻2𝑂 → 4𝑒 + 4𝐻 + 𝑂2 ● H and ATP are used in the light independent reactions. 𝑂2is released from stomata as a waste product. U6: Energy is needed to produce carbohydrates and other carbon compounds from carbon dioxide Step 2: Light Independent Reactions ● ATP and hydrogen (carried by NADPH) -> site of the light independent reactions 𝐻 + 𝐶𝑂2 → 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒𝑥 𝑜𝑟𝑔𝑎𝑛𝑖𝑐 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑝𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑠 ● The ATP provides the required energy to power these anabolic reactions and fix the carbon molecules together Skill: Drawing an ● The absorption spectrum indicates the wavelengths of light absorbed by absorption each pigment; spectrum for ● The action spectrum indicates the overall rate of photosynthesis at each chlorophyll and an wavelength of light; action spectrum Correlation: Both display: two main peaks – a larger peak at the blue region (~450 for photosynthesis nm) and a smaller peak at the red region (~670 nm); a trough in the green / yellow portion of the visible spectra (~550 nm).