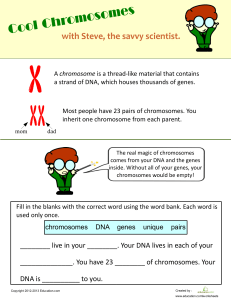
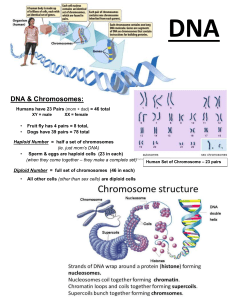
PCZO100 — FOUNDATIONS OF ZOOLOGY (LECTURE) MODULE 3 – Cell Division and Inheritance Cell Cycle ● ● o cyclical process of growth and mitosis Consists of interphase and mitosis Terminologies/notes ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Heterologous - chromatins are contributed from 2 different parents. Homologous -chromatins that contain the same genetic materials. Gametes - sex cells Humans contain 23 pairs of chromosomes with a total of 46 individual chromosomes. Female chromosome – XX Male chromosome – XY Genetic disorders that result from uncontrolled division – down syndrome Checkpoints before mitosis ● G1 phase – 1st checkpoint o Checking the materials are complete and if there are any errors in the cell. o Apoptosis – programmed cell death or G0 phase also known as resting phase. ● G2 phase – 2nd checkpoint. o Checking for replication error o Checking if there are enough organelles before cell division. o If there are mitotic spindles available. ● Metaphase – 3rd checkpoint o Check whether the spindle fibers are properly attached to the centromeres. Interphase ● ● ● ● ● ● Stage between cell division Occupies about 90% of the total cell cycle. The process wherein the cells duplicate themselves. The chromosomes appear in irregular – granular form and it maintained as chromatin fibers Normal activities of the cell during interphase: o Metabolism o Cellular respiration o Protein synthesis o Lipid synthesis Divided into subphases. o G1 phase ▪ early growth phase ▪ Cell continues to grow in volume. o S phase ▪ Synthesis phase ▪ Involved DNA replication. G2 period ▪ Prepares for cell division. ▪ Replication of mitochondria ▪ Synthesis of microtubules ▪ Chromosome condensation Mitosis ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Only applies to somatic cells. The goal is to produce 2 identical daughter cells. Also called duplication division For growth and development and replacements for old cells. Refers to the division of the nucleus (karyokinesis) Division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis) Consists of 4 phases PCZO100 — FOUNDATIONS OF ZOOLOGY (LECTURE) MODULE 3 – Cell Division and Inheritance Prophase ● ● ● ● Each chromosome consists of 2 chromatins that are joined at the centromere. Centrioles move to the opposite ends of the cell. Nucleus and nuclear envelope start to dissolve. Mitotic apparatus is nearly formed. (Asters and spindle fibers) Metaphase ● ● Mitotic spindles are now fully formed. The chromosomes align at the metaphase plate. Anaphase ● ● ● The phase of migration Chromatids separate to form two sets of identical chromosomes. Cytokinesis begins. o Plant cells – cell plate o Animal cell – cleavage furrow Telophase ● ● ● ● ● ● the phase of reconstruction chromosome uncoils. o Chromatins recondenses. Nucleus develops. Spindles disappear. formation of 2 new daughter cells with 23 pairs of chromosomes each. Ploidy level – diploid o Formula: 2n = 23 Meiosis ● ● Produces 4 daughter cells with the haploid number of chromosomes as parent cells. Also called reduction division o Reducing ploidy level from 2n -> n ● ● Involves meiosis I and II Formula = n = 23 Meiosis I ● ● Results in reducing the chromosomes. Accompanied by cytokinesis. number of Prophase I ● Crossing-over – process wherein the chromatids exchange segments and transfer genes. ● Chiasma – site of crossing over. ● Chiasmata – overlapping region during crossing over. Metaphase I ● Separates chromosomes (tetrads) and places them in the metaphase plate. ● Produces diversity in the 2 gametes. Anaphase I ● The chromosomes are separate pulling to either region of the cell Telophase I ● The chromosomes arrive at the pole of the cell ● Each pole has a haploid chromosome cell Meiosis II ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Prophase II – spindle fibers form Metaphase II – Line up at the metaphase plate Anaphase II – Separate the chromosomes. Telophase II – nuclei form at the poles Cytokinesis occurs. 23 individual chromosomes from the sperm 23 individual chromosomes from the egg 2 haploids = diploid PCZO100 — FOUNDATIONS OF ZOOLOGY (LECTURE) MODULE 3 – Cell Division and Inheritance Eukaryotic Chromosomes ● ● ● Eukaryotic chromosomes are composed of chromatin. Chromatin is the aggregate mass of DNA and histone proteins. The association of DNA with histones efficiently packs the DNA into chromosomes. DNA: The Genetic Material DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as the candidate: ● ● ● ● Organization of a Chromosome 1. Supercoil of chromatin within the chromosome. 2. Folding within the supercoil 3. An individual fiber in the supercoil consists of a nucleosome: DNA strand coiled around histones like beads on a string. 4. Linker proteins anchor DNA to the core and wind the chain into a cylinder. The Structure of DNA ● ● ● ● ● ● Sex Chromosomes and Autosomes ● ● Sex chromosomes (XY ♂ and XX ♀) differ in males and females, and function in sex determination. Autosomes are not involved in sex determination. Number of Chromosomes ● ● ● Number of chromosomes is constant within species. But chromosome number varies among different species. N identifies the number of different kinds of chromosomes. – 2 sets of ○ Diploid (2N) chromosomes ○ Haploid – 1 set of chromosomes ○ Polyploid – more than 2 sets of chromosomes Able to code for the sequence of amino acids in proteins and control protein synthesis Able to replicate itself prior to cell division Contained in the nuclei of eukaryotic cells Able to change over time to account for evolutionary change ● ● ● Double helix With major and minor grooves Complete spiral every 10 base pairs Antiparallel: 3’ – 5’ and 5’ – 3’ Nucleotide = nitrogenous base + deoxyribose sugar + phosphate group Base-pairing ○ Adenine – Thymine ○ Cytosine – Guanine Bases ○ Purine (2 rings): A, G ○ Pyrimidine (1 ring): C, T Hydrogen bonding of bases GC bonding - allow us to thrive in different environment DNA Replication Replication: DNA-DNA Semiconservative PCZO100 — FOUNDATIONS OF ZOOLOGY (LECTURE) MODULE 3 – Cell Division and Inheritance 1. Helicases unwind the parental double helix. 2. Single-strand binding proteins stabilize the unwound parental DNA. 3. The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5 -> 3 directions by DNA polymerase 4. The lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously. 5. Primase synthesizes a short RNA primer, which is extended by DNA polymerase to form an Okazaki fragment. 6. After the RNA primer is replaced by DNA, DNA ligase joins the Okazaki fragment to the growing strand. From Gene to Protein ● ● Translation: mRNA – protein ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● The process by which messenger RNA(mRNA) is translated into proteins. Synthesis of a protein tRNA converts codon information into amino acid sequence. catalyzed by rRNA. mRNAs are single-stranded RNA molecules. They are copied from the TEMPLATE strand of the gene, to give the SENSE strand in RNA They are transcribed from the 5’ to the 3’ end They are translated from the 5’ to the 3’ end The Genetic Code Gene – a DNA sequence that codes for one polypeptide or a trait Genetic information is transmitted from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where protein synthesis occurs. Transcription Terms: DNA Methylation – methyl group is added to nucleotides. Modifies DNA The process by which DNA is copied to RNA involves an enzyme called RNA Polymerase Steps to Transcribe DNA: 1. RNA Polymerase attaches to DNA at a sequence called the promoter. 2. DNA strand separates temporarily. 3. RNA polymerase adds RNA nucleotides to the DNA template. 4. RNA polymerase travels along the template strand. Inheritance Patters In Animals ● ● A gene or a DNA sequence coding for a trait is located at a specific locus or site in the chromosome. Different alleles of the gene occupy the same locus. Terminologies Trait – a characteristic brought by the expression of a gene PCZO100 — FOUNDATIONS OF ZOOLOGY (LECTURE) MODULE 3 – Cell Division and Inheritance 5 - 3 orientation antiparallel Alleles – alternative forms of a gene Multiple Alleles – when more than a pair of alleles control a trait Codominant – different alleles are both expressed in a heterozygote. Incomplete dominance – when one allele is not completely dominant over another. Genotype – genetic composition Phenotype – visual expression of the genotype Dominant Allele – Hides the expression of another allele. Recessive allele – expression is masked another allele. Heterozygous – two different alleles of the gene occupy the loci of homologous chromosome. Homozygous – two identical alleles of the gene occupy the loci homologous chromosome. Principle of Segregation ● ● Pairs of genes are distributed between gametes during gamete formation when homologous chromosomes are distributed to different gametes during meiosis. Law of segregation: Principle of Independent Assortment ● ● During Meiosis, pairs of genes segregate independently of one another. The distribution of genes for one trait is not influenced by the genes for another trait. Punnett Square dna replication 1. helicase unwinds the parental double helix 2. single strand binding protein stabilize the unwound parental DNA 3. DNA polymerase okazaki fragment DNA methylation- process methyl group is added in nucleotide 20 amino acids mutation increase wild type hemoglobin glutamic acid- Glu heat tolerant drought tolerant aneuploidy locus allele