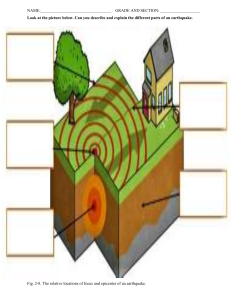
Name Class Date Ch.10 – Earthquakes Lesson Review (p. 214 – 229) Write true if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the underlined term to make the statement true. Write your answers in the spaces provided. 1. An instrument that detects and measures earthquakes is a seismic wave. 2. The place inside Earth where an earthquake starts is called the focus. 3. S Waves are the fastest moving seismic waves from an earthquake. 4. The place on Earth’s crust directly above the place where an earthquake starts is called the focus. 5. Small movements of Earth’s crust that may or may not be felt are called tremors. 6. A seismogram is a record of the movements of Earth’s crust. 7. Vibrations released during an earthquake are called focus waves. 8. The Fujita scale is used to represent the magnitude of an earthquake. 9. The higher the lines on a seismogram, the weaker the earthquake. 10. During an earthquake, Earth’s surface shakes hardest at the epicenter. Skill Challenge Skills: identifying, analyzing Use the terms in the box to label the diagrams below. Write your answers in the spaces provided. epicenter focus seismograph seismogram waves Name Class Date Ch.10 – Earthquakes: Seismic Waves Lesson Review (p. 214 – 229) Complete the table by placing check marks in the correct columns. CHARACTERISTICS OF SEISMIC WAVES Characteristic P-waves S-waves Surface waves 1. Travel through gases 2. Travel through liquids 3. Travel through solids 4. Fastest waves 5. First to arrive 6. Slowest waves 7. Push‐pull waves 8. Used to find the epicenter 9. Cause the most damage 10. Used to find travel time Skill Challenge Skills: analyzing, interpreting a diagram Use the diagrams to answer the following questions. 1. Which letter represents the epicenter of the earthquake? 2. Which seismograph station would have recorded P‐waves last? 3. Which seismograph station would have recorded P‐waves first? 4. At which letter would the most damage to buildings have occurred? 5. When were the first P‐waves recorded? 6. When were the first S‐waves recorded? 7. What was the S‐P interval? 7:55 8:00 8:05 8:10