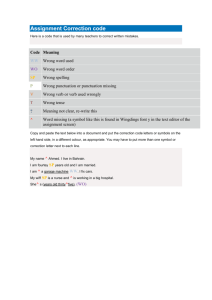
Assessing Writing: Two Approaches As important as planning activities to help students develop their writing skills is assessing their written work. It is invaluable to both students, who can learn from their errors, and teachers, who can check the students' progress. Plan 1- What to assess? 2- Why to assess? 3- How to assess? 1- What to assess? 5mns Study the following statements and say what categories from the following items they belong to: vocabulary- spelling – grammar- genre – content – cohesion and coherence. 1- The subject matter of a book, speech or programme………. 2- A particular type or style of writing i.e., speech- letter…….. 3- The rules in a language for changing the form of words and joining them into sentences……….. 4- The act of forming words correctly from individual letters……… 5- The words that people use when they are speaking or writing about a particular subject………… 6- A link and logical sequencing of different ideas……. 15mns 2- Why to assess? Whithin your group, fill in the GIVE ONE column with some ideas about the purpose of writing assessment. Walk around the room. Give one of your ideas to a partner from a different group and get an idea from him/ her. Write it in the GET ONE column and move to another partner from a different group. Give One Get One 15mns Purpose: Provide feedback to improve student writing. Teach students how to assess their own writing. Monitor students progress on ongoing basis. Demonstrate the effectiveness of instruction. Make autonomous and self-regulated learners and writers. 3- How to assess? What I Know What I Want To Learn What I have Learnt Watch the following video and identify the different scoring methods of writing assessment. Reorder the following words to get the write definition of each method. 1- A specific/ subcategories/ breaks/ It/ a test-taker’s/ down into/ written text/ (grammar…)/ a number of/ gives/ and / each/ for/ rating. Analytic Rubric ” It breaks a test-taker’s written text down into a number of subcategories (grammar…) and gives a specific rating for each“ H. Douglas Brown, 2001:241 5mns 2- overall/ which/ It/ to/ assigned/ an essay/ represents/ general/ assessment/ reader’s/ a/ is. Holistic Rubric ” It is assigned to an essay which represents a reader’s general overall assessment “ H. Douglas Brown, 2001:241 5mns Correcting Written Work What do you observe? - Every mistake is corrected . - Corrections written between the lines - The work is covered in red What’s your reaction as a learner? - It can be very discouraging . What do students learn from this kind of correction? If everything is corrected, learners will probably look over their work without thinking about any individual mistake. This method does not involve them in any kind of learning process. Which of the following items are not a correction technique? Design a specific and reliable correction system. Reteaching the target point. Mark selectively (selective correction). Mark positively. Additional practice. Use a c1ear correction code. 10 mns Correction Code Symbol Meaning Punct. Missing or wrong punctuation. Cap. Capitalization needed. spel Wrong spelling. Prep. Preposition missing. → V. T. SV. Indentation. (The beginning of each paragraph should be indented. Verb missing Wrong verb tense Subject verb agreement Alternative Ways of Writing Assessment Turn around the “Four Corners” and name each technique. 1- Self-assessment ………………………Students attempt to discover the problems, make their own corrections and return their work to the teacher. The students feel self-confident to reflect on their mistakes and make improvements to their writing. Peer-assessment 2- ………………………….Students work in pairs, they exchange their papers and attempt to correct each other's work. The teacher has to build in an extra checking stage, as students will often not be able to provide appropriate corrections. Whole-class assessment 3- …………………………………..The teacher select the common errors and highlights them on the white board for the whole class . They continue to correct their work either individually, in pairs or in small groups 10 mns Teacher-assessment Once the students have corrected as much 4- ……………………….. they can, the teacher concentrate on the remaining problems rather than just correction. Students need to understand how to make it right.