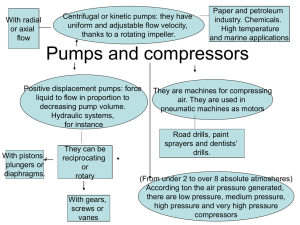
Selection, Sizing and Design of Pumps Overview Dynamic Pumps • Centrifugal • Flow • Axial • Mixed Flow • Radial • Suction • Single Suction • Double Suction • Construction • Impeller Design • Bearing Arrangement • Volute or Diffuser • Vertical Displacement Pumps • Reciprocating • Plunger/Piston • Direct Acting • Power Pump • Diaphragm • Pneumatic • Mechanical • Rotary • • • • Gear Lobe Screw Progressing Cavity Dynamic Pumps • Constant Head Machine • Dynamic pumps add energy to the working fluid in the form of velocity • The fluid velocity is then converted to pressure by slowing through a volute/diffuser • Bernoulli’s Principle: Displacement Pumps • Constant Flow Machine • Displacement pumps simply move fluid, increasing pressure by forcing the fluid against a resistance • Flowrate is proportional to speed and stroke length • Flowrate is irrespective of discharge pressure - will pump until failure Initial Selection • GPSA Fig 12-3 • Very preliminary • Outdated • Doesn’t cover a number of pumps • Requirements • Varying flow? • Varying pressure? • Metered flow? • Fluid properties • • • • Viscosity Multi-phase Lubricity Slurry/Emulsion/Solids Initial Selection Repsol Pump Selection Guide – 20-00153DC Centrifugal Pumps • ANSI / ISO • ANSI B73.1 (Horizontal, 2012), B73.2 (Vertical, 2016), B73.3 (Sealless, 2015) • Defines standard design dimensions • • • • Footprint Nozzle centerlines Shaft size Baseplates • Foot-mounted Installation considerations • Grouted vs non-grouted • Mounting feet, pads • Quality checks prior to installation and shipment (planarity, surface, prealignment) Commissioning Support • Installation practice (API 686) • Seal system setup and charging • Baseline vibration • Cold vs hot alignment • Pipe strain