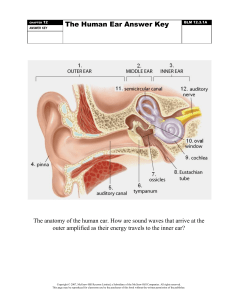
DATE: NAME: UNIT 1 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 1-21 Unit 1 Test Goal • Show your understanding of terms and concepts in Unit 1. What to Do Carefully read the instructions before answering each set of questions. True/False In the space provided, indicate whether each statement is true (T) or false (F). If you think that a statement is false, rewrite it to make it true. ___ 1. Homogeneous matter has at least two visible parts. ___ 2. All matter is made of tiny particles. ___ 3. Seawater is a solution. ___ 4. The particles in a mechanical mixture are smaller than the particles in a solution. ___ 5. Cold water contains less dissolved oxygen than the same amount of warm water. ___ 6. Distillation can be used to separate dissolved solids from a solution. ___ 7. Particles at a higher temperature move more slowly than particles at a lower temperature. ___ 8. Liquids have a fixed shape. ___ 9. More salt dissolves in 100 mL of cold water than in 100 mL of hot water. ___ 10. Rate of dissolving is a measure of how fast a solute dissolves in a solvent. ___ 11. A sugar cube dissolves faster than a teaspoon of granulated sugar. CopCopyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page.. DATE: NAME: UNIT 1 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 1-21 Unit 1 Test (continued) Multiple Choice Circle the letter for the best answer 12. Which list contains all pure substances? (a) milk, water, copper (b) gold, oxygen, sugar (c) tea, salt, concrete (d) orange juice, silver, soda water 13. Sugar dissolved in water is classified as (a) a pure substance (b) a particle (c) a homogeneous mixture (d) a heterogeneous mixture 14. Which of the following is a mechanical mixture? (a) milk (b) water and oil (c) tap water (d) vinegar 15. Two samples of the same pure substance always behave the same because (a) they are both solutions (c) they contain tiny particles (b) they are both homogeneous (d) they contain identical particles 16. Which list contains only heterogeneous mixtures? (a) dirty water, mouthwash, bowl of mixed nuts (b) tea, perfume, clean air (c) salad dressing, smog, hand cream (d) homogenized milk, ketchup, concrete 17. Which of the following is a homogeneous mixture? (a) petroleum (c) gold ore (b) antifreeze (d) milk 18. In which situation are particles moving most rapidly? (a) a glass of cold tap water (c) a glass of hot tap water (b) an ice cube (d) a rubber ball 19. The method that is used to separate the parts of a liquid solution is called (a) evaporation (c) distillation (b) condensation (d) filtration 20. Which substance is the most soluble in water? (a) sugar (b) carbon dioxide (c) Epsom salts (d) ethyl alcohol Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 1 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 1-21 Unit 1 Test (continued) 21. The acronym WHMIS stands for (a) Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (b) Workplace Hazardous Materials Information Sheet (c) Workplace Hazardous Mixtures Information System (d) Workplace Hazardous Mixtures Information Sheet 22. Which of the following is not a solution? (a) pepper in water (b) carbon dioxide in water (c) zinc in copper (d) naphthalene in air 23. Pressure in a fluid is exerted (a) upward only (b) sideways only (c) downward only (d) in all directions 24. The force of a fluid that pushes an object up is (a) pneumatics (b) hydraulics (c) buoyancy (d) gravity 25. The pressure of a fluid varies with depth because of (a) volume (c) temperature (b) gravity (d) all of the above 26. The buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of (a) the displaced fluid (c) the container (b) the object (d) the total volume of fluid 27. One factor that does not affect the viscosity of a liquid is (a) size of the particles (c) internal friction between particles (b) bulkiness of the particles (d) cost of the liquid Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 1 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 1-21 Unit 1 Test (continued) Short Answers Answer the following questions in the space provided. 28. (a) What is the name of the process that is used to recover pure water from dirty water? (b) What two changes of state does this process involve? (c) What is the name of the process that is used to remove salt from salty water? 29. (a) Use the particle model to describe how grains of sugar dissolve in a cup of water. (b) Use the particle model to explain why some materials dissolve while others do not. Long Answer 30. Explain how a hydraulic device or a pneumatic device can be used. Include a labelled illustration on the back of this page to clarify your explanation. Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 2 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 2-32 Unit 2 Test Goal • Assess your understanding of terms and concepts in Unit 2. What to Do Carefully read the instructions before answering each set of questions. Multiple Choice Circle the letter for the best answer. 1. If a dog barks when the door bell rings, what characteristic of living organisms does this show? (a) living organisms need energy (b) living organisms respond to their environment (c) living organisms grow (d) living organisms reproduce 2. What is a cell? (a) a complex living system (b) a part of all living things (c) made up of smaller organelles (d) all of the above 3. What do groups of similar cells form? (a) a system (b) an organ (c) a tissue (d) an organism 4. Who was one of the first people to view organisms made of one cell? (a) Theodore Schwann (b) Mattihias Schleiden (c) Anton van Leeuwenhoek (d) Rudolf Virchow 5. While viewing an object under medium power, you find that the object is larger than the field of view. What should you do to see the entire object? (a) increase the magnification by turning to a lower power (b) increase the magnification by turning to a higher power (c) decrease the magnification by turning to a higher power (d) decrease the magnification by turning to a lower power Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 2 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 2-32 Unit 2 Test (continued) 6. What could you do to observe the organelles of an onion cell better? (a) add a drop of salt water (b) add a drop of sugar water (c) add a drop of iodine (d) remove the excess water 7. If a slide is moved up and to the left, which way will the image move? (a) down and to the right (b) down and to the left (c) up and to the right (d) up and to the left 8. Plants do not have skeletons, yet they grown very large. What structure allows a plant to maintain its shape? (a) cell membrane (b) cell wall (c) vacuole (d) cytoplasm 9. What does a cell need to produce its own food through photosynthesis? (a) chloroplasts (b) a nucleus (c) vacuoles (d) a cell wall 10. What to do you use to focus under high power on a microscope? (a) the coarse adjustment knob (b) the revolving nose piece (c) the diaphragm (d) the fine adjustment knob 11. Water enters the roots through the semi-permeable membrane of the root hairs. What is this process called? (a) osmosis (b) transpiration (c) inhalation (d) evaporation Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 2 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 2-32 Unit 2 Test (continued) 12. Glucose (sugar) is produced in a plant’s leaves. What transports glucose to the rest of the plant? (a) xylem tissue (b) phloem tissue (c) connective tissue (d) guard cells 13. In which system of a plant would you find flowers, fruits, and seeds? (a) root system (b) shoot system (c) circulatory system (d) reproductive system 14. What happens if leaves are cut from a plant? (a) the rate of transpiration increases (b) the rate of transpiration decreases (c) the rate of osmosis increases (d) the rate of osmosis decreases 15. What do different types of tissues working together form? (a) a system (b) an organism (c) an organ (d) an organization 16. Where are oxygen and carbon dioxide exchanged in the lungs? (a) in the muscle tissue (b) in the epithelial tissue (c) in the villi (d) in the alveoli 17. Where are the digestive system and the circulatory system connected? (a) at the alveoli (b) at the villi (c) at the arteries (d) at the pancreas 18. How does nicotine harm the circulatory system? (a) expands the blood vessels causing an increase in both heart rate and blood pressure (b) expands the blood vessels causing a decrease in heart rate and an increase in blood pressure (c) constricts the blood vessels causing an increase in both heart rate and blood pressure (d) constricts the blood vessels causing a decrease in heart rate and an increase in blood pressure Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 2 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 2-32 Unit 2 Test (continued) 19. Where are the respiratory and circulatory systems connected? (a) at the alveoli and capillaries (b) at the alveoli and villi (c) at the villi and capillaries (d) at the villi and arteries 20. When the human body generates excess heat, where does it lose most of this heat from? (a) the lungs (b) the heart (c) the skin (d) breathing Diagram 21. Use the diagram of the microscope to complete the following chart. Microscope Parts and Functions Name Letter Function objective lenses connects the base and the tube B allows for the changing of lenses Short Answer Answer the following questions in the space provided. 22. What are two advantages to being multicelluar? Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 2 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 2-32 Unit 2 Test (continued) 23. Diet can affect many body systems. Choose one example of a poor diet and explain what effect the poor diet has on one particular system. 24. You are walking home alone after dark and you don’t hear a friend approaching from behind. Your friend taps you on the shoulder and scares you. (a) How would your body respond? (b) What body sytem(s) are involved in this response? 25. You want to conduct and experiment to determine the effect of different types of exercise on heart rate. (a) What would the manipulated variable in the experiment be? (b) What would the responding variable be? Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 2 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 2-32 Unit 2 Test (continued) (c) List 2 variables that would need to be controlled. Graphing 27. A carrot was hollowed out and filled with a sugar solution. A glass tube was inserted into a cork, and this was inserted into the top of the carrot and sealed. The carrot was placed into a beaker of water as illustrated in the diagram. The height of the water in the glass tube was measured for 72 hours. The data in the chart shows what happened to the water. Construct a line graph to show this data in another way. Rise of Water Over Time Time in hours Height in cm 0 0 12 15 24 28 36 41 48 60 60 74 72 90 28. Answer the following questions about the equipment. (a) What process caused the water to rise up the tube? (b) Why does the water rise up the tube? Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 2 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 2-32 Unit 2 Test (continued) (c) What would happen if the solution in the beaker and the carrot were the same? Long Answer Answer the following question in complete sentences. 29. Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of premature death in North America. Write a short paragraph explaining at least 3 effects cigarettes have on body systems. Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: CLASS: UNIT 3 BLM 3-29 ASSESSMENT Unit 3 Test Goal • Assess your knowledge of terms and concepts introduced in Unit 3. What to Do Carefully read the instructions before answering each set of questions. Fill in the Blanks Use the terms at the beginning of each section to complete the sentences that follow. Light Sun incandescent lightning hot television electrical streetlights thermal 1. Two natural light sources are the ___________ and ___________. Two artificial light sources are ___________ and ___________. 2. An ordinary light bulb is an ___________ light source. An incandescent light source becomes so ___________ that it glows. ___________ energy is changed into ___________ energy. A Camera and an Eye aperture diaphragm retina iris iris flex 3. The pupil is the opening to the human eye. On a camera, the ___________, like the pupil, opens and closes to let in more or less light. In a camera, film is the light-sensitive screen that retains the image. For humans, it is the ___________, the light-sensitive, internal screen where the eye focusses the image. 4. Just as the ___________ of a camera controls the aperture (the opening of the lens), the ___________ of the human eye controls the pupil. The change in the size of the pupil is called the ___________. Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: CLASS: UNIT 3 BLM 3-29 ASSESSMENT Unit 3 Test (continued) Multiple Choice Circle the best answer. 9. Light _____ from the Sun. (a) shines (b) radiates (c) glows (d) floats 10. Which quality of light determines how much energy a surface will receive? (a) intensity (c) source (b) power (d) weakness 11. Light travels in _____ lines from its source. (a) curved (b) infrared (c) straight (d) wavy (a) 12. As light passes through a lens, it (a) retracts (b) angles (c) reflects (d) refracts 13. If you wanted to see a virtual image (in other words, a “true” reflection of yourself), which type of mirror would you use? (a) convex (c) plane (b) curved (d) weighted Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 3 CLASS: BLM 3-29 ASSESSMENT Unit 3 Test (continued) Short Answers Answer the questions below in full sentences. 14. Are concave mirrors or convex mirrors used for security in stores? Explain your answer. 15. Some people are described as being near-sighted or far-sighted. For each condition, explain briefly what it means. Then describe the shape of the eye for people with each condition. Finally, describe where the images they see form in relation to the retina of the eye. 16. What are the two body parts that can be damaged by too much exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation? How can you protect yourself from UV radiation? Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 4-30 Unit 4 Test Goal • Assess your understanding of mechanical advantage and efficiency. What to Do Carefully read the instructions before answering each set of questions. Multiple Choice Circle the best answer. 1. In which of the following examples is work being done? (a) A weight lifter is holding a set of barbells high overhead. (b) A tow truck is pulling a car out of ditch using a winch. (c) A student is pushing against a locked door with all her strength. (d) Two students sit perfectly balanced on a seesaw. 2. In the diagram below, the plunger on the left is pushed down with a force of 600 N. With how much force will the plunger on the right push up? (a) (b) (c) (d) 1500 N 240 N 6000 N 150 N Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 4-30 Unit 4 Test (continued) 3. What is the mechanical advantage (MA) produced by the hydraulic lift illustrated in question 3? (a) 6.0 (b) 0.4 (c) 2.5 (d) 15.0 4. Suppose that the syringe on the right is question 3 is changed to a syringe with a plunger area of 5 cm2. How much force will it exert upward when the left syringe is depressed? (a) 12 000 N (b) 75.0 N (c) 4800 N (d) 30 N 5. What would happen if a hydraulic system had a leak and lost some of its fluid? (a) The pressure would remain the same, but less force would be transferred. (b) The pressure would be reduced, and less force would be transferred. (c) The pressure would increase, and more force would be transferred. (d) There would be little or no effort. 6. What happens when a gas is compressed within a closed container? (a) The particles get closer together, and their temperature decreases. (b) The particles get closer together, and their temperature increases. (c) The particles get farther apart, and their temperature increases. (d) The particles get farther apart, and their temperature decreases. Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 4-30 Unit 4 Test (continued) 7. The Canadian Standards Association is testing air bags. Scientists are studying how the speed of air bag inflation affects the amount of force that is transferred to the passenger. For each trial in one experiment, the same model of test car travelled at exactly the same speed and ran into the same barrier. The speed of air bag deployment varied with each trial. In this experiment, the independent (manipulated) variable was (a) the speed of the car (b) the speed of air bag deployment (c) the amount of force transferred to the passenger (d) the number of trials in the experiment 8. Which of the variables was controlled during the experiment in question 10? (a) the speed of the car (b) the speed of air bag deployment (c) the amount of force transferred to the passenger (d) the number of trials in the experiment 9. Air bags, seats, and seat belts are designed and positioned within a car to give the occupants a comfortable ride. The science that designs machines to fit people is called (a) biology (b) economics (c) ergonomics (d) chiropractics 10. Air bags are usually filled with air instead of fluids, such as water. Which of the following is not a reason for using air in air bags? (a) Air is easily compressed. (b) Air can be quickly injected into an air bag. (c) Compressed air is lightweight and easily stored. (d) An airbag does not change shape easily. Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 4-30 Unit 4 Test (continued) True or False In the space provided, indicate whether each statement is true (T) or false (F). If you think that a statement is false, rewrite it to make it true. 14. The part of a lever on which the lever arm pivots is called the fulcrum. 15. A winch is designed to move loads more quickly. 16. The follower gear always turns in the direction opposite to that of the gear driving it. 17. When a chain connects two sprockets, they turn in opposite directions. Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 4-30 Unit 4 Test (continued) Short Answers Answer the following questions briefly in the space provided. 18. Imagine that your are throwing a football. Where is the fulcrum, the load, and the effort force? 19. What is the purpose of a fixed pulley? 20. Describe three ways that the flow of a fluid through a pipeline could be increased. 21. Name two ways that a person’s blood pressure could (a) decrease (b) increase Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 4-30 Unit 4 Test (continued) 24. Some city buses have bumpers filled with water. This gives a bus extra protection if it is involved in a head-on collision. What happens to the bumper if a bus is involved in such a collision? 25. Which class of lever are you using if you use a hammer to pull a nail out of a board? 26. When you throw a football, what type of lever are you using? 27. Movers often use a ramp (an inclined plane) to move large objects into their trucks more easily. Suppose that movers have to exert a force of 1000 N to push a large box 4 m up a ramp. How much force would it take to lift the box 1 m straight up into the truck without using the ramp? Show your calculations. Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 5 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 5-24 Unit 5 Test Goal • Assess your understanding of terms and concepts in Unit 5. What to Do Carefully read the instructions before answering each set of questions. Diagram Answer the following question in the space provided. 1. Identify the appropriate term for the letters in the diagram: precipitation, evaporation, condensation, run-off, groundwater. A B C D E Matching Match each description in column A with the correct term in column B. Place the letter for the term on the line beside the description. A 2. free-floating aquatic plants 3. wearing away of rocks or soil by wind or water 4. the largest of the tidal movements 5. large underground reservoir of water, found in permeable rock 6. water that is fit to drink 7. variety of different organisms 8. large crack in the surface ice of a glacier 9. the difference between the highest tide and the lowest tide 10. remains of dead organisms that provide food for decomposers 11. large pile of eroded rocks and debris left by a melted glacier B (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) crevasse moraine tidal range spring tide erosion aquifer detritus potable phytoplankton diversity Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: UNIT 5 ASSESSMENT NAME: CLASS: BLM 5-24 Unit 5 Test (continued) Multiple Choice Circle the letter for the best answer. 12. Most of the water vapour in the atmosphere evaporated from (a) rivers and lakes (b) ground water (c) aquifers (d) oceans and seas 13. The most abundant form of water on Earth is (a) salt water (b) fresh water (c) groundwater (d) atmospheric water vapour 14. Which of the following statements about glaciers is true? (a) Glaciers advance until they reach the ocean. (b) Glaciers are found only at the North Pole and the South Pole. (c) Glaciers can retreat even when flowing downhill. (d) Glaciers are composed of salt water. 15. Which of the following processes is not part of the water cycle? (a) condensation (b) deposition (c) evaporation (d) precipitation Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 5 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 5-24 Unit 5 Test (continued) 16. What is the difference between a headwater river and a flood plain river? (a) A headwater river is larger and deposits more sediment. (b) A headwater river is larger and deposits less sediment. (c) A flood plain river is larger and deposits less sediment. (d) A flood plain river is larger and deposits more sediment. 17. An aquifer is possible when the rock layers are (a) porous and permeable (b) non-porous and permeable (c) porous and impermeable (d) non-porous and impermeable 18. A landfill that is contaminating local groundwater is considered to be (a) a point source, since the origin of the contaminants is known and from a small area (b) a non-point source, since the materials in the landfill come from a large area (c) a non-point source, since the contributors to the landfill are not known (d) a point source, since the materials in the landfill come from a variety of people and places Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 5 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 5-24 Unit 5 Test (continued) 19. Flooding can be the result of (a) slow spring melt and low precipitation (b) regulation of streamflow by the use of dams and diversion canals (c) rapid spring melt and high precipitation (d) increased temperatures and longer summers 20. The motion of water particles in a wave are (a) continuously in the same direction the wave is travelling (b) circular with a slow drift in one direction (c) straight up and down, never moving forward or backward (d) continuously in the opposite direction the wave is travelling 21. Salt in the ocean comes from (a) huge deposits that dissolve on the ocean floor (b) salts that were dissolved from rocks by rivers and were transported to the ocean (c) organisms that live in the ocean and produce salt (d) rain that contains salt from pollution of the atmosphere 22. The deepest part of the ocean is the (a) continental shelf (b) continental slope (c) abyssal plain (d) mid-ocean ridge 23. Why do breakers form near shore? (a) The bottom of a wave is held by friction, while the crest continues at the same speed to form a breaker. (b) Waves are affected much more by wind as they near shore. (c) Incoming waves collide with the outgoing tide, causing turbulence and breakers. (d) Sand picked up near shore makes the waves larger, and they become breakers. Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 5 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 5-24 Unit 5 Test (continued) 24. Surface currents in the ocean are not influenced by (a) the uneven heating of Earth by Sun (b) the rotation of Earth (c) the shapes of the continents (d) the position of Moon and Sun 25. How do ponds differ from lakes? (a) Light can reach the entire lake bed, so very few plants can grow. (b) Light can reach the entire bottom of a pond, so plant life is found everywhere. (c) Light reaches only the shallow water near shore in a lake, so plant life is everywhere. (d) Light reaches only the shallow water near shore in a pond, so very few plants can grow. 26. Which of the following adaptations can be found on a plant in a fast-moving stream? (a) buoyant structures (b) gills (c) holdfast (d) streamlined structure 27. When a body of water is polluted with excess nutrients, there is usually (a) an algal bloom (b) nothing left living in the water (c) too much dissolved oxygen (d) a more stable food chain Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. DATE: NAME: UNIT 5 ASSESSMENT CLASS: BLM 5-24 Unit 5 Test (continued) 28. Hard water refers to (a) the way that water freezes quickly (b) the fact that there is nothing dissolved in the water (c) how difficult it is to remove pollutants from the water (d) water with calcium and magnesium dissolved in it 29. Acid precipitation is caused by (a) burning fossil fuels, which release sulfur and nitrogen oxides into the air (b) dumping of wastes into rivers, streams, and lakes (c) a change in aquatic life as a result of global warming (d) acidic water evaporating from the ocean 30. Bioindicator species are species that (a) are unaffected by water temperature or quality (b) have become extinct as a result of pollution (c) live only in water with specific qualities, such as pH and temperature (d) change their form or colour when water quality changes Paragraph Answer Answer the following question in paragraph form. 31. Explain how water is purified for drinking purposes. Copyright © 2001, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in his/her classroom only. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page.