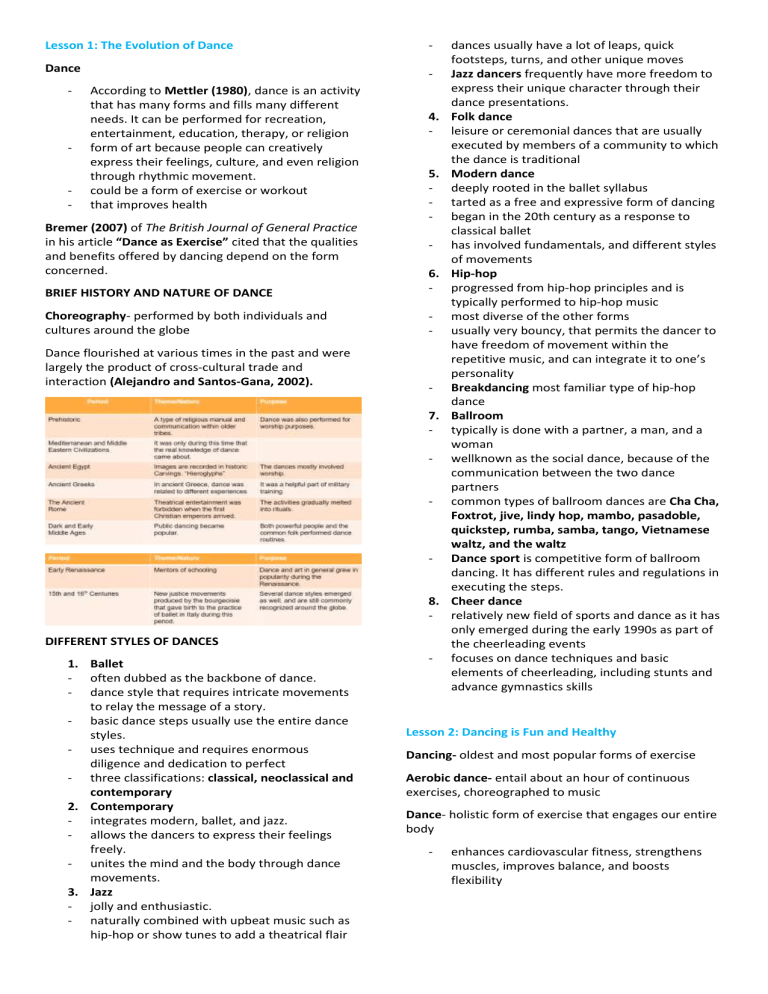
Lesson 1: The Evolution of Dance - Dance - - - - According to Mettler (1980), dance is an activity that has many forms and fills many different needs. It can be performed for recreation, entertainment, education, therapy, or religion form of art because people can creatively express their feelings, culture, and even religion through rhythmic movement. could be a form of exercise or workout that improves health Bremer (2007) of The British Journal of General Practice in his article “Dance as Exercise” cited that the qualities and benefits offered by dancing depend on the form concerned. 4. - 5. - BRIEF HISTORY AND NATURE OF DANCE 6. - Choreography- performed by both individuals and cultures around the globe - Dance flourished at various times in the past and were largely the product of cross-cultural trade and interaction (Alejandro and Santos-Gana, 2002). 7. - - - 8. DIFFERENT STYLES OF DANCES 1. Ballet - often dubbed as the backbone of dance. - dance style that requires intricate movements to relay the message of a story. - basic dance steps usually use the entire dance styles. - uses technique and requires enormous diligence and dedication to perfect - three classifications: classical, neoclassical and contemporary 2. Contemporary - integrates modern, ballet, and jazz. - allows the dancers to express their feelings freely. - unites the mind and the body through dance movements. 3. Jazz - jolly and enthusiastic. - naturally combined with upbeat music such as hip-hop or show tunes to add a theatrical flair - dances usually have a lot of leaps, quick footsteps, turns, and other unique moves Jazz dancers frequently have more freedom to express their unique character through their dance presentations. Folk dance leisure or ceremonial dances that are usually executed by members of a community to which the dance is traditional Modern dance deeply rooted in the ballet syllabus tarted as a free and expressive form of dancing began in the 20th century as a response to classical ballet has involved fundamentals, and different styles of movements Hip-hop progressed from hip-hop principles and is typically performed to hip-hop music most diverse of the other forms usually very bouncy, that permits the dancer to have freedom of movement within the repetitive music, and can integrate it to one’s personality Breakdancing most familiar type of hip-hop dance Ballroom typically is done with a partner, a man, and a woman wellknown as the social dance, because of the communication between the two dance partners common types of ballroom dances are Cha Cha, Foxtrot, jive, lindy hop, mambo, pasadoble, quickstep, rumba, samba, tango, Vietnamese waltz, and the waltz Dance sport is competitive form of ballroom dancing. It has different rules and regulations in executing the steps. Cheer dance relatively new field of sports and dance as it has only emerged during the early 1990s as part of the cheerleading events focuses on dance techniques and basic elements of cheerleading, including stunts and advance gymnastics skills Lesson 2: Dancing is Fun and Healthy Dancing- oldest and most popular forms of exercise Aerobic dance- entail about an hour of continuous exercises, choreographed to music Dance- holistic form of exercise that engages our entire body - enhances cardiovascular fitness, strengthens muscles, improves balance, and boosts flexibility The Joy of Dance Lesson 1: Dance Appreciation and Composition Dancing raises the physique and gives a feeling of satisfaction and hence is enjoyable. Dance, at its core, is about pure enjoyment. It's a form of self-expression, an art form that lets us convey our emotions, thoughts, and stories through movement. Elements of Dance o - Space place where dancers perform four parts: 1) direction - The dancers have the option of moving forward, sideward, backward, diagonally, circularly, and so on. They can also perform a single component or a series of phrases while facing any direction. 2) size - The steps can be big or small. 3) level - Routines might be at a high, medium, or low level. 4) focus - A performer may look in different directions to change their focus. o - Timing Timing of dance motions may be performed at different speeds (tempo). Artist shift in time to the rhythm of a sound known as beat or pulse. By going quicker or smoother that the usual beat, the pacing may be changed. BENEFITS OF DANCING ON DIFFERENT ASPECTS Physical, Mental, Social, and Cultural Physical o o o When done regularly, dancing is a good way to develop cardiovascular and muscular endurance, and body composition, (Malvar, 2006) Dance training also improves coordination (Rickett-Young, 1996). Thus, low to moderate dance exercise is as effective as other vigorous exercise regimens in improving fitness. Thus, dancing is also a great way to lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases. According to Flores (1995), an increased fitness results in a great lowering of the body mass index and resting heart rate for those who engage in a dance-based fitness activity compared to those who engage in other regular physical activities. It was also reported that there is a significant improvement in lipid metabolism when dancing (Malvar, 2006). Dance Therapy- has been used in different medical fields throughout history. - It aids in recovering coordination and other neuromuscular skills after an injury. - o ­ ­ Mental o o o Dance can be used as intervention in mental health nursing. They revealed that dance can offer “an acceptable way to release emotional and physical pressure.” Dancing also gives other psychological health benefits as compared to other forms of exercise. Dancing is a great way to improve one’s body image. Social o Dance provides a unique opportunity for meaningful group involvement as it encourages intense, positive social interaction and interpersonal relationships in a working group. They believe that “it contributes to each individual’s potential for the fullest possible self-actualization in society” Cultural o Dance promotes a place or a country’s rich culture through highlighting the different cultural dances. It is through looking at the different dances of other countries will one see the value of one’s culture. o - - Dance Energies The strength or power that propels the movements comes from force or energy . Force is used in starting or stopping a movement when dancing. Rhythm uses a variety of forces, and diverse use of these minimizes the repetition of a performer's gestures. The attributes of dance forces are listed below in six categories: 1. Sustained 2. Percussive 3. Vibratory 4. Suspended 5. Collapsing Bodily Shapes It corresponds to how the whole body is formed or how parts of the body are arranged. The shape of the individual may be circular , linear , or a mix. Other body types range from broad to short and large to small. They come in both balanced (symmetrical) and unbalanced (asymmetrical) varieties. o Symmetrical: balanced stature; same movements on both sides of the performer. o Asymmetrical: unbalanced stature; motion on one side is different on the other. Lesson 2: Characteristics of a Good Dance In order for a good dance to be successful, the moves or choreography must have a meaning. o o o Form is the process of arranging or combining ideas and elements into a coherent pattern that ends in harmony and continuity. (Lockhart, 1982). From the start to the end of the choreography, the form should advance over time (Minton, 2007). Phrases As they merge multiple movements into unity, you get a unit. “A phrase is the smallest unit of form in the whole dance” Motif To be capable of communicating its purpose to the viewer, a successful choreography must have a concept or motif. It may be a short action or a gesture that expresses the fashion and meaning.