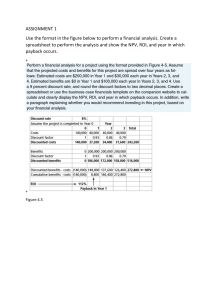
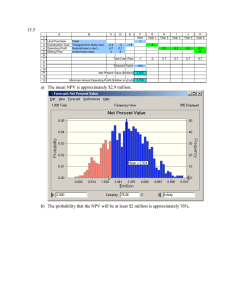
FINC Final Exam Review (Part II) 1. Surley, Inc. has sales revenue of $250,000. The company’s fixed costs total $65,000 and its variable costs are 30% of sales. The company’s interest expense is $45,000. If the company were to increase its sales revenue by 20%, by what percentage will it increase EBT? a. 20.00% b. 31.82% c. 53.85% d. 60.11% e. 19.88% 2. Acco, Inc. currently has $5 million in sales. Its variable costs total $1,500,000, its fixed costs are $1,200,000, and the company pays a 9% interest rate on its $5.5 million of debt. If the company’s earnings per share needs to increase by 25% this year, by how much will sales need to be increased? a. b. c. d. e. 20.00% 19.62% 12.89% 11.11% none of the above 3. Stacey and Taylor of Fikes & Gilbert Industries are trying to estimate the firm’s optimal capital structure. The company has $100 million in assets, which is financed with $30 million of debt and $70 million in equity. The risk-free rate, kRF, is 4%, the market risk premium, kM – kRF, is 9%, and the firm’s tax rate is 40%. Currently, the firm’s cost of equity (kS) is 18.04% which is determined on the basis of the CAPM. What would the firm’s estimated cost of equity be if it were to change its capital structure from its present capital structure to 20% debt and 80% equity? a. 14.61% b. 18.04% c. 15.49% d. 16.84% e. 17.26% 1 4. A father and mother are planning a savings program to put their daughter through college. Their daughter is now 8 years old. She plans to enroll at the university when she is 18 and it should take her 4 years to complete her education. Currently, the cost per year (for tuition, etc.) is $13,000, but a 3% inflation rate in these costs is forecasted. The cost for each year of college will be withdrawn when she turns 18, 19, 20, and 21. The daughter received $7,000 today from her grandmother; this money, which is invested in an account paying 9% interest compounded annually, will be used to help meet the cost of the daughter’s education. The rest of the costs will be met by money the parents will deposit in the savings account. They will make 5 equal annual deposits to the account, with the first deposit being made today on her 8th birthday and the last one being made on her 12th birthday. These deposits will also earn 9% interest compounded annually. How large must each deposit (from the parents) be in order to put the daughter through college? (Round cash flows to nearest dollar throughout). a. b. c. d. e. $4,270 $4,458 $4,757 $4,802 None of the above is within $10 of the correct answer. 8 9 10 11 12 D $7,000 D D D D 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 17,471 17,995 18,535 19,091 2 5. Anna Lubinsky is interested in building a new hotel in the little-known island in the Caribbean. Her company estimates that the hotel would require an initial investment of $22 million, would produce positive cash flows of $4 million a year at the end of each of the next 20 years and can be salvaged (after-tax) for $17 million at t=20. The company recognizes that the cash flows could, in fact, be much higher or lower, depending on whether that area becomes a popular tourist area. It is believed that at the end of two years, a 25% chance exists that tourism will NOT be spreading in that direction and the yearly cash flows will be only $2 million for 20 years with an after-tax salvage value of $15 million, and a 75% chance exists that tourism WILL be heading that way and the yearly cash flows will be $7 million for 20 years with an after-tax salvage value of $26 million. If the firm waits two years, the initial investment will be $24 million. The project’s cost of capital is 12%. Should the firm proceed with the project today or should it wait two years before deciding? (round to the nearest dollar). a. b. c. d. e. Wait 2 years; the NPV of building today is $8,899,710 worse than the NPV for waiting 2 years. Wait 2 years; the NPV of building today is $8,883,551 worse than the NPV for waiting 2 years. Wait 2 years; the NPV of building today is $7,387,595 worse than the NPV for waiting 2 years. Wait 2 years; the NPV of building today is $7,921,044 worse than the NPV for waiting 2 years. Wait 2 years; the NPV of building today is $8,698,026 worse than the NPV for waiting 2 years. 3 Use the following to answer questions 6 & 7: Singer, Inc. is planning to request a line of credit from the bank, and has asked you to prepare a cash budget to present to the bank using the following information: Month Sales Month November-18 December-18 January-19 $ 12,000 $ 13,000 $ 15,000 February-19 March-19 Sales $18,500 $ 20,500 Collections of sales is expected to be 40% within the month of sale, 50% the month following the sale, and 10% the second month following the sale. All sales are made on terms of 4/10 n/60. Inventory purchases are shown below. Payment for inventory is to be made in the month following the purchase. Month Purchases Month Purchases November-18 December-18 January-19 $ 4,000 $ 7,000 $ 8,000 February-19 March-19 $ 9,100 $ 14,000 The following costs are incurred: Wages Expense Rental Payments Depreciation Expense Income Tax Payments Insurance Premiums $4,000 per month $2,100 per month $1,100 per month $3,000 (made in December and March only) $2,200 (made in January only) Cash on hand on January 1st will be $3,000, and the firm’s target cash balance of $2,000 will be maintained throughout the cash budget period. Prepare a cash budget for January through March of 2019. You may find it helpful to include November and December data on your budget. (space provided for cash budget, then answer the questions on the following page) 4 (Cash Budget Workout space) 5 6. What are the total cash collections for January? a. $15,000 b. $8,000 c. $15,904 d. $13,460 e. none of the above 7. What is the ending cash balance for February? a. ($840) b. ($964) c. $840 d. $964 e. $2,964 8. Demny Credit Union offers to lend Jessica $16,000 to buy a car; the loan calls for payments of $300.48 per month for 5 years. Which of the following statements is most CORRECT? (Do not round.) a. The monthly rate of interest is .425000 percent. b. The nominal annual rate of interest is 5.1 percent. c. The monthly rate of interest is .512875 percent. d. The effective annual rate of interest is 4.9076 percent. e. The effective annual rate of interest is 5.2074 percent. 9. You recently graduated and received $10,000 from your parents. You have the choice to invest the money in a savings account earning 4 percent compounded annually or a global mutual fund earning 25 percent. Assume that you will leave the money invested for 10 years. How much more money will you have if you decided to invest in the mutual fund rather than the savings account at the end of 10 years? a. b. c. d. e. $84,111.88 $78,329.82 $14,802.44 $93,132.26 $15,121.08 6 Use the Following Information to answer the next 2 questions: Last year Miller, Inc. had $12 million in operating income. The company had depreciation expense of $2 million, interest expense of $1.4 million, and a corporate tax rate of 40%. The company has $18 million in current assets and $5 million in non-interest-bearing current liabilities; it has $18 million in net plant and equipment. It estimates that it has an after-tax cost of capital of 11.5%. Assume that its only noncash item was depreciation. 10. What was the company’s operating cash flow for the year? a. $11,400,000 b. $9,200,000 c. $10,840,000 d. $8,360,000 e. $12,600,000 11. Calculate the Economic Value Added (EVA) a. $3,635,000 b. $4,445,000 c. $9,200,000 d. $3,301,000 e. $3,911,000 12. Pfister & Associates was incorporated in 2018. It had taxable income (or loss) through 2024 as follows: Year 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 Taxable Income ($25,000) $10,000 $40,000 ($15,000) $5,000 ($20,000) $45,000 Which of the following is most CORRECT? a. Under the old tax laws, total tax credits equal $6,000. b. Under the old tax laws, total taxes paid over the 7-year period is $16,000. c. Under TCJA, total taxes paid over the 7-year period is $10,800. d. Under TCJA, total tax credits equal to $8,000 e. none of the above is correct. 7 13. Analysts predict that our company will have the following free cash flows (see timeline) from time periods t=1 through t=3. From t=3 forward, FCF is expected to grow at a constant 10 percent rate per year. The company’s WACC is 13%. The corporation has $24 million of debt and 4 million shares of stock outstanding. What is your estimate of the current price per share? 0 1 2 3 4 ∞ -14 million a. b. c. d. e. +18 million +24 million $141.51 $151.06 $163.94 $157.05 $133.52 14. You graduate and immediately discover an oil field. You are going to sell the oil field and use the money to make 70 annual UNEQUAL withdrawals from your savings, with the first withdrawal occurring at t=3 and the last occurring at t=72. You want each withdrawal to have the same purchasing power as $300,000 has today. Therefore, the withdrawals need to grow at a constant rate of 3% to compensate for expected inflation per year. Your account earns 12% per year. For how much must you sell the oil field and deposit in your account today to make the required withdrawals possible? a. b. c. d. e. $3,122,118 $2,895,471 $4,414,111 $2,018,898 $2,311,187 8 Use the following information to answer the next 2 questions The expected returns for Stock A and B have the following probability distributions: State of the Economy Below Average Average Above Average Probability 0.20 0.50 0.30 Stock A 5% 12% 29% Stock B -6% 22% 40% 15. Calculate the expected return for Stock A a. 16.00% b. 15.70% c. 16.80% d. 17.20% e. 17.60% 16. Calculate the coefficient of variation for Stock B, assuming B’s expected return is 21.80% a. 0.7312 b. 0.9831 c. 1.1488 d. 1.2532 e. 1.3875 17. Stock X has an expected return of 39%, a beta coefficient of 3.3. Stock Y has an expected return of 29% and a beta coefficient of 2.6. The risk-free rate is 2% and the required return on the overall market is 13%. On the basis of the two stocks’ expected and required returns, which stock(s) would be attractive to a diversified investor? a. Both stocks are attractive to a diversified investor. b. Neither stock is attractive to a diversified investor. c. Stock X only; the expected return for X exceeds the required return by 0.7%. d. Stock Y only; the expected return for Y exceeds the required return by 1.6%. e. Stock X only; its expected return is 7.7% higher than X’s required return. 9 18. Wilson, Incorporated has the following data: Assets: $250,000 Debt Ratio: 25% Profit Margin: 12% Interest Rate: 8.5% Tax rate: 40% Total Asset Turnover: 2.80 Calculate the EBIT a. b. c. d. e. $118,852.40 $126,693.30 $138,922.30 $145,312.50 $152,889.20 19. Given the following information, which of the following statements is most FALSE? Assume that the firm’s cost of capital is 12.5% and that both projects have normal cash flows. NPV IRR a. b. c. d. e. Project A $64 16% Project B $72 18% The NPV profiles may cross, but do not have to cross. Project A’s NPV profile intercepts the horizontal axis at 16% If there is a crossover, the crossover rate must be greater than 12.5% The projects do not have to be of either different size or length of life. Project B’s profile intercepts the vertical axis at a value greater than $72 10 20. A Treasury bond that matures in 6 years has a yield of 5.2%. A 6-year corporate bond has a yield of 6.4%. Assume that the liquidity premium on the corporate bond is 0.4%. What is the default risk premium on the corporate bond? a. b. c. d. e. 0.8% 1.0% 1.2% 1.4% 1.6% 21. The real risk-free rate of interest is 2.3%. Inflation is expected to be 3.4% each of the next 2 years and 3.0% in the third year. Assume that the expectations theory fully explains the yield curve. What is the yield on 3-year Treasury securities? a. 5.57% b. 4.80% c. 5.23% d. 4.91% e. None of the above 22. Last year, ABC Incorporated had sales revenue of $900,000. Costs other than depreciation and interest expense were 32% of sales. Depreciation expense was $280,000, interest expense was $60,000, dividends received were $20,000 and dividends paid were $36,000. Which of the following statements is FALSE? (Use the corporate tax table) a. b. c. d. e. The firm’s taxable income was $272,000. The firm’s average tax rate was 32.97 percent. The firm’s marginal tax rate was 39 percent. The firm’s tax for the year was $91,670. The after-tax income was $200,330. 11 23. Michael plans to make 4 equal annual deposits into an account beginning at t=1. If the interest rate is 6.5 percent, how much would his deposit have to be to be able to withdraw $3,000 each year at t=6, t=7, and t=8? 0 a. b. c. d. e. 1 2 3 4 D D D D 5 6 7 8 3,000 3,000 3,000 $1,692.81 $1,802.84 $1,589.49 $1,395.49 $1,670.61 24. You are the elderly parent of a 50-year-old handicapped individual and want to put some money into an account to secure your child’s future. You are going to put 4 equal annual deposits into an account earnings 5 percent. Your first deposit will be made today and the last deposit will be at t=3. You want the guardian of your child to be able to withdraw $18,000 per year for 20 years to help take care of your child. The first withdrawal will be at t=3 and the last withdrawal will be at t=22. How much will each of your deposits need to be? a. b. c. d. e. $54,647 $23,554 $56,221 $25,683 $53,635 12