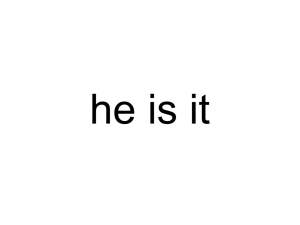International GCSE English as a Second Language Coursebook
advertisement

Published fo r OX F O R D AQ A I N T E R N AT I O N A L E XA M I N AT I O N S International GCSE ENGLISH A AS S E CO N D L A N G UAG E Mike Gould Lorna Pepper 2 Shutterstock ; p41: 1 Mitch p40: L arsZ/Shutterstock ; Gunn/Shutterstock ; sir travelalot/Shutterstock ; p45: antoniodiaz/Shutterstock ; Great Clarendon Street, University Oxford, Press is a OX2 6DP, department United of the Kingdom University p48: Uber It furthers and the University’s education by objective publishing of excellence worldwide. in Image trade mark of Oxford University Press in the Oxford UK © University and is in a Klemen rights published rights stored in of in Press the terms 2017 authors should or with the as have sent address to of the this or been CRE ATISTA/Shutterstock ; p52: p53: p56: p53: Syda Productions/Shutterstock ; hin255/Shutterstock ; p57: p56: thi/ YlinPhoto/Shutterstock ; Misic/Shutterstock ; p57: lightpoet/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; Picnote/Shutterstock ; p60: EPSTOCK/Shutterstock ; p65: p63: Alexander prior publication permission appropriate any outside Department, be law, the of by or Oxford of or under organization. the Jan Shutterstock ; by licence rights scope Oxford reproduced, form writing by reprographics reproduction Rights in permitted may in p67: Wasan /iStock ; p61: p58: Marisa p58: O.C Estivill/ Pressmaster/Shutterstock ; Brown/Shutterstock ; Chaikin/Shutterstock ; p66: p69: Greentellect Shutterstock ; Stock Ivoha/Shutterstock ; J/Shutterstock ; p68: Wiliam Tim Photo; p68: Xavier Studio/Shutterstock ; p71: p64: p62: AndjeiV/ malerapaso/ Perr y/Alamy p72: Bikeworldtravel/Shutterstock ; p73: Kobby p74: 5 p66: Dmitr y Stock Polonskiy/ ra2studio/Shutterstock ; MARCHANT/Shutterstock ; p69: Macpherson/Getty; p73: Nadezda p72: Murmakova/ ar tyme83/Shutterstock ; AleksOrel/Shutterstock ; above University Press, Dagan/Shutterstock ; p73: Michaelpuche/Shutterstock ; at second Studio/Shutterstock ; p75: Shirlaine Forrest/Getty; p76: above. not circulate this work in any other form and you p76: this same condition on any Obradovic/Shutterstock ; Cataloguing in p77: Dionisvera/Shutterstock ; p77: p78: mangostock/Shutterstock ; p77: p79: ESB suzz/ acquirer. Shutterstock ; Library mimagephotography/Shutterstock ; must Professional/Shutterstock ; British B Wlodarczyk/Alamy p68: L azar impose p62: gemphoto/Shutterstock ; p66: takayuki/Shutterstock ; must Guner_Gulyesil asserted. transmitted, expressly the concerning be part system, without Press, agreed Enquiries No retrieval means, Data Darren 2017 reserved. a University You p53: p58: Photo; the p50: Filimonov/Shutterstock ; Ritz/Shutterstock ; iStock ; any Ipatov/Shutterstock ; Iakov p45: Images/Shutterstock ; reg- Shutterstock ; All Business certain p62: moral First p44: countries Oxford The Gunn/Shutterstock ; research, p57: other p49: p52: Factor y/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; istered Monkey Images/Shutterstock ; PointImages/Shutterstock ; scholarship, Mitch of PR Oxford. p41: kodachrome25/iStock ; mimagephotography/Shutterstock ; p47: W hittingham/Shutterstock ; Oxford p43: Publication Data Shutterstock ; available p80: p81: wong Catalin/Shutterstock ; p82: Dudarev yu Tetiana liang/Shutterstock ; p80: Iatsenko/Shutterstock ; p82: Monkey Business Mikhail/Shutterstock ; p83: BonNontawat/ p81: Pop Paul- Images/Shutterstock ; Kiselev Andrey Valerevich/ 978-019-841713-2 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Shutterstock ; p84: Allen.G/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; p87: imageBROKER/Alamy; p89: Paper used product in made the production from wood of this grown in book is a natural, sustainable recyclable forests. Syda Productions/Shutterstock ; Anetlanda/Shutterstock ; process conforms to the Printed in of the the country United of p88: CK Khoroshkov/ ildogesto/Shutterstock ; Foto/Shutterstock ; moomsabuy/Shutterstock ; p91: p90: Marios Stock Photo; p92: John Wollwer th/Shutterstock ; p93: environmental blew_s/Shutterstock ; regulations p90: Nickolay The Forsos/Alamy manufacturing p90: p84: p94: Michael Bogner/Shutterstock ; p94: neelsky/ origin. Shutterstock ; p95: wavebreakmedia/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; p97: Patrick AVENTURIER/Getty; p95: p98: Andrea Citizen Izzotti/ of the Planet/ Kingdom Alamy Stock Eduard p101: Photo; p99: Citizen of Kyslynskyy/Shutterstock ; Denis Pepin/Shutterstock ; the Planet/Alamy p101: p102: Daniel Stock Photo; p100: Pr udek/Shutterstock ; OlegD/Shutterstock ; p102: Rudmer Acknowledgements Zwer ver/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; e publisher and authors would like to thank the following for use photographs and other copyright image: Shutterstock ; p3: Jerey p3: Coolidge/Getty Images; zulufoto/Shutterstock ; arek_malang/Shutterstock ; p5: NAN728/Shutterstock ; p3: p2: L ange/Shutterstock ; p4/5: p4/5: VCG/Getty; p6: p6: aaronj9/Shutterstock ; K aren p106: DenisFilm/Shutterstock ; p8: oneinchpunch/Shutterstock ; /iStock ; p6: p8: p11: p7: antolikjan/iStock ; p14: Brendan p11: p12: Rix/Shutterstock ; p16: Melissa Bell/Alamy Borges zhu difeng/Shutterstock ; p16: p17: Bokic Stock Photo; King/Shutterstock ; Business Coman/Shutterstock ; Ar tizarus/Shutterstock ; p18 (both): p21: Syda p21: Patr yk Productions/Shutterstock ; p23: George p25: Hermin/Shutterstock ; Rudy/Shutterstock ; p16: M. p115: Allpor t/Shutterstock ; p24: View Apar t/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; iStock ; p30: p28: p27: beta757/Shutterstock ; p16: Photo; p22: Blazej sjenner13/iStock ; p29: p31: p28: Oleksii Everett Professional/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; p33: Gods_Kings/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; p34: R awpixel.com/Shutterstock ; asife/Shutterstock ; p39: Marisa p119: p121: p115: Estivill/Shutterstock ; Jess Kraft/Shutterstock ; p121: xmo/Shutterstock ; p124: p124: Rober t Giannis p120: p121: p122: Tinapat GUDKOV Kneschke/Shutterstock ; Papanikos/Shutterstock ; Wittayayut/Shutterstock ; p127: Monkey Business p127: Syda p124: p124: Travel Rido/ Productions/ Images/Shutterstock ; Images; p38: p128: ober-ar t/Shutterstock ; p128: p126: ober-ar t/ p26: Shutterstock ; p129: miya227/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; p130: TungCheung/Shutterstock ; p129: Shutterstock ; p130: Rober t wavebreakmedia/ Sidorov/ p130: Collection p32: p32: p34: Kneschke/Shutterstock ; Rob p130: Byron/ Monkey Inc/ Images/Shutterstock ; p131: Phuong D. Nguyen/Shutterstock ; Prov910/ My Life Catwalk Photos/Shutterstock ; p133: JJ pixs/Shutterstock ; p134: Graphic/ Szczygiel/Shutterstock ; p135: Valeria Aksakova/Shutterstock ; SpeedKingz/ p37: james cheadle/Alamy; p137: Richard Wayman/Alamy; p137: Travel YadvigaGr/ p137: Marco Saroldi/Shutterstock ; p138: Ruth Black/ R awpixel.com/Shutterstock ; Productions/Shutterstock ; Halfpoint/Shutterstock ; p39: R adu Shutterstock ; p138: Hung Chung Shutterstock ; p140: Everett Chih/Shutterstock ; p139: kiatipol2426/ p39: Collection Historical/Alamy; R azvan/ Continues ii p115: Son/Shutterstock ; FamVeld/Shutterstock ; p127: Stock/Shutterstock ; Syda p116: Shutterstock ; p137: p39: van Shutterstock ; Mariusz Bridgeman Fotos593/Shutterstock ; p17: p132: p37: p114: Brendan VikramR aghuvanshi/ Lyjak/Shutterstock ; ESB muzsy/Shutterstock ; p112: BestPhotoStudio/Shutterstock ; p32: p39: C/Shutterstock ; totallypic/Shutterstock ; Guillem/Shutterstock ; R awpixel.com/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; p113: g-stockstudio/Shutterstock ; Duda/Shutterstock ; p31: Mircea Kosmider/Shutterstock ; cherezo/Shutterstock ; Sebastian Stock p108: wizdata/Shutterstock ; R awpixel. Business Alamy p109: Matyas koya979/Shutterstock ; p25: p107: Images/Shutterstock ; p15: Images/Shutterstock ; Antonio p111: TonyMurano/Shutterstock ; Kuzmin/Shutterstock ; Stock/Shutterstock ; p20: Uber p9: ANDREY/Shutterstock ; Lucian Ryzhov/Shutterstock ; 101/Shutterstock ; robuar t/Shutterstock ; Bojan/Shutterstock ; Monkey p108: suriyakan/Shutterstock ; Kotumrongsak/Shutterstock ; com/Shutterstock ; Sergey foto Photography/Shutterstock ; lovelypeace/Shutterstock ; Rehak/Shutterstock ; Prof littleny/ p117: Jane Woolfenden/Shutterstock ; p106: p107: Andrushko/Shutterstock ; Andrew p13: David Groomee/ vapadi/Shutterstock ; Miami2you/Shutterstock ; Stock-Asso/Shutterstock ; p106: William Ivan Shutterstock ; p106: Bourdages/Shutterstock ; Stock p113: p10: S -F/Shutterstock ; L ande/Shutterstock ; p4/5: WWP/TRVL/Alamy wavebreakmedia/Shutterstock ; ladendron Photodiem/Shutterstock ; Brandon K atr jyan/Shutterstock ; warangkhana Shutterstock ; Alexandra ZouZou/Shutterstock ; Ijansempoi/Shutterstock ; Horizons p106: p106: p110: Perugini/Shutterstock ; p106: p106: Samuel Photo; p106: Ewais/ absolute-india/ Galyna Hasbro/REX/Shutterstock ; SCOT TCHAN/Shutterstock ; p103: material: Philip Cover roberaten/Shutterstock ; permission p106: to p104: p102: on the last page CONT ENTS Theme 1 – Identity Unit 1 – All Unit 2 – Keeping Unit 3 – Free-time Theme 2 about – 4 – W here Unit 5 – Social Unit 6 – Global Unit 7 – Travel 3 – I live and My Unit 9 – Life Unit 10 – Education Unit 11 – Jobs, This – This of GCSE interest ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ and future study and the choices 88 106 employment and ambitions ................................................................................................................................................................. to the words: the syllabus English Book as is a listening the Second supported lesson Book for plans, Oxford Language by the teacher ideas exercises as Experienced course of Teacher the as words book, the the prepared answers to beyond make examiners including content possible. questions. Useful the that hints, well and AQA Using for GCSE this book exam level. as been detailed adheres the learning have The at to planning the will level, features phrases highlight be the are shown to vocabulary 124 178 below and helpful to you in your all closely you also are effective aspects ensure as that and in are for as well studies designed as to possible. Glossary Glossary that to syllabus ensure this interesting involved REMEMBER: will 72 book differentiation Student Useful and 56 post-16 .............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 160 this includes guidance, transcripts all of papers ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 194 covers Student which activity areas ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... career use fully International Guide, global school ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 142 Practice to book (9280). 2 20 preparation 12 How studies and ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... Current – international ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... tourism 8 Unit national, ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... issues Unit Exam ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ activities .................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 38 issues at culture ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ touch Local, Unit Theme me in and boxes meanings may not for give the words give that you understand advice knowledge Remember and you recap have boxes on the already gained studies Hint: Hint boxes give helpful tips Vocabulary Challenge and advice Grammar LISTENING Vocabulary are The audio CD is included with clearly to provide listening grammar differentiated sections by boxes chance push fun and to give you yourself stretching the through activities. a this coloured book and Challenge background. exercises. iii E xam You will Paper format have 1: What’s to complete four assessments to complete Writing course. Paper assessed Communicating the 2: What’s effectively in writing for a variety of written How How Written 60 assessed exam: 1 hour 15 minutes 30% of 60 international GCSE assessment are four skills. The tasks be the to marks based on themes Paper – 3: What’s How 40 Each the content. of a level the nal in one range of writing three themes task or of challenge, rst following The study test in will more tasks named allow of as the do of types of it’s assessed exam: 1 hour 15 minutes of international GCSE assessment Short in answer response questions to written and multiple passages – 60 choice questions marks. will students named marks. Listening Paper and responding to different types of language. 45 a How minutes international Speaking assessed Communicating for assessed exam: 4: What’s variety it’s of and GCSE assessment minutes 40 marks of effectively in speech assessed 10 20% interacting purposes. Non-assessment marks 20% different in assessed it’s Written of their 60 which increase one Understanding written tasks awarded. on Subject draw to Questions There the responding marks 30% Questions and language. Written marks assessed Understanding purposes. it’s Reading + exam preparation international GCSE time assessment Questions Students will questions (Each the exam be a asked range includes question played.) iv on paper to of 5 listen spoken minutes before the to and texts Questions answer – reading listening 40 marks. time • Photocard • General • audio – 15 marks (3–4 minutes) of stimulus conversation – 25 marks (6–7 minutes) is recorded by teacher and marked examiner . The AO1 TO Assessment READING: WRITTEN R1: R2: UNDERSTAND are AND as follows: RESPOND AO3 LANGUAGE Identify and Objectives and select LISTENING: RESPOND relevant detail, key points L1: longer understanding of vocabular y, ideas and L2: Collate, R4: Draw in organise and inferences, recognise present make implicit relevant deductions, detail. a key L3: variety a variety abstract L4: WRITING: COMMUNICATE IN of Write shor t exchange texts to convey Produce of shor t and and more and longer complex collate shor t and and key spoken longer texts, language. information complex points spoken language from texts, and more pur pose, meaning and implied feelings in meaning , extended texts. and information. clear to range message shor t some Recognise and coherent text of present key points, SPEAKING: COMMUNICATE extended AND length a WRITING AO4 W2: from material. attitudes W1: of some involving AO2 overall Understand meaning. LANGUAGE details the involving and AND texts. Identify pur pose. R3: SPOKEN Identify ideas. Show TO UNDERSTAND details INTERACT IN SPEECH and S1: Communicate clearly using speech ideas. appropriate W3: Make accurate use of vocabular y S2: grammatical structures; spell to situation and audience. and and Make appropriate and accurate use of a variety punctuate of vocabular y and grammatical structures. accurately. S3: W4: Manipulate f luenc y and the language creativity with for a Produce extended sequences of speech, increasing variety answering and, questions, and as appropriate, asking of expressing opinions with pur poses. spontaneity S4: and Demonstrate f luenc y. appropriate pronunciation and intonation. At the beginning of UNIT 1 each unit use can All This R1 W1 L1 S1 this is you unit you identify write which assessment about unit people In see and key about you, will be covered in this unit, for example: me your family and the know. will short identify all objectives learn select texts communicate relevant to details to… convey from clearly a detail, meaning range using key of speech points and and ideas exchange short and information longer appropriate to texts situation and audience. v All UNIT This 1 about unit people In this unit, write W1 you will and key and learn select texts you, your family and the to: relevant to details communicate S1 about know. short identify L1 all you identify R1 is me convey from clearly a detail, meaning range using key of speech points and and ideas exchange short and information longer appropriate to texts situation audience. Family e word family means dierent may have dierent views may have dierent ideas. 1.1 Me and my to things younger to dierent people. people. People in Older dierent people cultures family Abdul Time Spend your a to few think minutes family, or the (grandfather) thinking people you about are your living family. with, to Draw show a diagram who is of who. Nadia It might Or you look might Time In ✪ something pairs, to take Show think your the own example diagram shown to on show the right. (mother) relationships. talk it your of like in Sameera Ali turns diagram to to talk your and ask par tner (older questions. and explain (younger brother) sister) who Zara is in your family. (ME) ✪ Do you know nephews, see ✪ great-grandparents? cousins? Tell your par tner Do you about have them nieces and or when you them. Describe a or your time Useful one when of the you members had a good of your time family. with them. Tell one another words: aunt, cousin, nephew, uncle, about niece, great-grandparent, brother-in-law, stepfather , widow, Check a sister-in-law, stepmother , widower that meaning 2 grandfather , grandmother , of you all dictionary to know these help the words. or to Use check. Unit 1.2 Different Look at the thinking in the the on the right. dierent Spend kinds of a little family there are to think Which countries do you think these families are from? ✪ How ✪ Is ✪ In many your talk generations family what ways Time ✪ speaking time ✪ these and world. Time Now Thinking families pictures about 1: to any your of there in each picture? these? family the same – or different? talk about prompts like is are some to get of the you pictures with a par tner. Use some of star ted: Choose a picture. Take it in turns to describe the family in the picture. What are they doing? What might they be thinking or feeling? ✪ W hich ✪ What do all the families seem to have in common in these pictures? ✪ W hat are the advantages of being in ✪ W hat are the advantages of being an ✪ Is good it a W hy 1.3 family or My of are or prepare, similar to to have your own several family a and large only in what ways? family? child? generations living close together? not? friend to going them idea why Time You is ✪ how long ✪ where ✪ what they ✪ what you ✪ if friend talk think make a look was – a friend you in you to could advance. known this your classmates. describe ink them. Find To a help picture you about: friend met like about time what a how notes have how like about about few you and there think to them you and were happened and why angr y how or sad you because made of things this better. REMEMBER: Time to notes Give a three-minute talk about your friend to a small group looking Make them in your the talk face interesting and by developing speaking your clearly ideas. when you read are out talking of – classmates. Don’t talk and loudly, it will doesn’t few sound mistakes words. very matter Just understand if or make search make you boring. you sure It a for people clearly. 3 Unit 1: Reading non-fiction READING In this section, read a learn some learn what learn to useful is might and be text vocabular y meant identify by and on the skimming select topic and relevant of friends and family scanning details, key points and ideas. about… non-ction families will: non-fiction Think e you NON-FICTION text you friends like in the are aect going us. It to also read asks is about what some these of the friends ways and family future. Hasbro Will We your humans happiness the as next close a who not throughout you pets, too. and stressful as purr , have not healing the group in of the does broken Of course, or cannot not can friend But see and friends sometimes all know the talk benefits to it how after a are isn’t possible people of important may owning bad day – a to turn pet, for A all afford bother robot they of cat purr an is USA The have two that proved groups didn’t. study that it that of They group you both that than can one robot cat have to a pet someone someone a stress improve group groups rises in stroke mental pets people, put showed when relieve who the cat in it owned people blood other . and but of physical that Other listen actually in pressure were remarkable to its soothing speeds up the bones! people the can cost animal. available and a our own a pet such as a cat. Many live in flats, Paro the - robot? Family We to pet-owning shown only a lives. need. studied situations. high studies in They one our we a you. scientists health, is be humans. Everyone and judge friend other friendships loves Now half need companion. does best meow. of an But in help the They animal, is at shops are able or hand now. to perhaps for The those pets respond they to just don’t facing have – to being stroked loneliness. realistic petting responds want just fur , like and a Glossary normal be let Japan out, is But, and one unlike they of the Many homes robot seal, support. mental not It cuddle, die. health, been as and cat, these require leaders the in in Paro’s faces. depression homes not or Japan only to now job is out help but it never the up at 3 a.m. to mental to make to can around you robots seek Paro — wake grooming. developing programmed care will feeding elderly Paro. remember such Hospitals for called has and real world special touch, a never people. and 4 cat. give eye help regular and needs now use of be a love respond problems to fed make to with and use physical for receive contact, relieve world care of to does Paro. do to with do the with mind the body Unit Developing your W hen for and you to scan. reading You look that may want called getting word. You to know ‘the paragraph to to see and in a text, scanning you are need two to be able dierent to ways skim of useful. gist’ skim-read subheadings four information ver y Comprehension skills Skimming are 1: what or the the guide what a piece ‘main text. you. that For Or you of text idea’. is You example, can paragraph look is about generally. don’t you at the about. need can rst e to look is read out is ever y for sentence text on page 4 of a has paragraphs. A Answer word 1 to in the these text questions on page 4. quickly, Each without answer is a re-reading paragraph ever y number, 4. 1 W hich 2 Which paragraph will be about a robot that can help look after people? paragraph 3 W hich paragraph will be about how people 4 W hich paragraph will be about how robot Extending You is may where detail your need your you carefully, to will out scanning need, about how pets can improve need pets our friends can health? and replace family? real ones? skills nd decide perhaps be a special skill on picking piece comes the right out a key of into information action. section word of in To text, the or help a detail. you then nd read is the more text. B Now 1 Look Give 2 read at at Look at ways tick 4 How two carefully 1. How can a 2. Give two pet and help answer some the people questions. feel happier? ways a pet can improve people’s health. paragraph the has more ways. paragraph physical 3 text paragraph two Look the robot been does cat 3. is done the Copy for robot the similar table to and opposite different and tick from a to real show cat. the One you. seal Makes show love and suppor t to people? Give a purring Real Robot cat cat ✔ sound ways. Has to Needs be to fed be groomed C Research other robots designed to act as human helpers or Responds friends. Choose one and make a labelled picture of the when robot stroked showing its main features and abilities. Present your picture to Wakes the class, explaining what the robot can do and what you the about you up in think morning it. 5 Unit 1: Vocabulary Vocabulary Word In this section, you To ✪ learn some ✪ learn about verbs ✪ learn about the useful vocabular y and the related subjects to of the theme of the unit verbs help e about article how a In b Friends c In d Look can at from and Answer these 3 what 6 4. 1 that that a fills tenses. robot?’ Answer means and past ‘a the us uses words these close make questions. friend’. feel happy. Choose gap: our word is be friends. minds with W hat simple well-being. that means another ‘to do phrase with our meaning ‘a body ’. home for they the to to correct your ‘ loneliness’. loneliness? have seem a the a similar in in in mother tongue. is one W hich words and Word then of the write below help have a you. two out To write two words Explain these Book . also to anxiety word? between above but two dictionar y depression thing. your English, a meaning , meaning questions meanings W hich Use isolation positive difference through in questions. refers denitions help the sadness ‘ loneliness’ the help find meaning Although Go word our and friend and paragraph paragraph Paragraph their the soothe family 2, next family find help solitude 3 1, present elderly ’? similar b your need paragraph the a we word Friends 2 ‘ Will paragraph one simple any a par tner words. the help to makes words you, notes with write that will you learn of vocabulary, to write Word 1 Book will: useful Book. it a is wide a range good words in idea your Unit 1: Grammar Grammar Ever y or a single classes, word and sentence. revise each e preposition, we use in group groups tells are: conjunction, English you noun, and belongs the to work verb, one that In eight those adjective, determiner. of words adverb, this unit, groups do in pronoun, we are going to verbs Verbs A verb being. I like 1 a ‘doing’ Look at robots. Paro the is is a verb Write word, these The robot a word verb seal. is The verb (Remember out all the robot b The c Many d You e People cat pets is love a and new their in or the state of and the is the the third-person ‘action’ of form of being.) sentences. shops now. they friend and which include homes robot pets, is, these the fur, care is verbs in realistic hospitals wanted verbs available have action like be. A shows examples: to a that use purr and meow. Paro. and now you have pets help their one. owners, in return. Hints Subject and verb • Sometimes the ‘understood’ Every sentence has a verb and also something or someone action of the verb. This something or someone is known as out of the verb. Look at this For is a robot verb is is. action of is, as not For The subject of the verb, the person or thing who to the verb is robot helps expensive. sentences have more than one verb, and more than one subject. robot it. people (The but robot in the is second clause.) welcomes people to the shop and the customers speak Sometimes of a that rst verb is welcomes and its subject is the robot. The is speak and its subject is the longer together to acting The at the sentences then write down the as robot in question 1. In each is of as main is part words a subject. word that the subject of each of the For subject of example: with all its expensive. electrical (The sentence, subject and act the verb. parts again nd subject customers. each Look the group second is verb nd give example: Try 2 sentence Paro. it. The to the does • The the actually understood Some what seal. is the or example: The The who sentence: might Paro is have the subject subject subject you doing work the – verbs is The robot.) you found. 7 Unit 1: Verb Grammar tenses: simple present Spelling To The tense of a verb gives more meaning to the verb. It lets you make has the two action main of the verb is happening. The simple present to show jobs: for that • the action of the verb takes place here and for You purr. The man likes the to it show still that the happens, action and happens will go on For all the time, happening, it for used to uncle designs robots. The runs. verbs He make shop sells and the after simple the present third person tense, (see robot • cats. -ch, goes. For you add Spelling -s or hints I example, sing. The You verb verb. For sing. to be is You/we/they Write the a in Human b My c The d She e My for 4 out verb My in of the We forms -es to the end verb sing. to 8 It -o, -ss, -x, They according you add -es. For She verbs of catches. ending + y, in you a change the y to ies. For example: ies. She hurries. sing: sing. to the subject of are in the Paris. sentences, to ll using the other (love) lady (want) she had (be) simple present tense of gaps. (need) brother the a human robots. pet cat. one. cer tain that his cats (be) good health. complete form of one be of see my friend the pets sentences the verbs carr y each her in the play morning bag below, on box using to c ycle and her back amazing , but this robot REMEMBER: Always the subject make sure beings. ll the each gap. give them when simple fresh she the water. to school. c in Paris. these feed b sings. different brackets and present I has grandad Copy a He/she/it (wish) his present beings little old simple plays. example: I/he/she/it 3 the after box). It For -s example: the verb add example: ending consonant To just For example: happen, He My person: cats. -sh • third usually verb. She • cats the now, example: The present tense the • simple know tense when hints the violin! verb and agree. Unit Verb The in tenses: simple the The To past, cats simple past for tense the Grammar past tells you that the action of the verb took place REMEMBER: Always the subject make sure example: purred. make 1: The simple man past liked tense, the you verb and agree. cats. usually add -ed to the verb. For example: He walked. The verb She laughed. ending does They not jumped change, whatever the subject of the verb. For example: I walked. There rule, For I are and many you You verb be Write in out The b He c It d The e W hen a little in past walked. verbs progress that They do through not walked follow learning the English. these We sang. forms They wrote according to the in sentences, to ll the doctor using the when excited he (know) I (be) W hen past the verb. simple in saw it I of (be) the a about Japan, sentences, tense past tense of the gaps. (be) these of Paris. boy out subject Paris. were about the and (hold) child, the human in my hand. body. (see) using its (run) all the way home. I verb robot. either the brackets a robot simple to ll father in a shop. present the (take) or gaps. good care me. b My best c My grandma (give) d you We (rain) this morning, so I simple of walked. simple as different (smile) Write the these taught. has brackets a 6 He was You/we/they verb He/she/it irregular learn ran. to I/he/she/it 5 walked. example: saw. The You friend her Brothers they (listen) (want) one and always last a mobile when phone I have so a problem. we week . sisters (be) often in (suppor t) one another when trouble. 9 Unit 1: Listening LISTENING out carefully for par ticular details. Exploring… Step my What’s family ’. Step ✪ 1: 2: Of Do which the topic? course, the answer that is questions is likely to ver y wide. give be any clues? correct ✪ A a, 1 b or W hat a 2 5 20 10 W hy did far hat? mother I b run in does the ever y with best did because your boy is ✪ who that ✪ where 10 years kilos night on the exciting make a person is might rollercoaster? b list it of speaking be. c c fit was the speaking they doctor? 15 dancing? him go was partner, who a for friends they it like keeps Saturday his W here the c morning? b it red become ago do ✪ 10 boy ’s o’clock b With her years because a the b a c is big How a 4 colour W hen a 3 c. to so fast key words Unit 1: Comprehension B hear Now work each statement answer Audio 1 – 2 many 4 no 5 6 7 8 is wrong the did the question, Histor y teacher You choose set 15 girl with the the c find the most the will correct class? 0 difficult? English boy b does this the boy hope to morning kind of b the does film does Bet films c Music c sore c the c romantic today? bad be cough back the the like b speaker like action at end throat college? of the week next day best? horror about b the films superhero films films? romance c the scener y 1.4 Marie’s father a to going W hat a did b superhero Audio questions. 1.3 W hat a questions voice W hat a each the c. homework later Audio answer 1.2 W hen a to For b W hat a twice. Histor y Audio 3 or own 10 W hich a b your 1.1 How a a, on is asks Marie cooking her to rain. the come b doing inside time for the house dinner. because it’s … c too sunny. c weeding the garden now? dinner b reading her book C Complete 1 Work in friends. what 2 Now pairs. They they use activities. Write are did. write should these one shor t talking In three a pairs, about record questions of these conversation where the about key they words) went last between weekend two and conversation. the words (100 or conversation. phrases: Each question W hat … ? W hen … ? W here … ? How far … ? How much … ? 3 Swap got recordings the answers and questions right. Identify with the another key words pair. that Check were that you used. 11 Unit 1: Grammar Grammar On pages present learn you learned tense and the about Verb On to 7–9 some page 8 revise called you the the You To are make with I the am You are are this verbs, section you the are simple going to simple present tense. This tense. This tense Now tense shows you is that are going sometimes an action is example: words now progressive, participle of the use the verb verb to (the verb be in the + ing). present For tense, example: reading The b I c The d We e They reading reading out of a is reading are Write forms In of progressive progressive these present tense. subjects tenses. continuous. For present the the reading They 1 present reading He/she/it We revised now. the verb verbs, past present present happening simple more tenses: about these the sentences, verbs in mother to to using brackets school her today. children for sandwiches football to the ll child. present the progressive gaps. (sing ) (walk) joy as while they we together. are watch so happy. TV . (jump) Spelling (eat) • (play) When you ending f My aunt g She h The i We j I k My the car while we wait. for friends the family. together. (make) and For to thank parents parents the us our good go then add friends. She the m I n My o ‘ W hat ball a news camping. long right now. (tell) + When ing you word friend and a taxi. I way. add sound double For really 12 ?’ shining -ing in a and you to a short a single usually have good time. (have) my mother asked. (eat) the consonant. example: shut you word the (hit) (wait) a a -ing. ➜ ending vowel (let) to for to drop (write) consonant, l -ing you (dance) • my add e, example: shine emails in (park) e cakes hints + ing ➜ shutting Unit Verb On tenses: page revise past the past, form was You 2 were tense, unnished the you of was that or the in is you are going sometimes action progress was at to called happening that moment the in in doorbell use the the verb rang. verb (the to be verb + in the ing). past For tense, with the example: reading. reading. reading. out in these sentences, brackets a I b They c You d We e I (eat) f I (leave) g This h My i We j My k I (walk) to to (hope) time last my cousins in that sister breakfast house my I same you the past met choir to the would when when I my (remember) how (work) just forms of friend. ever y week . cinema when I saw the realised I school had (study) last last (phone) last saw you. bus. forgotten for my bag. exams. week. much late I visit. brother us progressive gaps. when (visit) father using the the your the year, ll school (sing ) (take) fun we had last year. night. my friend when she rang first! l This m The morning wind n o shows Now tense reading. were verbs me tense. This reading. Write the past tense. tense was when participle were They simple example: this He/she/it We the This it Grammar progressive progressive that reading present I revised past and For was To you continuous. time. I 9 the past 1: we (learn) (blow) you The sun so strongly (listen) (set) and it about to robots. yesterday. me? (get) dark . 13 Unit 1: Reading non-fiction READING Read you the NON-FICTION following do not know, events and ideas. text keep as quickly on as reading you so can. you If there understand Nelson Mandela (1918–2013) was the rst black himself ). He is remembering his childhood and I walk was no sheep how to from the at its direction with of the As boys, We the to and became … sky footwork. the in It swim to in South life-stor y, A frica. written by the importance of friends. any From these simple a the rural of days I I – and feinting love an of wild milk streams, the after lear ned gather from my nature, I lear ned boy away date of to cold blows, that sweet wire. African breaking looking fields war m, clear, bits beauties the slingshot, parrying another, herd-boy, in drink sharpened to a was with roots, techniques, striking we we were made made ox-drawn The rocks we flat which stones lear ned taking came and my tur ns I bent mostly to We sleighs hills down lesson one climbing on head, up and tr ying to of into day and own straight and to to stick- became in one opponent the clean our from down unseat the an donkey dotted own of veld, line back bolted me, of coaster. our smooth We We sat but had my nearby did, clay. on … when a with of was large rocks and it out Nature donkey. into which played birds with roller large unruly its We and branches. were face devices. animals tree Qunu the the our molded out above transfor med slid jumped its left ourselves. playground. It main horizon. toys I of edible knowledge spaces, I fields. cow, twine various and quick open out a when the and of with essential adept five in birds udder fish – than fruits the freedom calves knock and catch fight more and honey to words president of is is an extract from Mandela’s autobiography (his A are been chance thor nbush. not Glossary before feinting the thor ns had pricked and scratched my face, embarrassing in in front highly of my friends. developed Like sense the of people dignity, or of the what East, the Africans Chinese have had lost face among my friends. Even though it was call a a him suffer me, an opponents I lear ned that unnecessarily without to humiliate cruel dishonoring fate. another Even as a boy, I is to defending yourself that a weapon make defeated my unruly hard to control them. veld 14 blow “face”. donkey person pretend ght from unseated a a parrying I making me grasslands in Africa Unit Applying To ‘get the your gist’ have to Now answer or 1: Comprehension skills get understand these the ever y main idea single questions of a piece of writing , you do not word. about the extract from Nelson Mandela’s autobiography. A be Here used are for heading four headings. paragraph does not 1? match For any it W hich paragraph of is a Nelson learned how bad b Nelson learned how impor tant c Nelson learned to make d Nelson learned to love his heading to the For b, c or d) could paragraph 3? One paragraphs. make anyone academic own nature 2? (a , feel small. education is. enter tainment. and the countr yside. B Now will 1 need read to the go questions back to the below. text and To answer read it each more question you carefully. Look at paragraph 1. Find one word that means each of the following: 2 a good b brought c someone Write his 3 to three up to in the fight the phrase super vised W hat countr yside against. different understanding Find 4 eat by in of things paragraph children complete the table. toy a … enjoyed which developed 2 that means the children were not adults. the make Nelson nature. did To that e use to make children their used own play things? Copy and … animal sleigh roller coaster C Nelson experiences lessons that refers to helped he two make learned ways him from in the his particular kind of that adult his he childhood was. Give two childhood. 15 Unit 1: Writing WRITING Writing about Think Here with Do are a some agree There earth than Thoma is quotations Discuss with any nothin more true s and childhood about… par tner. you friends to g what of on be about friends each and quotation friendship. Talk about these means. them? this prize d frien dship. Aquin as None away A true friend one tolerates your your so rich as to throw friend. who Turkish overlooks Doug is is a failures proverb and success! Larson The mirror friend cry it Charlie 16 is my becaus never e best when laughs. Chaplin I Unit Time to write: a good 1: Writing friend Choose a friend you would like to write about. e friend could be in your family, a pet, or someone you know well. is might be a friend you had when you were younger. It could even be an imagined ideal friend. You can use ✪ W ho ✪ W hat ✪ Think go ✪ is Write In the and the does a the extract on Make some ✪ where ✪ games ✪ your ✪ how you into an Now you get ideas. had that like? a good made time it thing together. W here did you memorable? about this person that makes page he the 14, played to childhood Nelson with make extract about his him again, your memories Mandela friends. the and own kind look wrote He of at also man your childhood about wrote he his childhood about how the became. answers memories. to section ink C. about: lived played / your toys friends write notes look impor tant write: notes you you words. helped through help friend? 100 games you happened to the Read when Time experiences friend most good about to friend? what is questions your about and W hat them these to think the experiences will affect you and help you grow adult. your help own you. autobiography Write about 100 about your childhood. Use your words. 17 Unit 1: One ONE step further STEP FURTHER Think In this unit, you’ve impor tant they think more On a the a bit piece other of being an ✪ being a ✪ having per fect size different ✪ who ✪ whether family, and challenge how yourself to topic. columns, one Make headed notes in ‘Advantages’ the columns of and the of: three family or four generations living together. you noted down, talk about your idea of the about: family do there the is work such and consider students large generations prepare After wards, were the should and Now partner ink the pair, of ideas the the a a of ✪ As of a of two friends others. child with ✪ to the disadvantages only family. about and about draw members some you ‘Disadvantages’. member Talk Using paper, and ✪ to deeply headed advantages thought are from a together involved thing then how living give far dierent as a the in the shor t running ‘per fect home family ’. presentation dierent cultures a the groups same or to the agreed. class. In what way dierent? Write Write could use a shor t use your ar ticle some own of on the the ideas topic of you’ve ‘ W hat makes discussed to a happy help you, family ’. or you You could ideas. Read is is Blake, a shor t an I was I told I was I told extract English angr y from poet with my a poem writing in called ‘A poison tree ’ by William 1793. friend: Glossary my wrath, my wrath did end. foe 18 angr y it with not, my my enemy foe: wrath did grow. wrath anger Unit Talk Talk ✪ about Is of what there how ✪ W hy ✪ Should Listen is to with any this it a this your One step further partner poem truth in might means what always hard be par tner ’s and Blake happen sometimes you 1: in to tr uthful ideas says? real tell and discuss life the to and one what questions. another might examples happen. tr uth? your add Give these friends? your own opinions. Write EI T HER: Imagine something You tell Write not an you – it them could the account are that a be friend has something asked quite you for small, your such opinion as a new about hairstyle. truth. for pleased your you diar y told the about what happened and whether or tr uth. OR: Prepare some questions for someone you know who is older than you, such as a grandparent, Reect In this and unit, check you: great-aunt or great-uncle. Find ✪ talked about ✪ learned ✪ read ✪ learned family and friends out in what ways family life has about skimming and scanning changed over the last 50 years or so. Use the to write In small results two or of your three a non-fiction take turns to another what useful about words robots and as friends phrases on the theme of you found and family tell ✪ one some paragraphs. friends groups, text inter view practised selecting relevant details, key points and ideas in out. written and ✪ learned to ✪ learned about past listened ✪ read ✪ wrote ✪ talked ✪ wrote an the to and personal about a verbs simple feel go help answered from and and their past subjects present, ar ticle about and you the need a about and and views diar y about all and on entr y section some answered friendship cultures’ confident to questions biography ar ticles back if a different shor t you for recognise extract necessar y, A sk texts present and progressive ✪ Check spoken or these and shor t audios questions childhood family life inter view. things. revise it If carefully. it! 19 Keeping UNIT This 2 unit social is media everyday In this unit, write W1 Social Have you groups Internet it or about ese are heard of 2.1 the way use you and use knowledge technology of short key learn select texts S1 communicate phrase? to of the It in a few often to to: relevant to details convey from clearly a detail, key meaning range using of speech points and and ideas exchange short and information longer appropriate to texts situation refers to each the ways other – communication dierent but in through the phones. W hatsApp, ser vices but you Twitter people may use. have and You similar Instagram? may not ser vices have in email In pairs, touch think with means meet or in minutes touch common up thinking your of and about friends and you family. communication? speak how For face-to-face, or communicate W hat is example, do you your do or most you mostly text them? Time to take talk it in turns to talk and ask questions. Useful ✪ Talk ✪ W hich W hy about is or the the why forms most of communication popular form? Is it you the use same most. for Do you have words: instant, both of you? image, chat, or still use a home phone (landline)? Can you use download, digital, text, email, landline that you want? W hy or why not? you know the it meaning whenever communication, upload, not? Check 20 in audience. with electronic mobile these, Keeping Time ✪ of countr y. Spend stay and identify communicate Facebook , some all this relates over W hat your of society par ticular your media heard in and will L1 and about touch life. you identify R1 all in of all these words. Unit 2.2 Mobile 2: Thinking to that think talk Spend a few minutes looking at this picture. It shows an you of technolog y that helps Look might about the up need any to picture. words help you Make a impor tant note piece speaking technology REMEMBER: Time and of them in your Word Book. drivers. What is happening in the picture? What is the equipment on the screen/ dashboard for? Time Talk to who uses 2.3 to your talk par tner this in Picturing Time Look W ho they at is the in to their taking car? use W ho? of technolog y. W hat might be Do you good or know bad anyone about it? think on picture? the this myself picture the about the right. W here are they? W hat are they doing? W hy are picture? Glossary app Time to (a Now talk about the picture with a par tner. Use some of these get you piece that Have ‘application’ of is software), especially downloaded to a star ted: mobile ✪ for prompts one to short talk you ever taken a ‘selfie’ or do you know friends who device do? prole W here? For what you ✪ Where would be your dream place to take a selfie, if you could choose? ✪ Can you selfies? think W ho of a personal summary of reason? any might reasons not like why it selfies might or not object to be a good people idea taking to take that sele people can see online a photo you take of yourself them? smartphone a phone that can do things such as take photos, access Applying Prepare your and then skills give a the Internet, send emails etc. shor t two- to three-minute talk on ‘seles’ or virtual ‘sat navs’ and what you think of them. Explain to your group or used something ✪ what they are and why they might be electronic popular not ✪ what you think of them – are they a good or bad to describe class: in that exists devices physical or in media only, reality thing? 21 Unit 2: Reading non-fiction READING In this section, ✪ read a ✪ learn you NON-FICTION will: non-fiction to points identify and text and and select learn useful relevant vocabular y details, key ideas. Exploring… We all and want social e text then use this sorry I is it didn’t turn see, used easy for explains many about family, of us. one media. Luis to his friend Amir and questions. time settings that a on my took me Let’s Luis it speak at could all crazily of the They was just soon. next say a I All all The of but I – I know and it to too long to to my you were was, ‘public helping clear up, have of and Street, to making clever! my big lawn. I told the the event’ could guys to disturbing them the ‘private People themselves up. party. and a and my parents social media still like see! on I hardly food. neighbours, nightmare! used at Facebook the adjust it else everyone that anyone Some front be Facebook. everyone about forgot up. street, a I using update event’ turned the was Unfortunately, would phone know Roselands parents’ and mistake. do I by Saj, instead a party. party friends 40 the thought Ella, had my I tell What shouldn’t silly take down place. day to people house and to the problem made around the up the to account, I come about address Hundreds over let p.m. night, because forgotten to see, invading all going the 8 didn’t – wrong? ‘event’ wandered all had was of Saturday everyone Facebook drove me. although it I went an disaster! litter forgiven all friends just leaving as Saturday started Others it tell on now. you planned to and party better thing I everyone motorbikes knew as media it my feel good create – only was a out come and you decided reminded the missed about how page I social college So, you hope probably You 22 this read and party! It It from the to friends Luis unwell. It made with Amir I’m I has touch going social email my I in Amir From: Hi are of answer To: keep media you person’s Read to haven’t this, Unit Developing W hen gist you (the reading or main phrase can read the phrases an – to – get unfamiliar As sense repeated clues to you reading a the Comprehension skills idea). text are give your 2: or text you learned it what it par ticular overall in quickly of generally Unit is you to can understand do questioning about. factual subject 1, without need Sometimes information is this by ever y key the skim- word words included. or Both matter. A Work with a partner to answer these questions about Luis ’semail. Glossary negative 1 W hat key noun appears in the subject line of the email, once in to unpleasant first 2 paragraph W hat factual and twice in information the is second given in when, Extending Another your of bad or the text? For example: who, noun the name place of a or idea do with person, where? method viewpoint with things paragraph? thing, what, do the is the positive to pleasant things good or skills to look for words or phrases that indicate the writer. B Answer 1 W hich W hat of 2 this on gist a Amir this, of such the is a Luis’s Luis Social well negative about dream how how words Luis nightmare the silly following in the text? feeling? wrong invading do is appear right perfectly statements sum up email? he didn’t go to the par ty as it was disaster. parents know made social you or helping glad doesn’t d tell disaster the c questions. positive disturbing Based b these does triumph litter these a media ever angr y mistake media should are with him but he why. to is when organise a he his terrible tried to use par ty. idea, which no one use. C How between parents? would Luis, For the Amir, views the example, on boys who the on party the might dier bikes be and Luis ’s ‘relieved’? 23 Unit 2: Grammar Grammar In this section, you will: ✪ review your knowledge of the main ✪ review your knowledge of the three Revising In this word unit, vocabulary a Here are is you have new helped of forms of sentences. the read to vocabulary you, you to related understanding work sentences out from its to its social media. function (the Where job it that does in meaning. Luis’s email: the main word classes underlined. Some my one classes main classes was sentence) word [1] big parents’ [1] [2] guys front determiner it [2] is specic adjective what the a word or a (plural) [4] preposition on [4] motorbikes drove [5] crazily [6] around noun that modies a noun, usually telling us whether general word ‘guys’ [3] [3] lawn. that were the adds detail to the noun, in this case telling us like name of a person, thing, place or idea a word which tells us about the relationship between two ‘things’, in this case the ‘guys’ and their bikes – they were riding them 1 [5] verb [6] adverb Identify sentence 2 Work tells us tells any underlined a partner words I’m b Unfor tunately, sorr y you I thought c I had d I reminded e It I missed be to silly following questions. or something adjectives was in done the decide which class each of the to. par ty turn on out Saturday as I night. planned – all because ever yone of the at college address and I about told the them par ty. the time. short sentence from the email and then disaster! Match noun 24 which mistake. the a in clever! the a my tell ever yone a to didn’t would forgotten just it Read was state nouns belongs answer It or manner remaining a 3 action the above. with was the us each word in pronoun the sentence to determiner one of the verb following classes. Unit b Think of an adjective c Think of an adverb 4 Copy and sentences the word below. classes Sentence Luis complete a–e are Luis could could the have table Read have the to added added to identify sentences to the the the 2: Grammar sentence. sentence. word carefully, classes as not in all of used. adjective noun adverb verb determiner a preposition Many b Facebook c d e a Many their b c closest is but are there Ever yone e 5 probably many wants social media for keeping in touch with to the most others popular social-media application, too. present themselves positively on the older population use common apps Twitter. Such Copy people and adverbs, sometimes complete adjectives Nearly all of us our misuse this or key sentence verbs to if we terms like adding LOL! appropriate nouns, it. _______________ _______________ lose use media. Increasingly, like regularly friends. Facebook social d people on social media and feel _______________ _______________ or our wi stops working. 25 Unit The 2: Grammar main For your lengths, The types writing, as three Simple actions. and a Luis main They main Compound For It If are you me They say Here, I to to are this I use simple, often a variety of sentence types and compound used at to least express one and complex clear , subject direct (the sentences. thoughts ‘doer’ of the or action) example: [subject] turned contain next haven’t add two just up [verb]. clauses of equally conjunctions or lots of a on used silly these its clause you [rst such weighted as and or ideas. so. or that develop and add social clause] then not like work is [conjuction] series this on linked further detail. [subordinate clause a sentences more media and clause]. Complex own) would of actions contain a dependent For you main or example: [main clause], clause]. its to own, the but main the main clause by the although can their up [second idea, mistake conjunction of me main subordinate ways reminder clear phrases have a to sentence. sense subordinate The to longer makes was day forgiven detail a clauses would. Rewrite the use subordinating a to email. coordinating shouldn’t it the clause of still (which although the are sentences subordinate 6 are For by need his contain people all wish want clause but in types must linked parents may ere will example: took my you verb. of sentence does sentences Hundreds They of use basic sentences, and forms develop should following the these help types you of with sentence your instructions work. in brackets. love taking selfies and I like receiving them. (Turn into two simple sentences.) b The mobile (Turn c We into were single phone a on behind compound the complex whenever, until 26 fell way to stove. We couldn’t reach it. sentence.) my sentence etc.) the brother ’s. joined by a The sat nav conjunction broke. such (Turn as into a after, while, Unit 7 2: Grammar Now read Amir ’s reply to Luis and then answer the questions. To: From: Luis Amir your I am to so see party glad I missed ever yone. better felt so par ty, ill. I was even though shivering it and would I was have been shaking. great But I feel now. a Identify b Write when I your a the different fur ther he is types single, going to of sentences compound see or Amir complex uses. sentence stating Luis. 27 Unit 2: Listening LISTENING from contextual clues when listening. Exploring… W hen we listen talking , we clues help to use to people all us sor ts of understand the meaning. For example, a group about expect favourite team, we might vocabular y spor t example fans talking their spor ts with are if to be score, to do used (for defend, opponent, etc.). However, (such such as as in the fan something a dierent weather), would context a word mean entirely dierent! A In a moment, you are going to hear three people speak a sentence each. e topic is digital technology. Before you listen to what they say, note down ve words or phrases that come into your mind when you think about digital technology (for example screen). Developing Listen Now, You to already W hat … ? W hich … ? Remember in topic the key Look is ‘digital word for or How … ? to Look for listen in technolog y ’. the to do with Look the to, mentions numbers, specific for meaning question something 28 the to How many … ? close questions. question. You For should listen example, if for the begins: ✪ the the know ✪ are skills 2.1. for related question ✪ Audio prepare answers your or explanations percentages of events, etc. outcomes etc. information. context linked ‘mobile that. for statistics, words, with, phone’, the you too. topic ese in know are words question. the answer So, will that if have Unit 2: Comprehension B Listen to Audio 2.1 again and, after each statement, answer the questions. For each question, choose the correct answer – a, b or c. 1 W hich 2 b the lower c the back does at 5,000 c at 10,000 does listening doing c storing 6 to fitness tracker beep? love? Bollywood while songs she is working skills Audio and 2.2, a Petra, shor t and dialogue then questions. did Petra her b Jamila’s c her uncle’s repair uncle’s was her phone? shop repair Jamila Petra’s brand b Petra’s uncle c Petra didn’t much take house a How phone homework songs a W hy to her Jamila W here cracked? beeps your the is steps Jamila b answer phone steps a listen the Marco’s b between 5 of 10,000 Now mobile section at Applying Petra’s places a W hat 4 of three W hen 3 par t a concerned of phone charges have discount a 15 per cent b 60 per cent c 50 per cent shop a a about has lot the cost? expensive of par ts. money. guarantee. did Petra get? C Listen of one asked to further Petra. answer. Use Audio 2.2 question en one ask of it the again and Jamila to a think could friend have to starters/prompts (W hat …, W hich …, W hy … etc.). 29 Unit 2: Punctuation Punctuation In this Basic section, you punctuation marks, question to make sure Look at these two my – revise the marks need For will bir thday I you use etc. use – and of practise full can using stops, have a punctuation basic commas, big impact punctuation. exclamation on meaning. You accurately. examples: got a kitten skateboard and some new clothes. After my smartphone broke my brother gave me his old one. W hat punctuation do you think is missing? In what way does the lack of punctuation make these sentences funny or confusing? Full stops question but not The sat are used marks (?) commas nav to or (,). broke. end sentences. exclamation For We They marks can (!) in be replaced certain by circumstances, example: ended up hopelessly lost. Correct ✔ not Hint: have The sat nav broke, we ended up hopelessly lost. Incorrect Although this as marks come after questions, but not statements questions. For with are the best apps? Correct wondered what the sat nav best apps were? Incorrect (for example marks to are express used to give surprise), to emphasis interrupt to or a to a or order . statement For ‘Take ‘OK, my OK! there laptop I’m was a crash inside!’ going!’ I could also give are used For them to sat nav my of thunder brother and it shouted, poured ‘before it with gets in smartphone a variety of Use It them had a to words has large separate shiny, or items in a list of three of more things. or with with and we ended lost. Questions when. what, You for all the features I need: apps, glossy why, often also who, use for and example: interchangeable screen. or It had a adjectives. glossy, shiny ‘You camera, a new phone, don’t you?’ screen. two how question half-statement For example: screen. Hint: Try not exclamation writing. 30 joined ways. want a a wet!’ marks and into replied. separate voice-control it rain! example: new up conjunction: broke hopelessly half-questions, My ended a begin Use make sentence REMEMBER: Commas We example: up Suddenly, broke. lost. coordinating The command stops: ✘ compound Exclamation separate full ✔ you I to example: hopelessly What correct with The indirect two is ✘ sentences Question it to over-use marks in your Unit 1 Write out and punctuate these sentences have a My phone b W hy c However, d It had lots of pictures of the beach the hotel my family I kept buy it punctuation, buzzing such had an a and cheap some wouldn’t none switch Punctuation correctly (some did incorrect 2: at all). off ? one amazing camera and even the airport. e Eventually Extending In texts of items broke your such can it as completely had to get a new one. skills repor ts, make I or things when clearer making than in notes, a a bullet sentence list of REMEMBER: items ver y For divided long it might make for ‘super ✪ laser-pencil ✪ ejector-seat ✪ invisibility ✪ micro- camera ✪ exploding e bullet words, as Write jungle the 3 commas. the example, sentence for if the seem list was a colon (:) It is before good a list to of have bullet points. clumsy. watch. these, too, can a bullet the to colon of all to the you list paragraph of the happened four and are some above of a basic not overly would include the items sentences items (see opening use what did list when make Remember a Bond: car useful like trek cloak James also Tr y explain spy ’ is and Write Start list trek . list trek . The For example: Gadgets 2 by complicated. take if text to for a report forms whether single the going on a introduce reminder). about of your jungle punctuation trek was to successful. this: not b egin well. As … 31 Unit 2: Reading non-fiction READING In this section, ✪ understand ✪ identify you will: the factual NON-FICTION difference between information in a fact and opinion text. Exploring… It is able ver y to impor tant distinguish Sometimes dicult Read to the two know these are In phones is the is life and facts closely in and education to be opinions. linked that it can be which. from now 2014, in in so which statements T echnology lives. both between so a speech: dominant research around showed that the there world were that it around rules 7 our billion operation. W hich is stated W hich statement fact here? Hint: sounds like a fact but is actually an A fact number , your are accept Tokyo Saj 20 is as is my per pieces true. the of capital brother ’s cent information For of to be a or statement that skills cannot Facts likely measurement, percentage Developing is opinion? that we would usually ‘water is a with form (for of Japan. rst people example: disagreed liquid’). example: of be name. in the sur vey did not own a smar tphone. Opinions from I the believe may way be directly something technolog y is is expressed written. damaging or For young inferred example: people. (O ther people may feel dierently.) or Technolog y is damaging young people. (is is still an opinion, but stated as a fact.) Our amazing phones are available online. meaning of this sentence – that their phones (e basic are available online – is likely to be a fact, but it is their opinion that their phones are ‘amazing ’.) Hint: An opinion assertion challenge 32 that or is an someone disagree could with. Unit 2: Comprehension A Talk decide about which have the the are following facts and which a partner and opinions. I 2 More people are buying smartphones than traditional mobile phones. 3 75 4 Social cent of media our is class the phone with 1 per worst-looking statements do reason in their why the school homework teenagers – it’s a joke! online. are so unhappy. B Now, read this text and answer the questions that follow it. Social-media use growing in India! A recent India Inter net most repor t (IAMAI), users popular Facebook updates. benefit with good 1 W hich Twitter the a There b Users c One is d Working and really 180 update the their get are facts have on the big in users access is to gets or working the to men and countr yside. especially cities. the in ar ticle? urban Facebook activities good students to on sharing ever yone to The profile and communities, stated Internet profiles that access to vir tual of million media. posting access isolated 180 social college expand come popular women just Association the your as impor tant also million most to well of use keeping as not benefit people Mobile cent regularly vitally need and per include following are of India current, women, more 66 media, We can and of it social Inter net that activities jobs. T echnology the urban However, from more in and non-working as by states and sharing social Hint India. Twitter. • look and updates. the media. or 2 W hich of the following are opinions stated in the For at question the scan same or • The IAMAI are ver y happy with the growth in social-media usage. b It is important that not just students and successful men have access. then check – it statement It Places is necessar y e Technolog y to increase access to people cities does have left need not more really access. benefit the isolated communities as what may is a the be text that fact, but says the the one – or not one in most them. scan your nd text. Hint: Applying to words women. wrong outside related stated gures exactly d ‘fact’ article ar ticle? a c key the B1: For the question text to nd B2, the again most skills relevant read it information carefully. and then Remember C Re-read the email on page 22 and then answer the that questions 1 List 2 Find at what below. least two five but facts sentences relating or to phrases what that happened indicate his to some not things actually might be likely, stated Luis. opinion about happened. 33 Unit 2: Writing WRITING Writing In this to inform section, ✪ generate ✪ structure ideas Think W hen mind you is You an ✪ information using write to the you inform, reader are topic must the must giving. text sentences. be key aspect to understand But how clear – is use this keep clearly in the achieved? paragraphs and sentences. should use relevant easy -to-understand Do to an writing structure topic ✪ for your clarity: Your will: about… information ✪ you not confuse persuade – factual is in form. writing this information to about inform with providing writing facts. Exploring… Paragraphs that share Topic A of the not study social sometimes On the to. improved accounts topic [2] fur ther Test your It of ✪ W hich on at and ey 75 than one) or usually the some not more idea. introduce of that number isolated hand, and a sentence. of per the har mful cent being (around depressed sizeable enhanced made the is star t anxiety them introduces provide focus the of topic their feel understanding is the states smaller sentences W hat that paragraph. at repor ted [1] (usually central sentences the has or of able 45 to per when effects respondents keep cent) up to said seeing date they what friends [2] sentence ✪ 34 A felt other [1] of sentences focus are feelings friends. up of come media. repor ted were sets focus always) recent with are common sentences explain (but a main details the to about focus of second, felt Getting the social ‘likes’ themselves. suppor t answering sentence? actually well-being. good the by minority on They paragraph the topic these sentence questions: incomplete media paragraph? their also … Unit Developing It is useful ideas Here into are to your of a ✪ 70 per cent said ✪ 25 per cent felt their ✪ 25 per cent felt it ✪ 60 per cent said ✪ 60 per cent ✪ 45 per cent admitted ✪ 40 per cent didn’t ✪ 20 per cent thought into t two the a or parents writing and organise the points or children to good able to too to how that decide paragraphs. of their media social contact their social how you Here are could some was could children to their social-media much. ‘spy ’ touch with when media private – their they to friends. should when children social-media were this possible social their children’s divide in friends on on accounts acceptable. keep contacting media access too media children time to the social much using know use that spent be to used children’s was they par tner sur vey: inter viewed. their liked three facts your dierent 100 with for paragraphs. results of ideas ✪ Work sets Writing skills generate clear the 2: they check be studying. were for out. dangers. accounts. like diaries. information categories. W hich above? General use Parents of social checking Playing media up games on on by their children children smar tphones Challenge Positive aspects of social-media use Look the Parental use of social media to contact at this social-media look at the paragraphs? A If so, recent Do any of them t parents about their children’s use of ✪ Contacting ✪ The repor t contact 150 100 responded friends also was asked their to an a repor t issue about for about many whether social rebmuN have of Singapore. 125 sur veyed media. Children in 150 your which? repor t ✪ to below. use shows fo social sentences sresu ✪ topic which family students Now graph, media. parents. parents used social 75 50 25 media children. 0 r e t issue of children’s privac y was also sur veyed. w Diaries i The ✪ t ✪ T are private proper ty and no one should look at them. Write Time to write: information one readers Choose any opening one topic paragraph, of the paragraphs sentence adding the at the you have beginning relevant paragraph to inform text of suppor ting selected. it. en Now write complete the the use in about social-media Singapore. general topic Start with a sentence. information. 35 Unit 2: One ONE step further STEP FURTHER Think In this unit, technolog y can Jot is, you on challenge down all social or Use some and fears to on a a of bit these force technolog y the the impact people more deeply questions: for good, developing? of or do do you issues. social you things and Now these think How there media you. about you not? Are social around media imagine about it that you? with of about those think thoughts and worr y Talk and considered, media excite thought life yourself some things have your the a partner ideas regarding you’ve social been media thinking and about to discuss your hopes technolog y. Read You are going modern Best always day Inches W hen e As at I I turn to out my the light. gold, me to my the constant in forget so dependence music You’re a to the world, and voices, dazzle, sing , mirror, a ever- changing Just Full think. and the And picture, thing. you’re or get you at on end, you a of is hear t you gone no and were desired. Mike Gould object, out, sound. box, screws My an grey, plastic once new. has make Yet slow, you’re light face lost, once, somebody Your link , many how sparkle to Find W hose end. bridge old forget In hand, as Play our when Grow night, precious Speak 36 and friends, You explores But of My which close, dearest You’re An poem away, cling With I a friend the You read technolog y. You’re In to wires, ever y thing Unit Talk W hat are is the same with the ‘ best clues? a One step further partner friend’ Do 2: you the poet depend on is talking your about? ‘ best friend’ W hat in the way? Write EI T HER: form of Write technolog y describing came could the along. tr y star ting your could writing like – world It own a poem. tablet before be about the could computer and funny It after or be for about example, modern serious technolog y (or in another technolog y both!). the or You same way, this: You’re....................... OR: last Write 100 an years television, for Reflect In ar ticle this or and could technolog y write about has the changed in telephone, the cars or check you: ✪ thought ✪ practised ✪ prepared ✪ read ✪ listened ✪ answered about different speaking and gave personal to identify revised a shor t spoken questions fact main in a of to a larger non-fiction about testing work conversations talks and text and and kinds clearly email positive between ✪ You how example. unit, a so. about digital your negative with other students group newspaper ar ticle technolog y ability to vocabular y, select and key details, distinguish opinion word classes and the three main types of sentences ✪ revised ✪ learned and ✪ and developed how wrote Check a writing your of basic writing punctuation using topic sentences you for feel go help or an information ar ticle confident back if an text using data and provided poem necessar y, A sk structure use paragraphs practised information ✪ to your you to the need about about technolog y. all section these and things. revise it If carefully. it! 37 Free-time UNIT This 3 unit their In this free unit, write W1 and As free people work. It yourself older impor tant and the activities people do in short learn texts key relevant to details to: convey from clearly a detail, key meaning range using of speech points and and ideas exchange short and information longer appropriate to texts situation audience. time grow is about select communicate S1 My will and identify L1 all time. you identify R1 is activities relax. they to face make W hat do the the you growing best do in use demands of your your free of free education time, to and enjoy Useful quality time? words: relaxation, pastime, pressure time, of stressful, hobby, work, keeping active 3.1 Outdoor activities Check that meaning Time Look at this to of you know these the words. think picture and think about the questions that follow it. Useful words: skatepark, physical, Look up skateboard, balance, tness, any trick, health words you need to 841714_ph2_16 help Add W ho is in the picture? W hat are they doing? W here do you think you talk them to W hat thinking makes and you think this? W hat do you imagine they are they answer you feeling? give W hat outdoor activities do you like to do with your friends? W hat – think you par ticularly you would like about these activities? Is there an outdoor 38 to tr y? is picture. Book. no exercise about the right is topic chance to to help and to practise do your activity a like Word There this the speaking you your the they REMEMBER: are? about partner . ideas clearly to Unit Time Now share picture Take add it on in your page of Look at people the talk par tner. W hen ✪ of the W here ✪ W hat ✪ Have ✪ W hat a is it are there and the right. ey are of young of to the ask pictures one answers, the another make to Take get your it in you a questions. own conversation prompts picture. with going. star ted: turns to describe what is happening taking the ever the any place? people done be this benefits or feeling? activity? of negative thinking doing this activity? effects? hobby an to nd think a picture activity picture, Practise – activities. keep these you home, doing questions on some to one Time At par tner. talk might My a the picture. ✪ 3.3 you you can talking of you enjoy. just about If or you describe the someone can’t the else nd activity. Useful activity. tness, sense To get speaking hobbies in par tner Tr y Choose Are ask par t to your and own. Remember some in to about with and about comment. Use 38 pictures taking Time Now ideas your Sports Thinking talk turns ideas 3.2 to 3: you star ted, think words: health muscles, of and co-ordination, balance, excitement, about: teamwork ✪ when you ✪ where ✪ special ✪ what star ted doing this activity Look up any other words that you you take par t in it need to talk about the pictures, clothing or equipment you need and note them in your Word Book. you Time Give a to class. listeners them to about in a small Make by the the activity. talk three-minute activity the like talk group your of talk speaking face, about and your hobby classmates interesting clearly and developing or for loudly, your or to your looking ideas. 39 Unit 3: Reading non-fiction READING In this section, ✪ read a ✪ learn some ✪ learn what you NON-FICTION will: non-fiction Think useful is text vocabular y meant by on ‘relevant the topic of spor t detail’. about… If you asked a friend to buy the ingredients for a pizza, and she brought home a cookbook about how to make pizzas, you’d berather annoyed. is was not what you asked for, however useful it might be. In the same way, learning how to make your answers relevant is an important skill. Check you answer the question you have been asked. Exploring… Read the sentences Swimming in fact, river, it if is a you costs below and popular swim at nothing hobby. your at then It local answer the doesn’t beach, question. cost or in much a – nearby all. According to the text, why might someone take up swimming? a It keeps Only one you t. answer statements is about Developing b It’s relevant a and swimming , your hobby. c correct. but they It’s e are a cheap other not two relevant pastime. answers to the are tr ue question. skills Read the text carefully, and then answer the questions that follow. Swimming Swimming swim But at it’s a may one person used to popular local want been Michael a great You ever 40 is your to the started take for to take or keep lessons. pushchair at the the It a at pool was nearby and have more greatest cost river, fun medals? much it – in costs with seriously. Olympic three watch for for your This fact, if nothing you at all. friends. is the swimmer story there of has Phelps. about to safer poolside. or doesn’t Michael swimming swimming fit, the American to It in swimming became him fun hobby. beach, way who – – his him Because he to years older be didn’t in of age. sisters the like His mother have water getting than his in his face Unit wet, he back. spent As you backstroke. He in started five days be year a the for at change how on to in seven in 2016, 28 Not he win everyone mental would can however, relaxing want Aged an remains a gold 23 of broke he great good in the stroke, was the and 365 youngest of In total This all the to next world Rio de now year records Janeiro, stands makes him at the time. and extraordinary sportsperson. Most sacrifices. anyone, physical had and setting one. great and hard His talent for of need wrist gold. necessary was his recognised. that one you his record pastime a – on at any workout? people Swimming, level. It’s up A to you. REMEMBER: relevant A Write 1 Find 2 Look a answers word at as these paragraph paragraph swimming 3 in to an 1. 1 Give Comprehension 2000. medals. natural the was Beijing, them learned butterfly trained in Olympian or in sportsperson the make splashabout but the about was session swimmer Olympic have of to – he talent he Olympics more with and 15, medals Olympic approach not an stroke practice Michael gold medals, first splashing Michael’s competitive 2007, four decorated a Sydney and and breaststroke years! eight won the 11, practised events he Olympic most in of missed successful In floating expect, five the time age never determination. went of training competitors T o lot might At years a a 3: Only details include in your answers. questions. that means three ‘ liked reasons why by many people people’. choose activity. Look at paragraph 3. What swimming stroke did Michael learn first? 4 Look at great determination. B 1 paragraphs Write In the answers Beijing 3 and to 4. Give these Olympics, two examples of Michael’s questions. how many world records did Michael break? 2 Copy and complete Michael’s rst facts about Michael noticed ______________________________ in the year 2007 became in the year _______ his whole Phelps won rst aged ____________ Michael the his Phelps. Michael medals in of took In par t table Michael Olympic 3 ability the Olympics swimmer with the aged ____________ most ever career, how many Olympic gold medals has Michael altogether? C Look to become at an the whole Olympic text. Write three qualities that you need champion. 41 Unit 3: Grammar Grammar In this section, you your will: ✪ review ✪ learn when ✪ learn how to use possessive pronouns acting as adjectives ✪ learn how to use possessive pronouns acting as nouns. Think On the to at keep This is and a is swim a at a pronoun over other or pages, me you popular local the swimming’s The I pronouns read hobby. beach, it this: It doesn’t costs cost nothing at much all. – But in it’s fact, a if you great way t. means you use of about… your Swimming if to previous Swimming swim knowledge same popular your it hobby. local great again. nouns. as: was way to used stop keep are your doesn’t swimming costs cost much nothing at – in all. fact, But t. instead Pronouns They Swimming beach, of writing useful writing short the word words becoming swimming that can repetitive stand and over in for boring. Pronouns Pronouns whether object to they of show may the the change are the depending subject sentence. two forms Here of or is each on the a chart Subject Object I me you you he him she her REMEMBER: is with other pronoun. form it it we us they them Use use in the chart the sentences above to help below. you Write choose out the the correct whole of pronoun each to sentence correctly. a I/me b They/Them is run to school, always but go she/her to the prefers g ym in to the c ycle. evenings when he/him/it quiet. c I/me know that he/him will be a good swimmer if he/him practises. d Michael won they/them. 42 many gold medals, and he/him was proud to wear of I or and me wasn’t Jack and a 1 noun word The If another coach lesson. I the use as if there. enjoy gave word noun, or me ignore the the the For I correct other example: swimming. Jack and me Unit e She/her for f the I/me helped Possessive adjectives, of we/us were training canoeing when I/me was on a trip. Possessive parts when Grammar marathon. learned school we/us 3: pronouns pronouns to the show are acting special possession, as adjectives pronouns including for that can be relations used and like friends or body. Pronoun as Pronoun as Possessive REMEMBER: subject object pronoun I me my • The an you you word its he him his she her her it it its we us our there them is words • The and but they’re is Katia my is your Michael On the take This broke Michael to and to wrist. pool same (part you to of means as all only to in the her. there sound their them’. that means (There place’ ‘they the means and are’.) the body) read: at about watch his three older years of sisters age. have His mother swimming used lessons. as: swimming Michael to the at about pool to three watch years of age. Michael’s Michael’s older sisters mother have lessons. possessive to just (relation) swimming started – (possession) pages, the the take swimming The his started him means used sister . previous Michael to football. ‘in it’ their, they’re means example: That have it apostrophe or words same, their to no his ‘belonging For not when your ‘belonging they does apostrophe stop pronouns having to he write and his Michael are over used and to make the writing clear over . 43 Unit 2 3: Grammar Write each out these sentences, using the correct pronoun to ll gap. Hint: a was impor tant for Michael page keep healthy when trained b competition. Cycling pump c makes hard Running is your hear t strong as has when good c ycle for children, a long to way. as have to use all muscles. d Aisha found had when e I did asked wallet 3 Jose at Choose the the bic ycle some if more energ y correct tennis and wheels. won his/her/its first national game. Michael he/she/it had won had they ’re four gone They/Their/They ’re they/their/ 44 it/it’s/its sentences. He/She/It loved of these c e one for My brother won his/her/its last race of the day. that lost word The After days park. b L adies’ the lost a d on exercise. had medals in Rio, they ’re/their/there hoping last gold that game of he/she/it with high they/their/they ’re the season. 43 if back you at need the table on reminding for of the Look to admitted hopes. will win the different pronouns. Unit Possessive The the as term thing a 1 possessive that noun. It This is my This is your Here is not The red The blue Fill is be of tennis carefully. gap may Use is are give is – it is as applies (a his to For thing thing you to acts example: belonging belonging (thing refer pronoun to to belonging me) you) to him) her) (things belonging (things correct to belonging possessive acting as adjectives words in brackets the when possessive (a or to as us) to them) pronoun. nouns help – e missing think REMEMBER: you. never a Louis said that the bicycle was use Possessive pronouns apostrophes. (the one belonging to him) and not (the one belonging to her). b (belonging (the c Grammar nouns emphasis. yours. theirs. the of mine. ours. are also kind belonging with be It It racquet (thing sweatshirts each to water . sweatshirts pronouns This used sandwich. hers. acting pronoun owned. can bottle the and pronouns 3: one to me) painting belonging to you) is is ver y dull but colour ful. We bought a new trampoline for the children when (the one belonging to them) broke because they had misused d (belonging to them) old one. Don’t use (belonging to me) cricket bat – it’s (the one belonging to me). (the one belonging to you) is over there. e The to teacher us) own told yoga us to mats bring as he (the (belonging was ones always having belonging to to lend us him). 45 Unit 3: Listening LISTENING In this section, to a you will: ✪ listen recording ✪ revise ✪ identify some ✪ practise answering some Think Before an you the looking that likely the around that will it) details in an questions is you might that the with people extended in and activities text different make mean are to to be listen can make to and an of formats. be your time If a informed to is its to prepare. consider about. that word carefully time to talked checking used. ver y use taking going questions likely have so talk connected recording , this ideas through you key shor t about… hear vocabular y a vocabular y examination, and of It you the also In topic means understand unfamiliar, context you (the the know words guess. Exploring… e recording is of an employer giving a talk to a group of Useful school words: interview, students. With a par tner, what the ✪ the ✪ whether talk advice is the likely to be employer language, about might impressions, this is likely topic or is likely to be about a par ticular job. (Discuss why these them unlikely.) a You are not tr ying to guess what activity is to help your brain the questions and answers might be focus on what you know about to make Developing Before the to listen out the Make for? sure testing this, shor t you Remember 46 on to Are any thing! skills the page for recording , 47. Are there you there any will any clues to have key the a few words sor t of minutes that you answers to will you the that you are going introduction understand talk you may have to all not to look the the use understood at question A1 carefully read need will and then talk. possible those what answers exact you words. heard. for question e words with in a understand mean – partner your Word don’t know. Use the tond? practise hear ready your listen questions need To you you you A1. question is what discuss and Book make of any – to topic, character sure note you this body give Make the condent, discuss: rst ✪ qualication, nervous, help or to check. a dictionary Unit 3: Comprehension A Read 1 question According probably a your the ask your home e your future listen After you W hat W hy ✪ Did then which the things instructions will the below. inter viewer about? education b your family background d your leisure activities plans introduction answered, phrases follow two town the have ‘ leisure ✪ to and talk , you recent c Now ✪ to 1 did the and think then about speaker use answer the question following that meant 1. questions: ‘education’ and activities’? were you the other remember options to give incorrect? two answers? B Now answer space 1 them. in 2 You down is the Give The one of inter view 5 may the speaker a it’s b you c the If you the the phrase right of the questions recording the be twice, before with a you short speaker uses that means ‘someone b you say able thing be able will how that prove to it you to to is the when better should most you talk not always impor tant to about refer tell the to thing your in tr uth an in the hobbies? inter view. an do. r un know for you a are a marathon. you are computer can computer you tell is … applying show speaker, pastimes employer are the sug gests might you you to because a c rest hear shor t according inter viewer 4 will the determined’? W hat, 3 through between. Write who read do other tr ustwor thy. course, the things, too. programming really good at is all different speaker you sug gests … do. spor ts, too. C Answer 1 According improved 2 W hich for these to by speaker, playing pastime someone police the questions. does who a what team the wants skill speaker to can be spor t? sug gest become a officer? 47 Unit 3: Grammar Grammar In this section, ✪ revise ✪ learn how pages ✪ ✪ to as my friend act as Copy use pronouns relative you adjectives mine. this as adjectives and nouns pronouns. learned to how show your nouns is acting pronouns 43–45 act This 1 will: possessive Possessive On you when That table you one and possession, birthday refer is possessive to for pronouns can: example: present the thing that is owned, for example: yours complete the gaps. Pronoun Pronoun Possessive Possessive as as pronoun pronoun subject I object (adjective) me (noun) REMEMBER: avoid mine your you your him his she her it it we us they them Relative hers its our ours pronouns On page 26 you revised how to make compound sentences using coordinating conjunctions (joining words) such as and and so. You also revised the use of subordinating conjunctions such as although, when and because to join subordinate clauses to one another or to the main clause. Another way Relative of join clauses pronouns, for is by using example who, a relative which and pronoun. that, are a special kind pronoun. Relative you to Look pronouns join concise 48 to at clauses and the help two are used together give to the smoothly. variety sentences start at to your the top description They can sentences. of page 49: of make nouns. your They writing help more Use repetition writing pronouns and more to to make interesting. Unit The swimmer They The In can be this It like who sentence, separate many joined swimmer , swimmer. to won is the many won subordinate a The swimmer came to our school. The The two The employer gave a talk that employer gave a talk which be gold came medals Notice to our describes how the school. the noun commas are used clause. employer can medals, clause. The sentences talk. gold many subordinate gave medals. Grammar this: won who a gold 3: talk joined was with was interesting. a relative pronoun: interesting. or The In this sentence subordinate the You The use doctor , doctor I an a Are a I a describes comma when the it is talk. at It the is a end of people. next You door , use that saved my away. (that or life. which (who to refer refers to to things. the that had run refers to the horse purse which correct or the she had dropped. (which refers to thing) word to ll each gap which. kind tennis, ver y of person likes like Mr to a A ziz , work make to keeps teacher, said with me Snowboarding want spor t fit. careers always e a the you play My I to lived horse the – that called d need challenge? me c not this. refer who up Choose who, to does person) the purse – b a like It animal) picked the 2 – caught – I who interesting. that/which was interesting clause. sentence was is is I should small join a drama group. children laugh. a spor t I really tr y. 49 Unit 3: Reading fiction READING In this section, an you extract FICTION will: ✪ read ✪ learn ✪ practise identifying and selecting relevant detail, key points and ideas. some from useful a fiction vocabular y text about children at play Word A Work box with another your with the and this to on then match the write the right. the words Check words on your and the left answers their of your meanings extract and then answer the questions that follow opponent confusion coveted helper chaos desired ying kites. Children glass, to make them shar p. ey tr y to cut the strings the other kites, of all using the string on their kite. e winner is the owner of the competition it. in powdered kite early winning the last kite ying. runner kite-fighting started enemy assistant in sometimes hold competitions where the strings are covered The tournament with skills In A fghanistan, as in many countries, children enjoy The Meaning the Book . Developing Read partner meanings pair, Word a in tournament the kite Glossary morning flew in the was on sky an the – I old day winter of the remember tradition contest one in and year the Afghanistan. didn’t end hordes It until large daylight. kids. streets The squinting Every up fighter to People filled the had with sky , an gathered kite trying assistant on sidewalks fighters, to – gain in jerking position my case, and and to roofs tugging cut Hassan the – to on cheer their fed the held line. spool reel rules Good when kite field, each who But fierce; ran for he on No rules. Fly your came of kite bulls. kite no And in, fun kite. began those One the year, in his could most when from snapped still one yard, a Cut who it I’d a the opponents. or kite a streets, about neighbourhood it from prize was weight And the cut. an when kid and a That down The once, the climbed kite in a chase shoved he was wind-blown spiralling rooftop. the read his was chased came swar med hands. kite when tree, under take last a Spain coveted the kids until on runners people branch runners, real someone’s the kite, The neighbourhoods those A with a in the kite. fell kite like tour nament. 50 runners hordes from a all. through dropping hands For simple: wasn’t kite other of the spool partly attempt clearly that the pretty tree were drifting roll looking with line. luck. Except or string eyes The pavements their lines, opponent’s who on squinting and of tournament sidewalks outlasted groups people fell a ones pine thir ty runner got past feet. had his him. was cut, the last there’d fallen be kite of absolute a winter chaos. closed to see in more Unit 3: Comprehension B Answer 1 In 2 first an The tournament b c In had stopped had star ted the found it W hat 5 W hich b c on that give had as the it hard to the would see be for tells many means you that kite f lying years. that the kite-f lying … dark. to to in kite word in done best life one kites jobs the to Introduction Introduction that rose. give the two Introduction done daylight’ was sun word sunset. paragraph, were one been ‘outlasted before after first 4 a activity went questions. paragraph, was a 3 the these the by bright the heading that kite for tells you children sky. f lyer ’s this the helper? extract? Afghanistan r unning how to f ly a kite C Answer 1 W hat 2 In a b c 3 They They had to were had writer after were run all to a how determined how high how the T he wr iter kite was the kites children one high boy the line of a bull-runners kite? in Spain? animal. another. fell children would a cut the trees. who were descr ibes wild had like f ly from were when prepared kite as to a to tree. hold the This on to strings push ‘spiralling ’ one is an their were T his of … kites. cut. another down. example off trees. means the … a drifting b falling ver y ver y spinning W hy a pushing of the children after climb tells someone the b c 5 They way questions. a c 4 happened what The these was slowly quickly around there as ‘chaos’ down. to it the ground. fell. when the last kite was cut free? 51 Unit 3: Writing WRITING Writing In this ✪ to section, gather do explain you together will: ideas for a piece of writing that explains how to something ✪ consider ✪ make and how use of to develop paragraphs subordinate structures of clauses in using your details writing and to examples var y the lengths sentences. Exploring… In the us what the rst writer We paragraph happened explains went paper. and cross course, and to We had up leave to Choose an classroom game you enjoyed he and and hours have our hundred glue. friend day thin own feet We’d just read, tournaments. bought the make five and you his every cutting to text kite-ying made tissue string of then their bamboo, shaving string hang your activity when glue, … We’d line played doing at with you were a school, a liked to child, or sibling an or do for outside example activity parent. you the a Hosseini in the in some string, for And go through the skills that you kites bamboo paper … Khaled Earlier dry. Developing 52 to glass the bazaar spars, ground it how spent we feed the of during a in centre of the mixture between detail. and the then, out tells book, yard of the trees, Unit Take it in turns ✪ what ✪ how ✪ where ✪ some Now Use you you Make a and bullet have favourite Time W hen and you three now sentence par tner: others did when you remember points of ‘My 2, your took most par t about it. separately. list Unit the were things You In tell written you you or four a each are of points under paragraph short to the satised headings. each plan heading. for a shor t ar ticle on activity ’ write: learned as basic childhood to for above use topic four with article sentences. paragraphs your topic in Now, your write a topic paragraph sentences, you can plan. write your REMEMBER: have shor t ar ticle. Use your notes to get your ideas, but don’t be used change or improve them. Include some facts and to explain the activity clearly. You could details give in help the reader you’re writing places to (also sh known about from. as he shing , You gives Look facts what give might jargon) boots with spikes. where understand an use again at with how details, and were doing. example some connected and you some of special the how or made he you uses for his a chose - if the conjunctions it for the ordinar y a smooth they and you all have make helpful written sense for the your and that the examples them and through factual and your to activities with and one share your ar ticles about details are clear a childhood a leaet leaet to ✪ explain explain about a hobby or pastime that you enjoy should be it details 100–150 about ✪ what ✪ how to ✪ why you the what costs could the about it. the but have produce school an magazine. include: need you words. could about you start to it if there would be any Include: would do ✪ are why and how overcome you want to you them do it. star t Remember read pastime do, equipment/clothing how Make to or to and a difficulties ✪ writing? now. ✪ is your and another. write: to variety games learn Write like for you to to hobby Research ✪ Time ‘feel’ give tried. article then help check reader. writing to would You Check use relative word, you read and Challenge note technical reader. paragraphs, of made football never W hen you best Choose explaining have words example kite – examples example, technical activity, Khaled where For you each pronouns to that kinds afraid of paragraph Check different sentences to Writing prepared you work the to 3: recommend to You keep your should hobby you ar ticle assume are sure you only include it. relevant that your for the reader person knows who nothing is going at all relevant information that writing and your is and factual clear explaining. 53 Unit 3: One ONE step further STEP FURTHER Think In this unit, activities helpful these throughout is the and are most might why so, people and at in maintain a said stressful be about do the their spor ts, spare physical hobbies time. and and You’ve mental other considered health, now how and life. with sometimes thought others to your Talk It you’ve you partner that time how your the of far examination your you stage of life. With agree. life years a feel school partner, Together, might at consider make under and a list of college why the are this reasons pressure. Read Read this Many leaet, written students really feel exhausted beginning. Food As and Healthy means drink – – Don’t the they students haven’t sick , that saying is. goes: who got It is have time to much just take star ted care better to of college. their take physical action early and on, as is a must many not fruit sweet, meals when you – – limit prevention is better than cure. and zzy food. vegetables drinks you’ ll get junk only full ll of up as And you possible, know and what water that to caeine. on unhealthy chocolate bars and over-hungr y. Exercise Find ways to build exercise into your day. If you can, use a bicycle or walk to college – don’t always use a car, bus or train. And this will save you money, too. Make exercise something they ’ ll help fun. Take new. Find a you make a friend game new and that go you to a enjoy new – spor ts team club games – are learn per fect, as friends! Sleep Take too Be a nap long , aware them 54 and and not that less sleeping now able too lack to pattern. then of – close sleep this to can you a boost of energ y. But not for bedtime. doesn’t concentrate give and just do make well at people their gr umpy studies. – it Have makes a regular mental to drink food skip crisps or for health develop good – until habits they from get the Unit 3: One step further Stress Make and then keep to a routine – plan your day and make sure you have time for relaxation as well as work. Be honest evening. Ask for help academic can be your better if you sta feel don’t with cure’ these ✪ Do ✪ How ✪ W hich ✪ Can a par tner, than Consider Share yourself – sometimes you are realise being that you does pieces you your EI T HER: star t First of add ideas decide – and at also with this of the that all the advice advice extra with your OR: advice you own had your leaet. relate do you other that to you think of is Write of call or years’, set letter to you can’t do as much as you’d like in one day or the the work same that is deadline. being With set. a Speak bit of up – sometimes planning , the burden age and advice students in to your In be at word advice of the for. you you. before advice students ‘How make understand the saying ‘Prevention is ‘prioritise’. offered? your be add friends useful to you? Are any too difficult to follow? list? class. this and unit, check you: ✪ talked about your ✪ talked about spor ts, en ✪ learned some useful words and phrases about free-time activities ✪ read to ✪ learned wish you a non-fiction spoken write about selecting Note leaet your to your for age. help through up now? for the free time and how you use it ✪ You your the own exam title. learned relevant to ✪ listened ✪ read ✪ learned ✪ wrote ✪ did ✪ wrote Check an and about an impor tance details, and a the talk and key given how plan to explain letter you feel go help or a other activities Olympic of that you do swimmer relevance points by and and and and ideas you an who, employer about about free-time wrote the need pronouns pronouns set leaf let to the novel confident back if a about research use relative from to a recognise to some for text extract necessar y, A sk the hobbies practised in written and texts pronouns an you the experience given daughter or together year. writing past ideas it: the being could letter. could all Check understand advice pieces students the are include parents son a school on you someone down has by Reect Write their your help admit partner look any younger students use to questions: agree far to have swamped ever yone Write given you lifted. Talk With with Prioritise. a about and which to some children writing and to possessive that students f lying kites explain magazine information all section me, activities school giving I these and ar ticle and advice. things. revise it If carefully. it! 55 Where UNIT This 4 unit all about neighbourhood In this unit show R2 key learn make and details the appropriate your home, town, region. to: of and vocabulary, text texts, and of ideas and extended purpose length to present ideas message spoken grammatical live coherent overall longer and and clear points, and S2 will and understanding identify L2 home you produce W2 My is I and key involving accurate points some use of live in. in more a a variety complex variety of of short language vocabulary structures. neighbourhood Glossary is unit Look at is the about the photos place on you these call two ‘home’ pages. and ey the all area show you places we local nearby would neighbours call ‘home’, but look how dierent they are! next to, or nickname title for a ere are physical means lots how your 56 ways structure something wherethey How of you long nd feel you with else. family about or to neighbours its walls For or your your describe and many home the roof, not safety will have building (but friends, family and the also lived residents but the all), and be it you word home means inuenced your live the – the often place security. there, of where your by what it relationship village or town. is like, with a to, the particular who your familiar , person residents a people close or live home informal place people building who or live area in Unit 4: Thinking and speaking When we talk about where we live, we also use the word neighbourhood. is means the street you live in (if you live in one), or the immediate area around your home – the local So, roads, shops, parks, elds etc. how 4.1 would My describe your home and neighbourhood? home Time ink you to about ✪ How ✪ W hat ✪ Have some long is think of have it the you like? following lived W ho in lives questions: your there current with home? you? Useful people moved in or out while you have been rooms, ✪ Did you live somewhere else before your current words: family, relatives, there? upstairs, downstairs, home? street Check Time to that meaning Spend turns 4.2 a few to minutes talk My you and thinking ask about questions with these a things friend or and then take it of all neighbourhood Time to think Does it about have a the immediate name? area (sometimes around areas where have you official live. have names, and they are given local ‘nicknames’ as homes be live ✪ many too people many and W here to how long would do you count, you you say or know just have your a by name handful, been in be the point neighbourhood your area? depending on (There where than others) others at which, you ✪ ✪ to leave, begins you think and – ‘I ends? have If you it begins W ho live knows reason the Give a in for not do not want things if to. Use the word my to describe the now ’.) you other opening ideas the and reveal do (Think left talk your and there.) neighbourhood as to to comfortable may the Time be (some you area share to say enough more neighbourhood Now, you lucky or REMEMBER: about Remember what well) they How may bigger press sometimes in think people ✪ the words. group. sensitive ✪ these in REMEMBER: Now, know talk with same a friend area as or your live in, and some vocabulary from of this section. group. friends, do you agree on where ends? the that most (for people example in their because neighbourhood? their family has Is there lived a there longest)? shor t talk – no and neighbourhood. you lived in, that is more If you ne than ve would minutes prefer to – talk describing about a your home previous place too. 57 Unit 4: Reading non-fiction READING In this section, settings and around types you of show understanding of vocabular y to do with about… the world, village, think will buildings. Think All you NON-FICTION people town these or places live city. are? in Look How ver y at dierent the would photos you sor ts on of this describe buildings page. and W here do them? Exploring… e third image Indonesian explaining on this village. what page Read the kampungs is of a ‘kampung ’ extract are below, a traditional which is from a website like. http://www.kidcyber .com.au/indonesia-housing/ While in many villages, Traditional woods reeds, people known kampungs the there have Families work animals. They corn, in sold the at cooking e writer that, they the uses The electricity and to rice, clear vocabular y is are and are half the styles of as from with in Indonesians land built thatched harvest as live farmers. bamboo palm most tools ducks, and people near their bananas, keep the description to on and leaves or kampungs. Most television. such where than work houses They share more and housing plant fruit kampung ver y of and cassava. market the cities, roofs mixture kampung If use a together local oil. is big kampung forests. grow potatoes People in kampungs, Indonesian from but live as crops and chickens, equipment. can sea to buy the tell Any clothes, people us and raise vegetables about pigs and extra as goats. food utensils can their such is and fish. kampungs. To do describe: the construction of the houses in kampungs (what they are made from) what 58 the people who live in them grow or keep as farmers. A kampung Unit 4: Comprehension A Re-read the two bullets ‘bamboo’ or the something is vocabular y when tell (for list bottom as any of nouns page something that 58. they For use tell us about example, to build is houses grow? your can words and the they impor tant general at mentioned Developing It text skills you you. are is example writing means ‘corn’ to focus looking rather on for than what the par ticular specic rather than ‘ vegetable’). B Write 1 W hich answers of the to these following questions. would be accurate statements about kampungs? a They b The are built villagers from sell materials ducks and which goats come to buy from the bamboo big to cities. build the houses. c The d Many e 2 houses The houses villagers Create a below, from are made have grow vocabular y verbs the that from materials electricity and blackberries bank of from nearby forests. televisions. and words taken cabbages. used for each of the categories text: describe the villagers’ work as farmers, for example grow nouns Applying Here is style of that tell your another house what they buy at the market. skills shor t in us extract from the same website, but about another Indonesia. http://www.kidcyber .com.au/indonesia-housing/ The Toraja with are is long built where decorate people bamboo inland the the of South roofs facing gods live. houses Sulawesi that the to build a mountains, Above as rise the symbols beautiful point at which doorways, of each the Toraja horns strength and carved end. of houses These people water houses believe buffalo power . C Based impression need to on of check the details what the the given Toraja description in this people’s extract, houses draw look your like. own You will carefully! 59 Unit 4: Grammar Grammar W hen we several ✪ write ways using to describe, do this. it Two prepositions people ✪ to to is impor tant key ways indicate to add detail. ere are are: the relationships between objects, etc. adding simple adverbial clauses at the front of sentences (fronted adverbials). Prepositions Prepositions They the are relationship sentence. • the the My house way detail, 1 go by Work We of to a live to Write say if but them they 2 Here tell are or as or by, under , pronouns. pronoun and to or They other with. show words in a for example: The gardener came at 11 a.m. work. people, river . It for is example: between two tall buildings. kitchen. which My something my – nd in 2002. as play is and is loud then reader We both nothing chat and Riku’s bedroom me the to friends about is done, or to add further list were music about the lucky very all can a a music and television. prepositions the to get an worked noisy time. I in time some other since, Position over, Way/manner from, common before, flat! The across, of, by city. people complained next (T), to them position to (P) or prepositions: until, on, through, the apartment the do. note in city. parents under make all home my we about (W ). Time 60 or station there out way/manner in Osaka railway above it, noun Monday. the partner paragraph the about the over such nouns example: began things of happens, school. Unfortunately, who on he near is the for thing manner bus moved near a words front example: with following in between house is or for short used storm, bedroom the I the the position Our often describe, when left After • They time They • are generally ago towards, into, onto Unit Write one For I at of least the one sentence prepositions in for the each table of at these the categories bottom of Grammar using page 60. example: have been Fronted ver y happy phrases phrases that when where or sentence • add since the move. adverbials Adverbial tell they often us contain more prepositions. about something a verb happens. or When a They are sentence, placed at usually such the as front REMEMBER: how, of • the on can: variety to The adverbial its own clause the way sentences begin • You • provide For important or additional – that must comma does it not needs work the main follows. always after the use a adverbial. information. example: After we Because Behind 3 4: Copy moved it was the and in, so life improved. (adverbial of time) quiet, we all slept wonderfully! (adverbial of reason) house, we complete grew vegetables these and sentences, fruit. which (adverbial have of place) fronted adverbials. a Because of the rain, we b the porch drinking c After d On e Suddenly, 4 of the the have but entr y of sat on star ted the to year, . sentences I moved the prepositions of Start to a day at e like box house or at using some below. around house house the least new All of a sudden morning Write in a the the new isn’t. rst and In town. area in Looking looked your about adverbials happy side adverbial. I . fronted other nice, last three W herever You down, I Incredibly 5 went a holiday Write sun tea. a on is diar y house. one Use fronted this: We moved in today ... 61 Unit 4: Listening LISTENING In this in a section, you will identify the overall message and key points text. Exploring… W hen ever y or you listen detail of viewpoint. to someone what For saw and describe end you might they example, the speaking , say, actor a but you friend they it is often usually might liked, or tell the dicult recall you the about exciting to remember general a lm message they moments. At Glossary the facilities remember In your overall not that exam, remember they you enjoyed will need all the things they liked, but you would it. to do both: pick out the details, and the viewpoint. A You Follow 1 the Think ✪ can about by a your would river, W hat in would facilities? ✪ W hat W hat it a it A be? big would it ( W hat like? For with a partner. example: location (How room? would f loor, be working – by the sea, in the hills, city?) look of by house. cinema types skill below. dream furnishings car pets, ✪ this instructions W here ✪ practise it A many W hat special librar y?) have? (For wallpaper, made rooms? from? example paint (For furniture, colour?) example wood, bricks, concrete?) ink 2 about Now, your 3 talk you asking The for ‘ W hy ✪ ‘ W hat would to two want these minutes features and designs. about your ‘dream house’ much your par tner to finished, two see how questions should be ones about that what require you have more than remembers told just them. a yes/no example: …?’ …?’ ask questions that have more than one response: example: ‘ W hat room Were special and a they dream 62 have them ✪ possible, for one questions answer, If for you friend. W hen by why rooms marble was I have?’ (where the answer was ‘a cinema bathroom’). listening? house would Or like? did they only get a general idea of what your life better features that make Unit Developing You are now travelled his Listen In a for to 4.1 once. if you – see you ✪ balcony what Applying – be will see are listen your questions a is It dierent three you is a dialogue. place. He is on A boy the has phone to in. questions. locate the In each correct case, listen information. out For was: the for looking for recording. staying given from is a ver y he looking Farel to help question Farel ✪ will that the what the to Audio ✪ Read home place can – listen the words example, W hat his to Comprehension skills about moment, key the going from father your 4: this balcony? a ‘thing ’ or the an key words would be: event at word about the house. skills below. en listen to Audio 4.1 again and answer questions. B Answer 1 W hy 2 W hat he 3 is the these area details mentions W hy is Farel questions. so cold? about about the Give house two reasons. does Farel talk about? Give two things it. looking for ward to going to Vienna? Give two reasons. C inking the big gest about the dierence text Farel as a whole, notices what about life would in the you say is mountains? 63 Unit 4: Vocabulary Vocabulary It is impor tant texts, root but and one words a key or one to be way the is precise of doing stems of through and this add is words. the use detail, to develop is of for can your be prexes example descriptive vocabular y done and in in a range around of ways, suxes. Prexes A prex word. in a group four of most letters Meaning in-, not im-, that common Prex ir-, 1 is The are placed groups of before prexes E xamples injustice, il- irregular, in (stem unnecessar y, re- again review, dis- not, Look at these these words, words. write their your in bold) unclear disloyal knowledge meanings a reappear disappear, Using word of are: illegal not of stem impractical, un- opposite the English of the stem words Hint: down. If you synonym similar impolite unfashionable reset rediscover disallow and prexes I think your to it complete the is home can you can e some Write you 64 would time spend .....arrange Many 3 impor tant to the say freshen down think at what the to .....new time. lots of It the money, or home the up top of – but do I the walls. .....agree: if it! page the means, indicates. of you .....paint Can prex the be but prexes. word look may .....necessar y, your short to adding words. furniture it’s paragraph other paragraph, underlined from .....possible this you 65 contains locate and them? also what word meaning) saying word Copy think of that – a has rather a than distrust just 2 (a can appropriate – ‘not’ then and use it. then the Unit If we could update all decrease the environment. our Some other anti- we you need do will meaning (against) auto- (self ) down- extra- inter- (reduce (more or lower) than) (between) (in the middle trac in engines, children prexes and the diesel Also, pre-school Prex mid- old of ) our it more not nd neighbourhood, would make subways face fumes useful or a they Vocabulary and much healthier under passes when 4: go so the that park . are: E xample Prex antiseptic mis- autobiography non- downgrade semi- extraordinar y super- inter view tele- midnight trans- & meaning (wrong , E xample incorrect) (not) non-prot (half ) semi- circle (above, (at a misspelled beyond) distance) superstar television (across) translate Sufxes A sufx The is most Some group of common other letters sufx common that turns sufxes are placed singular after nouns the into Meaning E xamples -ing , present looking -ion, -tion, -ation, par ticiple, and past of verb a act, of a (s word. and es). are: Sux -ed stem plurals tense forms racing (race) looked, process (look), raced description, suspension ition -ly added to an adjective sadly, angrily Spelling to make an Adding -ment action, process agreement, government added to There -ful, are -ic, many -ity/ty, to make others, -ive, an a kindness, shop example: -itive, -less, -able, -ous, -ible, -ious Add suxes to the root words on the -al/-ial, -en, -er , lie -est, ➜ You may be able to think of right several to make word. spelling of (Be careful the root – you word may of the root example: ➜ shopped lying new words sometimes need to ➜ hungrily new for tire ction respect each adapt root for etc. large words. sometimes spelling slightly, hungry 4 sufx the happiness noun for -ative, adjective a changes word -ness hints adverb change hope help compete the slightly.) 65 Unit 4: Reading non-fiction READING NON-FICTION Glossary In this section, you will: deforestation ✪ show ✪ explore understanding the pur pose of of vocabular y a text and in its a more key complex trees text or chopping down forests ideas. endangered in danger of dying out Think about… landlocked W hat as is it living like in a to live on a tropical landlocked island? countr y? W hat Do you might think be the it is the having same advantages no surrounded by land, coastline and sedate calm or quiet disadvantages? Exploring… You are what going the more to read pur pose than Have one of has of 17,508 don’t the let that globe, thriving of A visit most is and to on If beasts through and birds perfect. and is considered diving. 90 that of some blown text one think may about have rst). visiting largest of most in wildlife. even by the With group a we – but on bustling, as can – scenery languages Dutch what or world beautiful different and away archipelago, country the many – it, should! spellbinding and read the main populated English you For the chance example, only and per our who cent third 500 the left; could of all largest deforestation It do more It is one and also your word not to see some Sumatran the our spoken well as offer. although other the – world’s though dragon – it a wonder ful orang-utans island, of tiger Komodo forget the and of over If as the the last we come you, pulse to in the they , world too, can are activities. In of in that the paradises waters Bali fits see for the then case, Gods’ on you perhaps the due earth. which fascinating Indonesians and racing, visit. ‘Island 20,000 that’s interest, it, your place crystal-clear has for set sedate known culture-vultures. Whatever 66 a beaches, our the you life is take of be give lizard; Bali for for world’s is As mind you Jakarta, perhaps Nearly prefer or There you’ll will with would long out most Indonesian, Borneo, endangered Beach the variety creatures. great orang-utans? found is fourth capital, Indonesia amazing frightening look in thought and huge (Bear not, off. Indonesia. wildlife endangered be a dialects, the If the you Bahasa local Spot put modern including lots also is. but ever islands, It’s about text pur pose, you islands. text the Indonesia? It a It temples to has can its of beauty, exquisite go and you island surfing palaces, bill. have the yourself! answer. But don’t set your pulse you excited racing make Unit Developing In order look be at to work 1 out language positive A your or Look at the clues, these the pur pose such – or as of the the use text, of somewhere it can be adjectives. in a good ese idea can to often between. questions. adjectives in the box on the right. Decide where you pleasant would place them along the line attractive ugly below: pretty ver y Comprehension skills negative Answer 4: positive ver y plain beautiful negative hideous 2 Now a 3 look full Look of at on 5 paragraphs describing what purpose of to inform b to persuade to How other you than Extending e text phrases uses that meanings an your of used on to to is that means: magical. 3. of read, adjective Find a fur ther five positive Indonesia. what the would you correct think answer, the a, b main or c. Indonesia do more visit the to save the wildlife Indonesia pur pose? Tr y to give at least one reason adjectives. skills number are than this use and Choose about readers the a is? readers tell 2 aspects have text readers persuade can you the a c Find b through Based 1. life adjectives 4 paragraph of in rst idioms English to make which its may point. have ese slightly are typical dierent appearance. B Work with a partner to answer these questions. 1 What do you think the idiomatic phrase ‘you’ll be blown away ’ means? 2 W hat phrase in 3 W hat do think you paragraph paragraph the 3 means phrase ‘suits per fectly ’? ‘culture-vultures’ means in Hint: 3? Think greedily Applying your about devouring vultures their food. skills C Now, down W hen re-read what you the have the main whole point nished, text. or For focus complete of the each it paragraph, write is. following sentences: The overall purpose of the text is to … However, it also … 67 Unit 4: Writing WRITING Writing In this length to section, to you be you come to those may produce points, describe pictures have provided. will key clear details and and coherent text of extended ideas. about… want Capturing But you present Think W hen describe help en, in in your a place, words your task pictures is exam will be the – to come secret for to into good example, use it to your description. the make mind. picture your might description alive. Exploring… W hat ✪ is Be good description? specic: Indonesia? houses ✪ and how You can You can smell. them they even I caught the also cool, go as things ar ticle detail ‘palm to about about ‘plants’, fur ther use will the not [touch] by palm the remember the ‘reeds’. you are: kampungs materials leaves’, unless adding leaves’, senses: be when enticing soft key then from in which Tr y not add what to the use they are, look. mind the such ‘long , wavy You in was the constructed: words example: ✪ remember ere were general e able sand of ‘thick , tough sight, to use describing aroma appropriate of places. [smell] the sound, all of a all touch the time, and but keep example: barbecue golden for reeds’. taste, them For adjectives, [sight] as I strolled beach along … A Write 1 Copy fill a and the complete Enjoy sentences, using appropriate of the moved the any a lion b a jeweller y sensor y words or phrases sleeping onions steadily icebergs. following: a the trees. ship list along the The each 68 these questions. walk between Quickly c these a between 2 to gaps. path b answers box cooking on a market stall. for adjectives to Unit Developing A slightly use or A more imager y – simile or e is as. old when For lion way of pictures and in e which sea is a describing often things created by is to similes also is the a say greedy your to work you will a one tatty one thing to another using did that is sack is under stronger another. gobbling up tree. than For the the a simile, example: sand. skills make sure not on help old thing monster sentences, these like comparison you need detailed compare example: Extending You you looked metaphor of skills dicult word Writing metaphors like A your 4: a list pages you you add of develop shor t, 60–61 detail on to your descriptions unconnected prepositions what you ideas. and and write Look full, again adverbials. at Both write. B Answer 1 Copy and The thin b The wind c questions. complete a the 2 these man is these towered simile over and us metaphor like descriptions. a . a/an swooping through valleys. The moon Identify the shone brightly prepositions like and a . fronted adverbials in the following paragraph. Under day, the icy sharks scattered knew of in the Applying Look at this water, the patrolled the it, sand, ship’s your image shipwrecked diving but no boat through one saw the lay on the seabed. port-holes. them. Above Gold the Every coins surface, lay no one existence. skills of an Indonesian temple. C Write can see. a paragraph Follow ✪ Start with ✪ Then add ✪ Add a the a final describes Use a these sentence second if sentences describing sentence sentence, and, three describing what you steps: something senses of the which perhaps whole focuses starting scene. on with one an detail. adverbial that else. you can, at least one simile or metaphor. 69 Unit 4: One ONE step further STEP FURTHER Think In this what unit, it other is you like, people. about these have as thought well Now as you issues. ideas can Jot about about the challenge down some place your area yourself thoughts you or to live: think on your region, these a home and bit and those more of deeply questions: ✪ Do you think it is good to remain in the same place for most of your life? ✪ Are ✪ Where would you choose to live if you could be anywhere in the world? there Talk advantages with a of not having a fixed place to live or call home? partner With a partner, talk about some of the ideas you’ve been thinking about. Read You are going growing up Ever yone have We my live a the the hob, my if I it – ready am her make to quite a oldest child our in, on we to crowd. top twin of is food seem both to to get to girls), is a boy of from so describes park at eir black our kettle to or be the own younger aunt live is and – in seem family six the to of us next miss to I It is a who uncle live always away too, the on so radio, cousins pretend where bedroom I’d – to like but ‘our ’ brothers. (six for of (four supper, the – I and ere despite or table them boys street. – is young around out and people open aliens. aunt’s sitting is stage my it. and door listen my of whistling my even my family end aunt door isn’t to big usually My and to – front front open getting go the anywhere friends. a sure. it family always a pretending I’m who not homework ever yone my a crash either my families! or come house. do me, one W hen I which to with Equally, tr uth ere ’s and in am usually honest, the grandparents in road tr ying with us. I road sometimes see, it Yet, neighbours there being share lucky tumbledown will You the enough our room dive am by. my day and I tea-making. I’m I close uses are pop come mention quite if as it me tree-lined large, door ever y parents), 70 in space. family told piece place. for will but bedroom, Almost a you descriptive living one up in if boys) own always no bedroom (two like us and even so a par ticular pleasant, walk opposite open a read relatives in or in has cul-de-sac drive to is we forgot my never being the Unit And if you are at shouts loudest a moment quiet headphones me it’s e rude truth older I’ ll point, for now. I is, and I dierent that at you for just of our condence, family; one! to there’s Recently music at a peace and noisy at the a week’s It’s then no I’ve forget point taken table, to though quiet. time. of But the that holiday not cousins my and this some homes. countr y. no it. further W hoever waiting for wearing my step my father tells that will I I’m sure know family time will away, suddenly on but a appear at is I get way own far while some out, long my it I’m that move seems camping far when too, in o a enough am tent. partner writer like sympathy life of up own outside any bit fondness booked the the the a grow their with have grateful for with will sure doesn’t lacking in isn’t listening yearn peace or One anti-social. have be quiet heard there back have Talk Do I par t can sitting W hat and ever yone married – and look all gets 4: he about for his him, or home-life do you at the think he moment? should be has? Write EI T HER: it (what OR: about happened, Write explain more Write an why than a who ar ticle home a in can building busy was family there which mean that event and you felt about etc.). you much Reect and check people In live how this unit, you: in. ✪ thought about ✪ practised ✪ prepared ✪ read ✪ listened to a spoken text about a boy visiting a ver y cold countr y ✪ answered asking and website identify revised ✪ learned and gave and questions correct to talks uses and of and questions to a larger about locations in conversations group Indonesia ability vocabular y, to and select key details, distinguish information adverbials, a home your incorrect write of ar ticles testing prepositions, how kinds answering shor t print par ticular between ✪ different prefixes descriptive text and using suffixes similes and metaphors ✪ wrote Check about you necessar y, A sk for feel go help a family back if event confident you to the need or what about all section home these and means. things. revise it If carefully. it! 71 Social UNIT This 5 we unit live, help In this R3 collate, at ourselves these two as will clear accurate the longer and and and issues and fortunate learn details the health, less organise identify and about understanding points, make L2 Look you produce key Helping such unit, show W3 all others R2 W2 is issues of overall than vocabulary, present coherent spoken also affect how we how can ourselves. to: and use that of ideas relevant text of and purpose detail extended length to present ideas vocabulary message texts, and and key involving grammatical points some in more a structures variety complex of short language. others photos. Keeping ourselves t and healthy is important. Some people like to exercise or play sports. Some are very careful about what they eat and drink. But not everyone can avoid illness or hardship. We all want to help others, and lots of people do so through charity work and volunteering Glossary charity 5.1 Keeping people healthy work who are volunteering Time Look at the ✪ W hat ✪ W here is to think photo the on free the woman left above doing? and think about these time she doing the Have you ever been on 72 was it like? If up your others W hy? words: a r unning machine or similar jogging, equipment? energy, W hat need giving help helps gym, sport, activity? active, ✪ in that questions. Useful is to work not, would you like to tr y one out? pace machine, sweat, Unit Time Spend page or few minutes 72 and then Fun Time right here. to at people ink about you might Have to? 5.3 take it second are the in about turns you picture running too following think there to the talk questions and ask at the bottom questions with a of friend they are – on page and 72 they and look the like pictures they ’re on the enjoying it! questions: r unning just to keep fit? W hat other reasons be? ever done something like this? If not, would you like W hy? Time Share thinking think the ese ✪ speaking runs look Do and group. Now, ✪ Thinking talk a small 5.2 to 5: your to talk ideas with your Volunteering Time to par tner and or group. charity work think Glossary ink about the following questions: sponsors ✪ Have you ever taken par t in a ‘fun r un’ to raise money for charity? money such If so, ✪ How ✪ Have who did a you in one, W hat you raise money? to other – you it for? W here Did activities exercise or you for some did do it it for ve donate your goal, kilometres happen? by charity? other run who achieve getting If event so, or sponsors? what? Did they experience? How talk about would it as people you after wards? talk event talk done feel shor t charity was physical Time Give what you involve did or if no more have an than been event one involved you or two in. would If like minutes you to – haven’t do. ( W ho describing been any involved would it be for? involve?) 73 Unit 5: Reading non-fiction READING In this its section, main its you of learn how to identify the pur pose of a text and about… read pur pose range will points. Think W hen you NON-FICTION – a text, what ways, ✪ selecting ✪ examining for the example, e information can main at points the your of understanding the writer was. if You you can consider do this in a through: par ticular look help intention example the For it the made words leaet on and the phrases the writer has used. right. Make what the cause given is. But in the the leaet words includes and the phrases sale, that when tell us it the is, and pur pose charity are: great fun money ‘Make sure you come along …’, ‘It’ll be great fun …’ and sure cake 1 Based W hich on of this, the answer following do the you following think is the for question. pur pose of the text? to persuade people how tasty the cakes are and how clever the cook is b to inform c to persuade d none of the that people to wheelchair come to ramps the sale are and going help to be raise built money above Exploring… Often about celebrities Soccer charity, of the Unicef. text help Aid, As might to which you promote comes do so, a par ticular from the consider cause. website what the of Read the this text children’s pur pose (or pur poses) be. https://www.unicef.org.uk/press-releases/soccer-aid-raises-record-amount-unicefs-work-… Unicef UK can exclusively today ITV, life-saving work Soccer 2016 and Aid was legends to play the 74 on for come an place live together enthralling world’s leading raised children. took broadcast announce has on for at a packed The the out match tenth of children’s Soccer Aid 2016, record-breaking broadcast £6.6 million for its … ITV. game that a Old saw Trafford celebrities anniversary football whilst organisation. of the raising … a come on you will worthy along to our Saturday. It’ll help cause – us to be raise build ‘a worthy cause’. a people sale and wheelchair A you on 5th and June star-studded vital 2016 football funds for event Unicef, ramps around the school. Unit Robbie “We Williams, said we Unicef wanted to UK Ambassador smash our and co-founder fundraising record of for Soccer Unicef Aid and 5: Comprehension said: we did Glossary it! Thank you so much to everyone who came to the match or donated on enthralling the night; you ten years since can help could keep only helped make Soccer even dream Aid more of it the biggest began we’ve children when Soccer safe. Aid and best raised That’s began £24 Soccer million incredible all Aid those so for and years far . In Unicef so they something we ITV a UK-based Sheen, Unicef UK Ambassador and Rest of the World “What a match! I admit I was disappointed England snatched back from Rest of the World this year , but Soccer Aid than football. Thanks to the generosity of the channel the the UK trophy much more Old to Trafford raised more money raised through Soccer Aid 2016 will and Zimbabwe, the world them nutrition with from 1 Write Look at sug gest 2 3 your ver y about Williams W hat positive W hat picture The final Can you one fact one adjective the Copy children’s lives.” help the women well vaccines these and Unicef to United as and and children providing clean Fund in children water , Nations improve and all over protecting abuse. questions. sentence. work they about your and purpose from as English Unicef can create tells does the adjective ‘ life-saving ’ does? you of the W hat identify the in football reader more the second paragraph? match? about Unicef ’s work. identify: b C to paragraph a Applying food, adjectives do million an skills first the 1.2 Ethiopia, exploitation answers the over and life-saving violence, Developing B for Myanmar Manchester star Children’s health actor than Unicef The Welsh government pop ever and really will help Unicef make a difference a United’s football stadium Robbie matching donations pound for pound, this year’s event Sheen captain added: is about so public and television ago.” Michael Michael fascinating the of children that helped describes by how Unicef important the work is? skills complete the the article. following Add at paragraph least one to explain language example text. The purpose of the article is to inform readers about a charity football match, but also to persuade them that Unicef is ____________________________________________. This can be seen from the use of phrases such as _________________________________________________ and _________________________________________________. 75 Unit 5: Grammar Grammar In this section, ✪ revise ✪ learn Word In word I 1 the Unit 1 you and Can I you than met recall Jiao a that by – the these indicate gate in to the and different types an the of action other them The to the bright subject make verb, [subject] many comes but, subject the are But man they run in can often object in sentences. word word or a classes has a or groups different in function. state: word all (in classes some were? cases Here used is a more park and we then set off for our run, sun. in sense, it equally explains sentences only needs one importantly, who or it what of these must does also the word have action. something the is stated like this, the subject sentence. names, blue also as would felt of [verb]. pronouns or noun phrases. For example: jogged. the [verb W hich where front [pronoun] The jogged cases at Subjects 76 subject example: Jiao 2 of contains the the subject. To about what the slowly sentence classes He speech’) healthy. Identifying In the of once): jogging For of each verbs feel sentence a use learned how example, For (‘par ts classes swim. I will: classes about English For you be top verbs. subject] be [noun the is For phrase] example: exhilarating! subject in the following examples? a Talia b To c She made her mind up then and there to start swimming regularly. do incredibly jogged. more unhealthy. exercise would be ideal. Unit Understanding Another acts as This in is the In important the the often about take She the sentences thing this or is the person the subject, the of of word who or phrase that ‘receives’ the action be if it the For [object]. water because ‘drinking’, you is order that one). slice is action reason, say, just water would this to the object the turned often of not said many object it is this be a thing it. around that – English sentences can the doing is noun ‘The is an subject, phrase example: apple. verb paragraph. the beaten each and There object are some in these other sentences words used in too, so bottle Another above clause. of me Exhausted, include However , passed of as the In it bottle SVO of I fell onto the soft, lush grass. direct lots of objects – sentences there is include only one several not this of (plus water . thing this is writing the the bottle is me ? object, way the water about shows line. me. example: passed indirect 4 the For what This the remember not examples in objects. Priya is juicy crossed object But object care. had Priya But the For That words, same funny Priya.’ object. loved The ‘receiving’ how drank Identify All – language. Priya as the (several the example: above, Think the For sentence verb, 3 described [verb] water of many drank drunk She of [subject] being SVO part role Grammar object. sentence. Priya the 5: being case, the we main sentence water to indirect passed call this thing so is the second direct object ‘receiving’ the object. the action. is: me. object) sequence more clearly. Can you identify the direct and indirect objects here? Write the sentences out, underlining the direct objects and circling the indirect objects. a ‘ You b I c ‘e gave Time 5 gave her me a school to no sad will warning!’ look. give you the athletics prize.’ write Write a paragraph about a race – for example a school sports day race or just a race between friends. Include at least one short sentence that uses the SVO sequence and a longer one that includes an indirect object too. 77 Unit 5: Listening LISTENING In this and section, longer you texts will identify related to the charity key and points and voluntar y pur pose of shor t work. Exploring… You have types already and lengths. information, abstract had but points some e you or practice easier will deal ones also with in of listening these encounter less to deal with listening obvious texts of dierent mostly texts Glossary factual that have abstract more feelings of subjects. to ink about ink about: ✪ ✪ ✪ charity the actual the pur pose the people the work the challenges you do it? was, who talk work to them told for W hy? your the one when do of what it took or par tner. heard happened, about who or was taken par t involved, Tell ✪ W hat me How my two did I seen, or objects touched to that etc.) what place benefited they from felt? charity and event – could listen minutes W hen you questions facts say about have about the charity nished, what you ask have about about the the charity people event who I took described. par t or who REMEMBER: key would own money Listen now for to a a to factual going to charity. moment, more event? your Audio In describe confident Developing are you charity ner vous, 78 things opposite relates in. benefited? You which thoughts, them. ✪ ✪ be – to (the not? talk two a have who think running to following you you – par t W hy to that work took how Time Now, work charity – can think ideas ‘concrete’ physical Time relating or 5.1 you about did I r unning sound skills One to of two the audio speakers recordings appears that in concern both raising recordings. once. will ideas. feelings example, uninterested? listen information abstract or my For be given from ve the questions. telephone Some call, and of these some will will relate relate to words Listen in the out for the questions. Unit Applying Listen A 1 to Audio Answer W hat a, 2 b is or It b ere c All Give is is a on a the hard problem Wong then answer the questions play park? are surface with Choose the correct and one of one the of the swings to give money to star t to the park does Henri talk does Henri Choose mean the when correct he says the ere are no green spaces for children to play. c e jungle is invading the city. d e trees are made of concrete. He Now e help to help is building She to Audio given the paint 5.2. city is a ‘concrete en copy and complete the gaps below. swing by who had some left over . with too his of big the for new him brother the boating alone has so lake all promised he will be able to do is to take with the the lake. Saira help works their Her paint given However, Name: Give Arif job Job: to painting Name: about? Felipe was Job: listen information to after with? answer. It’s an exciting place to live and work. Job: broken. examples. b Name: is swings. a the answer, broken. reluctant improvements W hat C below. examples. jungle’? in and questions. with swings Ms two three B again, these built the is W hat skills 5.1 wrong Comprehension c. a W hy 3 your 5: with in new a top-selling parents the will slide who have promised to give her slide. use their to deliver it. 79 Unit 5: Vocabulary Vocabulary In this and section, how they Think L anguages even you can will be build used in your vocabular y by learning about idioms writing. about… are not millennia. xed, Par t of but evolve over many what makes studying decades, language centuries so and interesting REMEMBER: is the par ticular ways people use it. You can probably think of phrases strange who to or are you funny not they phrases familiar seem that with people your per fectly often language use may in not your language. understand People them, but Idioms key element language in Unit Often, or Saj: Jo: On idioms at No, I the to terms use are short you on still feel mend is your as if the do with so it As health and Sometimes be is too will speaking have come and writing across a these briey in work the difcult to to that be they taken use comparisons literally. For example, that with but to is out to means xing it are an an with the better’. object, doesn’t pleasant (It but doesn’t when have you are ill to are of the many important idiom In the how be have anything caught in bad literally to weather , meaning.) some there helps. guess (It idiomatic that what ‘feeling broken ‘broken’!) isn’t its such do a ‘unwell’. living mind it weather . slightly context something means not yet? means clue because you is healthy bearing do do wet, a This are the idiom weather give mend to body getting does perhaps this You dialogue: an it How understanding, which under literally worth of idioms. gurative. the anything is of situations this Are Under 80 in the 4. refer look is focuses idioms part of for this related our unit, to it is health – lives. means? example the person meanings of the above, is I still feeling, idioms. so feel it tells would us not in are English typical that slightly different than on appearance. are normal! used have rst commonly ideas A Idioms several in a vivid used way. to may meanings They express Unit 1 Can you work following agree After had my the no see a a as illness, so he end are reading at of some about all. It – I It gave more me a still out – had as lost days sor ts, picked felt with although of month’s I I several but I’d them a in the friend and case. down. me idioms up as a of lot I of get didn’t weight, back feel thought some course fit to I so a sor t of on quite I’d and as better tropical medicine. For tunately, fiddle. or you might healthy living. nd useful when writing or REMEMBER: clues 2 Tr y to work out the meaning of the final two idioms to help meaning. before Idiom bad 1, out work For out example, in look of at the sorts. It wording says Meaning although shape in a poor physical unwell condition this, back contextual you table. question in Use in the the Vocabulary skills idioms health run out course, your Discuss work was underlined each took to tur ned the in really back before Developing Here was went doctor. the I the mean? denition trip, I what account energy feet. unwell at on out 5: into shape I as do didn’t feel before … you think . out quite as Based of on sorts If you need to get ‘back into shape’, it means means you need to do more exercise (for example extremely something less unwell? Or worrying? to lose weight, build muscles up etc.) ready up to and drop exhausted about – but such as being back to your can worn be out normal used by self a in situations family having par ty! been unwell feel on take 3 a top turn Write of the for the world the worse opening you describe You could how start paragraph you like feel of after a a letter really to a long friend in shopping which trip. this: Hi ________________ I’m writing to explain why I haven’t been in touch. You see, I haven’t been well! It all started when … 81 Unit 5: Reading non-fiction READING In this section, ✪ show ✪ organise it do busy lives vocabular y from that and text ideas for a in a more par ticular complex text pur pose. about… think pictures and of information you creates outside will: understanding Think W hat you NON-FICTION in living and of when your an mind active deciding you hear of life? what to the fresh But words food, how spend ‘healthy or perhaps realistic money living ’? on is spending that? can be Perhaps a time Ever yone real lives challenge! Exploring… Now read spending this a Hints One that we we conditions checking you grape meals’. know well to idea. as you plan you can What use are small shown are the not the take part of way . film, suggest a If a healthy is you food may simple can life without a you it is we well could simply can you. For develop example, brand of white doughnuts? of that or if prevent consumption that food microwave often full a advance easy cities your best stairs! or for By you well-known already seem planning walk buy, bad four and potentially disease. planning in example, salt, of have seems for each or has been like a preservatives menu on ‘ready the day make as week. or If night, larger meals. in the the by a For and you or life! lives are eat make of use the oven them several are for an to of as busy meals’ going one lift, going into This so is eat. and what good sugar such we sugar hear t of serving health avoid that walking to live shape, and are much fresh what much content ‘ready for is decay have are re-use changes that about you but can healthy better foods pop can a too single as exercise? countryside, in affecting up to about one quickly what quantities which people You you health far sugar However, salt. of dental or that aspect how for keep contains Many prepared good as salt about juice Another aspect consume such awareness tips would the about money. and down did of impor tant known cut ar ticle lot to or if life more forms Or of and live in lovely areas. active. your your a so bus friends taking However , Research exercise, shorten meet cycle you built-up next ride for a healthy there has time by you walking pizza or Glossary consumption of the things above costs a lot of time or money. But they slow break-down do preservatives take commitment. However, once you make these small 82 will see the benefits. chemicals that changes, prevent you or picnic. decay None eating drinking food from going bad Unit Developing W hen we we need are to your tr ying 5: Comprehension skills to decide distinguish what between the main key and ideas are in suppor ting a paragraph, information. A Answer correct 1 answer, W hich first 2 of the a we b dental c white best c healthy d cutting and B 1 down phrases done for for or statements Answer at Now, sugar 2, choose the best sums up the sums and salt disease contains a each. up as much the sugar content of as four the doughnuts second paragraph? for. select For would first identify and salt four th Make or sure paragraphs. you other or reuse example, healthier practical and focus on Write the your main own idea and not links. skills these the sugar evidence you it above contain much heart third your need tips on the suppor ting Look 2 and living information have 1 planning Extending ‘key questions salt re-read you and these of subheadings of For c. too juice meal Now, far decay b what or grape sugar e b following consume a the a, questions. paragraph? W hich 3 these life’. not texts Just writing ver y you had out the much to depends produce main ideas a on leaet as you work. questions. paragraph advice and from imagine note on again. what down W hat the the sentence reader practical or should tips in sentences do? the remaining paragraphs. Time to write: leaet C Create the tips You nd could on your from the own illustrate the leaet article your plus called any leaet ‘ Tips of your with for healthy own you drawings or living ’. can think pictures Use of. you internet. 83 Unit 5: Writing WRITING Writing In this to persuade section, you will: ✪ learn about ✪ write persuasive Think positive and negative vocabular y texts. about… Can you think of any texts you have seen or heard in the last 24 hours that tried to persuade you to do or buy something? Where was the text (for example on a computer or television screen, in a magazine or on a billboard)? What ‘thing’ or idea was being promoted? Exploring… Writers text use about lots of healthy ways to living persuade on page readers 82, to evidence act. is Sometimes, used to as persuade in the the Glossary reader. On other occasions, the writer selects par ticular vocabular y to foul make points that have an emotional impact. For (powerful disgusting menace Worried Join of our the your foul ‘Foul’ nal is one sentence. Developing your campaign menace local to rid the pollution. to put suffocating dirty (strong noun) threat health? city Write a or rid to stop smoke or (powerful make verb) throw disappear to and diesel. adjective W hat your of children’s councillor factories, deadly A about adjective) example: two the other writer uses power ful to make adjectives a point are in the used? skills As you can see, the power or emotional strength of certain words is designed to make the reader feel strongly – and in some cases act in a particular way. Choosing particularly positive or negative words can help achieve this. B Look at right. W hich which are ‘neutral’ the of words these negative? (neither words negative the in or each in the words Are any positive column neutral. table are of or on the positive the Verbs Nouns smelly smother stink scented choke smell aromatic suocate aroma pungent cover scent per fumed cloak per fume words negative)? into Adjectives and either Sort positive, lie 84 (on top of ) odour out Unit Applying C 1 your Answer Copy new from of and the the questions. complete that table Writing skills these factor y 5: this has on extract been page 84 from built (but near a letter your check complaining house. that you You use can the about use a words correct form verb). I am writing to complain about the ___________ new factory that has been built at the end of our road. The smoke from the chimneys ___________ us as we walk to school and the disgusting ___________ remains in our nostrils all day. 2 Now to read fill this each of second the Eating healthily than ___________ fat a yoghur t? and Or succulent mixing fruit does a not need apple or to pear ___________ papaya? and persuasive text. T hink of positive adjectives gaps. boring! chopped smoothie Create vegetables be your up with own What could with a be dollop ___________ ___________ better of low- mango recipes by together. REMEMBER: Time to write: persuasive Try text to include idioms Choose a health or social issue that is impor tant to you. about any suitable health or social Explain: issues. ✪ what ✪ why the you issue feel is strongly about You learned in previous a use Tr y to write about 100 words, and use positive or to persuade the reader and explain them in unit, connectives but try combination to here. negative For vocabular y about it. why you feel example: Not only is it strongly. important but also that people …, …. 85 Unit 5: One ONE step further STEP FURTHER Think In this unit, ou environmental more generall. deepl or about we greater eat, Now these to Talk some about social ou decide whether an live with of the we a of ou good for healthil, ever one health ourself example, is and personall challenge For live social how our and around or to so on? – a a bit should health? – aecting think much us issues Isn’t Or do dut world more authorities it up we to the to have us a encourage lives? partner ideas aspects can what for better about aecting issues. responsibilit ever one Use thought concerns governments what have ou’ve societ been ou thinking would about. change in With a relation par tner, to talk health or issues. Read You are now explaining going some to read changes a letter the from school a headteacher plans to to all parents make. Dear Parents and Guardians, I have now been Headteacher of Green Bay High for a year and and well-being of our children. I have to say that what I this has have seen children choose the healthy options and often choose sugar y many prefer to go to their classrooms and play on computers g iven worries drink s and me a chance to obser ve the health me greatly. At lunchtime, ver y foods with rather than enjoy the high levels of few fat. A fter lunch, outdoor space to play sports. In the afternoon, many strug gle to concentrate. I do not blame you, the parents. I know how dicult it is to encourage a healthy lifestyle when you are busy with work or other matters. So, I have decided to take the bull by the horns and make my own changes in school. Firstly, I am introducing a ‘ breakfast club’ so that anyone who did not have something to eat before they home will have the chance to eat breakfast at school. is will oer fresh fruit, simple cereals without left much sugar, and a hot drink (tea) or water. I have also revolutionised the lunch menu. ere will no longer be ‘fast-food ’ style choices pizza, but healthy meals including vegetarian and/or vegan ones. nuts or equally nutritious options. However, on Fridays – food style meals will be allowed. A treat is a good Dessert will generally there will be a relaxation thing ever y now and of such as burgers, fries or be low-fat yoghurt, fruit, the ‘rules’ and some fast- again! Finally, I am introducing a compulsor y 15-minute walk! After lunch, all children must walk at least twice around the playing eld. ere will be rewards for those who do more exercise than this, or sign up for sports clubs. I hope you will support me in these eorts. I am sure ever yone will benet. 86 Unit Talk W hat do work? school or with ou How (if think do ou should a have One step further partner of these 5: the headteacher proposals lunch)? for Are plans? lunch there Do ou compare other think with things the the those at will our headteacher could do? Write EI T HER: were a health wh new feel use ou think an health ma to the the the letter and school OR won’t as sug gest if is ou additional disagree work. this was in unit, and sa should be activit good or margin how and bad to ou how took it idea!). give ou up made You a ou could some ideas. check you: thought ✪ prepared ✪ read a a the and ✪ for explaining spor t it picture Reect about and our gave own and shor t promotional others’ talks poster to and a an health and larger group ar ticle about well-being a charit event Unicef ✪ listened ✪ answered to pur pose identif spoken of a text, par ticular revised word ✪ revised idioms ✪ learned how negative wrote a texts questions ✪ ✪ to agree plans ar ticle or (whether In response words. Write the a You changes 100–150 OR: Write parent. testing select uses classes, to about and related write to a our ke of raising abilit details to from vocabular the mone subject in a identif pla more object park the paragraphs, a and for and complex in text sentences health persuasive text using positive or vocabular letter or an ar ticle exploring ideas around health activities. Check you necessar y, A sk for feel go help confident back if you to the need about all section these and things. revise it If carefully. it! 87 Global UNIT This 6 unit is everyone In this unit, show R2 key and Natural disasters clear the learn and of and overall appropriate and many issues facing to: vocabulary, coherent text of ideas and extended purpose length to present ideas message spoken grammatical the world. details longer make S2 the will points, and about understanding identify L2 in you produce W2 all issues texts, and and key involving accurate points some use of a in more a variety complex variety of of short language vocabulary structures. other global issues Useful words: earthquake, In this section, you will consider natural disasters and other and how they aect Natural to disasters think ✪ Make a ✪ W hat personal ✪ Make notes or note heard Time ✪ Talk ✪ W hich to the the are 88 to by you you ‘natural had have of disasters’. any? experienced about your knowledge of world map there are to affected help more you by share natural natural your knowledge. disasters now? think times High the the 1990s, previous (From: examples par tner of Use strong 500–800 meant have disasters. Time stor ms, is talk par ts Why During about your disasters? 6.2 what experience about. with natural about a year four Noon: natural winds, 20 disasters – floods, torrential rains, and more decades Global sure meaning add Time storm, drought, avalanche people. Make 6.1 ood, disaster , global volcano, issues, natural cost and than droughts, mudslides $600 – billion, ear thquakes, hit the more world than in combined. Problems, 20 Years T o Solve Them, by Jean-Francois Rischard) you of them know these to your the words Word and Book. Unit ink about account for what the has changed increase in over natural the last 100 disasters. years Make or notes so of that your 6: Thinking and speaking might ideas, Glossary ready to talk about them. climate change weather Time to the book quoted on page 88, Jean-Francois Rischard goes on to views on why there are more natural disasters cushion accounts for the rise? can ecosystems natural are examples. the severity Global are cushioning of now role Dams – … warming is so frayed that deforestation often droughts and making disturb floods things they and the no longer wetland flow of play rivers and use with some a of par tner the and words in protect decide the exactly where and worse. what the or More global means. Tr y to air , factory ome to other issues fossil ✪ pover ty ✪ health think global for gases live sent into car fumes, smoke that are: fuels frayed is sources world of oil, energy, that living things ago or piece breaking or from long worn a natural coal formed died (when ✪ place plants example example were issues and Glossar y. for Time down interact environment 6.3 chopping natural animals emissions writer you) forests ecosystem increase … much soft their destruction the Work something deforestation trees Many protecting is today: that What in time give (a his over talk cushioning In change conditions broken of up string it is up or said to cloth be education ‘frayed’) ✪ food shor tages ✪ access to clean drinking global water Earth’s ✪ war ✪ homelessness. Can you think of other global issues? Add to the list if you warming rise in the temperature can. Challenge ✪ Decide on the three most impor tant issues for your ✪ Decide on the three most impor tant issues facing countr y the world today. Choose is ✪ W hat can be done about these issues, if an really In ✪ a small How to talk group, far do people discuss you agree your on ideas the and most your reasons impor tant for Do you agree on any thing the individual Prepare issues? person or countr y to how this your and a class you think issue area, the world. three-minute to affects your explain why talk to you can think do in country them. the ✪ that any thing? Research Time issue important. this is such an important help? matter . ✪ Tell the class about your discussion. Suggest could ways people help. 89 Unit 6: Thinking and speaking LISTENING In this section, you will: Useful water ✪ listen to a recorded inter view about water words: supply, learn some ✪ identify useful some vocabular y key points in on this shor t topic and drains, longer spoken texts. Make listening have already already have is talked some about about water shor tages dierent knowledge on global the around issues topic. e the in world. this unit, vocabular y any You so familiar previously to you. thought Think With a likely answer come these ✪ W hy is ✪ W hat are ✪ W hat can ✪ W hat are are exper t water As you main on listen about, in in a the impor tant the main cause the lack of effects your to uses hear water for the of topic is should one you talk about it in the turns ideas to that ask are and the world? water? of water? rst par t he time, of an makes consider inter view three what with main she Luc y points says Howdon, about about water. these three points: 2 why water is Point 3 why much of need up when has same may did for want you something 1 hear know fresh paper you that points to else? of when nished stop to think in Ear th about water at all impor tant the pieces number she the three so never 2 numbered hear her talk 1, 2 is hard and about to get at. 3. point 1, and lower point. and Audio when water 3. 6.1 Luc y twice was to going be to able star t to do this. talking about crops, know these words With turns to a to the words. your partner , make also have condent. Take the lack rst Point 90 group, in supplies. people How the skills many You feel that water? of why Do can recording. 1 Hold you small Point You recognise questions: going an or up Developing You you of Add Word take it in you about… par tner, to W hen you of Book. for be sure new pollution, scarcity meaning text water irrigation ooding, Exploring… e dam, shor tages evaporation, ✪ drought, reservoir , it each word. up a sentence Unit Applying A 1 Listen W hy 2 your do W hat to three 6.1 people again, find examples it does and hard Luc y then to answer imagine give of life how the questions. without humans tap use water? REMEMBER: questions water, start apar t from drinking W hat percentage of the world’s water is fresh water? Choose a about c 4 answer, less W hy is 70 than it a, per 1 b hard or to case, for b less than 3 per it the at the fresh water on the Hold up are the pollution Hold up human B the skills and W hat 2 Name 3 How 4 W hat (Audio asked 1 2 are Use can number the the when Luc y 2 when she now causes rain what Lucy she of to water can lack of hear own water a be of some the explains says your give to of that cause Luc y going Here, talks of the inter view. about the eect about that answer general of topic. Listen will to carefully – the tell be a to the question you that change being there of is topic. of how much listen to Audio 6.2 sources of drinking people the of mentions? pollution. water? wasting part lack Luc y of the water following water? inter view has many questions – knowledge. cause: hunger c lack d failure education billion en shor tage nal b many par t talks carefully. disease How second 1 below workplaces does from of In listen questions. main much lack to water. five example guess How with three too number 6.2, a of 3 can Audio questions the you supplies. answer the hear with waste the 6.3). results. don’t paper are You to water beings 1 C paper on Read again going help planet? going you will change interviewer Now you recording. cent get your a cent Hint: Extending to the c. cent per listening read before the out correct Always through it? this 3 Comprehension skills Audio some 6: people in the of world the are hotel badly industr y? affected by a lack water? W hat was correct the pur pose answer, a, b or of this par t of the talk? Choose the c. a to tell people about the eects of water shortage b to tell people about the causes of water shortage c to tell people about the types of water shortage 91 Unit 6: Grammar Grammar In this section, ✪ review ✪ revise or ✪ a your how the water water. to and verb use of must subject agree and with verb its subject, whether it is a noun par ts for the The are and plural verb forms. paragraph: of the family. children the singular verb following many Here knowledge the when Subject In will: pronoun learn Read you verbs world, They get and children have tired the to and subjects wake walk some of the for up at dawn several miss verbs miles school in the and as to a collect get result. paragraph above. REMEMBER: verb Subject Verb children wake is action children (understood) collect They have The get children some At other (as 92 in walk) (tired) miss Sometimes, because (to it instead is times, the of repeating understood to second avoid (as in the the repetition, sentence – subject, rst the They). it is just missed out sentence). word is replaced by a pronoun the of The subject person the verb. who of the does the Unit 1 Draw verbs a table and know subjects a I b Many people water f lows c We d Trees that have out destroy you agree. whether 2 Select the the the on page following water good 92 and write of all the sentences. conser vation supply down Grammar water; for they many turn years. on the tap and demand. ver y careless from and waste evaporating too far too quickly, much so it is water. a shame when forests. agreement write, Think a on water one studied have Subject-verb When the in Luc y become stop people like 6: you about verb is have to whether in correct the remember the past word to to subject or the ll make is present each the singular gap subject or and plural. verb Think tense. from the words in brackets. a I b W hen c Many years never __________ d __________ In her (am/is/are) cooking , talk climate we ago, __________ when we to have clean (use/uses) __________ a the scientist __________ water lot of (were/was) (think/thinks/thought) yesterday, change lucky about __________ (cause/causes) a to drink . water. children, we water. (say/says/said) scarcity of that water. 93 Unit 6: Grammar Singular or plural? Sometimes you singular plural. Do not the In or be confused to if think there these sentences, cow costs The cow with the the – a lot the second middle the of long money horns sentence, it does Trees b One hundred trees grow c One hundred trees that grow the need The a and if verb. the a between the the subject subject is and Neither is Luc y green and the verb is feed. costs a ignore lot the the to of money phrase subject ignore with and in to feed. the verb long horns in agreement. sentences b and c below? For goat there. help up work save of two water or together grow more and there. nouns/pronouns form a plural subject and example: eat surround a lot of food. us. nouns/pronouns oak tree human are joined by or or nor, use a singular or nor the an r tree animal has lives to be cut without down. water . correct. following brackets and water to have made they verb. the two a the highlighted example: the the you is and, water Neither from by and For Either In in whether there. plural cow do subject connected is change a When words you not W hich 4 words subject 3 But are about yellow. The Air carefully verb. highlighted In have the sentences, to ll the inter viewer choose gap the correct word correctly. __________ (was/were) talking about scarcity. b Lucy, like many scientists, __________ (blame/blames) global warming. c Neither the situation 94 is inter viewer hopeless. nor Luc y __________ (feel/feels) that the Unit When to the more subject than collective nouns The herd The forest My gives family However , of the My of if are a trees the to collective – family is family have then herd, good grows save noun takes family, supply well – of a the crew singular noun singular and team. verb. For that refers Examples of example: milk. near wants individuals, very it Grammar the river . water . sentence as a a thing us tries group is one 6: happy you then group to think you’ll of of need people. the to different use a (singular plural members verb. verb) but My The their team always The team wear You have birthdays wins its away in different matches. months. (singular (plural verb) verb) but 5 Choose following to class b The boat c We hard correct has (plural which word to or decided/have crew take verb) use! words to complete each of the a has decided managed/have photo when the to raise managed school of money to find whales together. a school of whales. sur face/Sur faces breathe. d The forest e The crowd 6 shirts sentences. The to think the a will red Choose a of corals waved is/are being its/their suitable verb f lags to fill destroyed. and banners. each gap in the following sentences. a The save b football team __________ on ar tificial grass to water. Clean water and enough food __________ necessar y for sur vival. c The d W hen to range at save of mountains home, the __________ prime minister enormous. and his wife __________ water. e The number of f The shoal fish of people on Ear th __________ __________ around the doubled. coral. 95 Unit 6: Reading non-ction READING NON-FICTION Glossary In this section, you will: debris ✪ read a magazine ✪ learn ✪ practise understanding ✪ practise recognising some ar ticle useful vocabular y about ideas in a sea pollution bits of that been has pur pose waste, the something larger broken text garbage the of remains of a US word for text. ‘rubbish’, as in ‘garbage can’ (dustbin/wastebin) Think Synonyms the right, W hen about… are words which people with includes write ver y similar synonyms about facts, for they meanings. Read the Glossar y on ‘rubbish’. need to use litter pieces paper , bottles in precise words. If a public writing words, or about use new things, comparisons to they may help us even have imagine to what make they up are rubbish, or cans, open often left lying space they trash are or of new describing. US word something in the on you ‘Trash’ your for ‘rubbish’; throw can you away, may as have computer Exploring… waste something disposed Plastic In 1997, after he competing human was in a was yacht astonishing but sailing race. In back the discover y. Charles middle He Moore from was saw Hawaii of the miles to Pacific from plastic Califor nia any waste Ocean, land floating and all him. met, seemed no an Moore habitation, around ‘I Charles made no soup as far as the unbelievable, matter what time eye but of I day could never I see, with found looked, a the sight of clear spot. For plastic debris was plastic. a It week, floating 1 ever ywhere,’ nets, This plastic vast it does spinning eventually The idea plastic patch’ of Patch’. not – The floating debris Most the area breaks of a ‘garbage mostly made pictures do collected kilometre of the not make up to of the (Moore, 96 C 1997 in Mindfully, and is bits 2009) a few as drawn tinier on. be a fragments of the of look of like this of items. Pacific huge, That means the plastic pieces. in island fact, plastic, seen the ‘Great into Instead, solid But, ‘garbage water 1 just known that pieces the Patch. bottles, disappear. walk tiny 750,000 Garbage now always show name suggests could up found non-biodegradable. or tinier patch’ can’t is is down into to waste ocean you These microplastics have of wear down something is of He Moore. toothbrushes, naturally ‘microplastics’. satellite Charles bags, area Garbage slowly said by a naked as cloudy microplastic of ‘garbage called the patch’ made the in a eye. solid soup. a Even area. Scientists single square longer Make or sure words and to rid or of know the slight between your is once it is wanted you differences them got used that Word these them. Book. Add Unit The seafloor trash the heap bottom threat to bits After – it of sea jellyfish, in under sea. that Here, creatures. favourite about the Sea patch 70% larger tur tles food. may of sea be an marine pieces often Other also of underwater debris debris mistake will sinks pose plastic creatures Comprehension a bags get to great for tangled up plastic. retur ning ar ticles garbage thought the their of is the 6: to problem tell from Applying from the the expedition, world about his Charles findings Moore and began how we writing can stop this occurring. your skills REMEMBER: When you come A Read the text again and then answer the following across word Look at new understand, questions. 1 a paragraphs 1 and up word try into to that you break chunks don’t the that you do 2. understand. W hat Give 2 was two W hat are it about the plastic waste that astonished Charles? For example, the word can looking For each of these questions, choose the correct work at b or W hat its – ‘can does ‘can’t be seen by the naked eye’ harmless be You need to b You need to c You need a use a microscope to see wear goggles to see into satellite camera to – harmless ‘can to the text, how does a Turtles drown b Turtles get tangled c Turtles eat the 1 2 pur pose a to persuade b to tell c to advertise a in the by this to see the means them. plastic waste harm – ‘can not be tur tles? up by natural means’. soup. old plastic. mistake. text pick the broken by is up … plastic extent written by of sea debris. pollution. Charles Moore. questions. comparison Patch looks does of book these plastic plastic about W hat How the people people Answer is 3 main in be pieces them. broken C up them. Non-biodegradable According The broken pieces’ mean? natural 3 by answer, up 2 meaning prexes Bio-degradable a uses c. into 1 out the Degradable a, article non-biodegradable. ‘microplastics’? You B the things. in the text helps explain what the Pacific Garbage like? this comparison help you understand what the patch like? How much of the plastic waste ends up on the seabed? 97 Unit 6: Grammar Grammar In this section, ✪ revise ✪ learn Tense and tense all Plastic was oating to a make piece in the currents. sailing felt clauses together. sure of that you writing. keep For to the correct example: Pacic 70 per Ocean. cent of It the moves waste around falls slowly down to decides huge to out is In They of 15 who together. The newspapers the Pacic. of 2008, want to He all saw a huge area of plastic it. the He the also sets awareness plastic bottles. fasten 2600 present the Pacific plastic. organisation bottles, the the from tense. present Write into past change. across raise goes over to in verbs floating old clean raft written the verbs about 15,000 children, is all sailing area write Califor nia. project. below are Moore a across horried. changing ere across 98 have through sea paragraph raft join oor . and Charles a is the again, tenses. to tense waste, in of ocean e you way waste Charles out consistenc y ways tense because it write, the Present 1 tense different consistency you Past will: practise some When the you miles. world. on It He up Ocean feels a sea They the is when the are Junk filmed helped tops and comes that he organisation pollution. bottle he shocked research creates of so Raft They by and make school tie appears them in Unit 2 ese with a a In ve partner 1997, decide b He sentences to decide Charles what then to sails have felt do to errors what sad about in tense changes about the you consistency. should pollution but, at 6: Grammar Work make. first, cannot it. America and ended up star ting his own organisation. c Charles about now ships d He wanted e He will Who, In to 3 you allows you writing There Use who verb). whose 3 it is complained he makes a good star t. star t. complex pronouns to forms the is the it is whom when your of sentences (who, using which, sentence the subject man the subordinating that). structures pronoun of who the verb sailed object everyone you want whose English, expect you to these Using and these makes your who – (does whom the and action whose of the of the across verb the Pacic. (receives the action of the to praised, show helped build a raft. possession. organisation set up the Junk Raft Project, is a whom know is how becoming to sentences, use less the using common, word but some people whom who, whom or whose to ll gaps. a __________ b I c The d __________ e ea think the ship by Charles ‘plastic are the people owners, tur tles, bags f making variety other Moore, Rewrite the will he sailor . modern still he and where sea. concise. when Use In world the example: children, keen now magazines in example: The Charles the relative add Moore For for r ubbish whose and two whom verb). or when For Charles Use to more are stop revised conjunctions ar ticles change never whom Unit writes throwing do people responsible __________ __________ you are for the responsible r ubbish is in pollution? should the sea, pay are to fines. blame. blame? __________ favourite food is jellyfish, often eat plastic mistake. Moore, __________ found the f loating r ubbish, called it soup’. 99 Unit 6: Reading non-fiction READING In this section, ✪ read ✪ learn a ✪ practise Read against useful text giving arguments vocabular y recognising the about pur pose of for animal what and against a view conser vation you read. about… the tr ying Should and will: non-fiction some Think view. you NON-FICTION following to save we ar ticle, rare which looks at the reasons for and animals. save endangered animals Glossary plants? becoming We all know that many animals and plants are in danger extinct altogether , becoming the 40 wild. per Amur extinct. The cent There population in the leopard, is last also 30 in are of only around giraffes years. grave A in the less 880 wild mountain has gone well-known danger of gorillas down animal, extinction. Only dying remain The list of in the wild. A endangered noctur nal animals creature, grows it lives longer by and the conservation nature the and why would That spend cost money drinking money $76 billion could water for be on a conservation? year spent several to on preserve hunts funding a One study hospital, wildlife to land may be animals hard like to that lives kinds providing which difficult, Another goes and valid on poisonous even are why are a anyone threat in the snakes ver y argument safe food one chain Think about to would people want and to save and is or spiders. They livestock. make that absence play. But Finally, rich it who person India So, why they role in in But extinction of humans. and in be to be fear that of to pollinating vegetables a the and tr y is a natural Dinosaurs sabre-toothed to humans of the want to reason, lives from another pollen plants Or process argument supported with a reason Make sure you these words evidence no may save tigers when – had few. them After in a animals? Well, one They honeybees, par t all, look up reason a a in is that valuable would be any a partner words you to they’re village play there phrases. with they a because families honeybees. Without seeds. privileged and longer tigers have understand that tigers? conserve Consider plants. and view good us. between spreading fertilising don’t know. Word Book. now? might their we vital although them Europe is should can fruits, 100 are misses seems beautiful. ago, links ugly. mammoths long of people’s and disappeared danger the species Discuss exist. in villages. understand wolves, of money it animals. valid some with out pollinating It do endangered showed or of alone. day. threatened protection around dying But out in around economic 70 disappearing of no Add them to your Unit Another people pay reason love huge USA, Park the sums economic study A 1 will found in be the to Africa all of huge save an to the when animals. ear n see grey for a Not living elephants wolf into tourists. only from or do them. giraffes. Yellowstone So it made many T ourists In the National good them. is in effect the baboons these draw nature have that, of a of many a on state the number increased, of balance. food of chain. lions If In we decreased, causing great lose Africa, one one the problems for area. of these statements ere are 70 Amur b ere are 30 mountain c ere are 40 giraes Amur a spends b is most c is not W hat is leopard its is time active is tr ue leopards left gorillas left in according the left the nocturnal. in in to paragraph the wild. wild. This means that it … alone. at night. well-known. the main point of paragraph 3? to show why people want to save spiders and wolves b to c to give examples of dangerous or unpleasant creatures suggest Answer Give two 1? wild. a B 1 visit now a The 3 beauty but Comprehension For each of these questions, choose the correct answer, a, b or c. W hich 2 to know it population people to sense we species, the – reintroduction proved Finally, is them 6: that these some animals are ver y useful questions. things the writer would prefer to use money for, instead of saving animals. 2 W hich from 3 animal no W hat fault reason animals, C 1 W hich 2 Paragraph 3 of sentence 6 honeybees fruit, c bees for the can three saving an say became extinct writer are sug gest for not saving some beautiful? questions. a turning word cost vegetables play writer marks uses b the they these a W hat if the humans? does even Answer does a and reasons lot does endangered ‘ valuable’. of seeds impor tant point the Here, it ar ticle? means that … money. are par t the in expensive. in plant-growing. writer give animals? 101 Unit 6: Writing WRITING Writing In this to argue section, ✪ collect ✪ plan ✪ consider you ideas your a point of view will: for a piece of writing that argues a point of view paragraphs how to develop ideas using details and examples. Points AGAINST (conser ving Think animals) about… 1 expensive 2 animals 3 extinct 4 only to save animals In the previous reading activity, you noticed that there was a turning point unpleasant in the article – the sentence: So, why should we tr y to conserve animals? e rst par t conser ving reasons You the ar ticle animals. for could of After conser ving sum up the gave the arguments turning (or point, logical the reasons) second par t animals rich people reason needed the care animals. ar ticle in tables like the ones on the Points right. Exploring… evidence, missed gave F OR (conser ving Each not against an example argument could to not suppor t convince it – evidence. Without the anyone. Copy and complete the table below with the example or detail that was animals) 1 animals vital 2 animals beautiful 3 good 4 keeps for to us economy balance of nature used to support each point. Points AGAINST (conser ving E xample animals) expensive costs 2 animals wolves 3 extinct 4 only unpleasant animals people Developing Choose one of ✪ All ✪ No ✪ Ever yone in cars coal poor in countr y ✪ Ever yone ✪ ugar kill livestock missed connected banned be rich animals) 1 animals vital 2 animals beautiful 3 good 4 keeps for to us economy balance of nature skills topics be used to from with global issues: towns. produce countries a should should and draw billion E xample should electricity. give half their wages to people countries. Our against. these should $76 care your should ✪ Now not F OR (conser ving 1 rich Points Find become sugar y table at as stop foods above. least one paying for its army. vegetarian. should Give be taxed three example, 50 reasons fact or per for detail cent. and to three suppor t reasons each reason. Hint: of You research internet 102 may to in have a help to book you. do or a on bit the Unit Think e We ar ticle all You will pages that 100–101 many star ted animals and with this plants sentence: are in danger of extinct. have against – facts show it noticed was that the introducing rst the paragraph topic. In this was not case, it arguing was for giving or some REMEMBER: to that there is a problem concerning endangered you idea are to writing star t about with an a topic with points for and against, it is a good introduction always one you you a chose little a on par tner the research, introduction – a Developing In Unit 3, you to the and, ✪ But who page. perhaps your add misses get go some some with into an introduction notes and, statistics three or four or if to the necessar y, facts. you to use Write It your a you are it should with can at give argument statistic from least extra if a source. topic do your sentences. skills at the interest with could Make to paragraph looked structures ar ticle last what point, support reliable with a example. weight Exploring… Discuss When animals. arguing If Writing about… on know becoming 6: a impor tance to your par tner, them now? of writing. discuss using Look why the a at variety these writer of sentence questions asked each from one. [T he writer expects you to answer ‘no one’.] ✪ But is fear ✪ o, that of a their why good lives should reason, from we tr y when tigers? to families in a village in India are in [The writer expects you to answer ‘no’.] conser ve animals? [T he writer goes on to answer the question.] Writers expect you often an are answer, expected rhetorical Time Now make use use but to of to questions make think the an in their eect. answer is It writing can be obvious. a – not because question is is they where known as a question to the write: ideas and magazine examples in article your table to write a magazine REMEMBER: ar ticle of your own. Aim at around 100–150 have used different sentences. Extending Choose some your another details skills topic and and write question a magazine Check that you words. ar ticle of your own. Include interest Have to to add your kinds you of included variety and a give writing? statistics. 103 Unit 6: One ONE step further STEP FURTHER Think In this going unit, to you’ve consider Talk in thought one a of about the a wide greatest variety challenges of global facing the issues world – both in the natural future and – man-made. food Now you are shor tages. group In a small group of three/four, explain to one another what the situation is like in your own country as regards food availability. Consider: ✪ To what extent does ever yone have enough food? Too little? Too much? ✪ Does ✪ W hy ever yone do some eat healthily? par ts of the W hy world or why suffer not? from food shor tages? Read Here is an inter view Journalist: Aleefa: How W hen understand I serious people the Journalist: between live problem know is a journalist the in countries facing you’ve problem the done of a food world where world some and as the a exper t. food problem whole. research shor tages, into It is the is Aleefa? often ver y too much serious subject. Can food, it is hard for them to indeed. you give some statistics? Aleefa: e United Nations estimates that today around 795 million people in the world do not have enough food to eat. A shocking statistic is that about 3.1 million children die of malnutrition every year – to give you an idea of the scale of the problem, that’s around 350 every hour. Journalist: sure that Aleefa: at really ever yone It’s a ver y gets is a shocking enough complex to issue. statistic. eat. But, W hat’s yes, if But I’ve going the read that the world has enough resources to make wrong? world made it a priority, I believe we could solve the year. More people problem. Journalist: I Aleefa: indeed. less Yes, food and suppose water the e to go rise in world’s population population around. At the is is same par tly to blame. increasing time, by climate around change 79 is million having a an means eect. Journalist: Climate change means hotter weather, right? More droughts. Aleefa: Yes, global warming helps cause droughts. But it also leads to more extreme weather conditions, so there can be freak storms and ooding that destroy crops. Already we are nding that fewer staple crops – such as maize or rice – are being produced. For example, over the past year, in Malawi, crops and killed more than 100 people. Around 340,000 people lost their homes. fall in the staple Journalist: maize Pover ty crop must in be that a It all oods led up to destroyed a 28 per cent year. cause, too. Aleefa: Strangely, no. As countries become richer, people expect to eat more and more meat. Well, it takes ve kilos of grain to produce one kilo of meat. So the richer the country, the more grain that country uses to produce 104 Unit 6: One step further less food. Land that could be used to produce soya or other protein-rich crops is being used to produce foodstu for cattle! Rainforests are being cleared in parts of South America to grow cattle food – so there’s another terrible eect of this growing demand for meat. Journalist: It really is a ver y complex issue. Maybe in the future we ’ ll all become vegetarian. Aleefa: In my opinion, in the future there’ll be no choice – everyone will have to become vegetarian or vegan, and be much healthier as a result! Talk 1 2 a partner Work out the meanings of the following, and then use a dictionary to check: a freak d complex Look the storm again subject How 3 with can Now, issue at in speaker ’s the they you still b make e it priority vegetarian inter view. are a or protein-rich food vegan Discuss discussing. c W ho how the feels two speakers strongly about feel the about subject? tell? pairs, feelings read as the you conversation aloud and tr y to express the read. Reect and check Write In EI T HER: Imagine journalist in above. the Write an you are this unit, ✪ talked problem ar ticle some done where of for ✪ learned food you improve explain shor tage sug gestions to man-made disasters for the some more complex words and phrases about the and what issues ✪ listened to an ✪ learned to written and learned about inter view about water shor tages give can situation recognise the overall message and key points of be spoken texts in complex Write the more you and subject-verb agreement, including more future. OR: in natural a ✪ the about conversation global magazine you: the of the will (hopeful) view shor t future, have stor y a of inspired ideas read. the in an about by the Decide show or stor y one life or inter view rst if your optimistic pessimistic ✪ (negative) read examples, non-fiction for example ar ticles about collective plastic nouns waste and animal conser vation ✪ learned to use prefixes and suffixes to understand new vocabulary ✪ revised ✪ used ✪ learned future. tenses relative how examples ✪ learned to and about including and tense pronouns argue a consistenc y to join point clauses of view, including how to use statistics var ying rhetorical sentence types and str uctures, questions ✪ wrote a magazine article arguing for and/or against a point of view ✪ wrote Check an you necessar y, A sk for ar ticle feel go help or shor t confident back if a you to the need stor y about about all section food these and shor tages. things. revise it If carefully. it! 105 Travel UNIT This 7 unit is distances look at In unit, this collate, W3 make you accurate produce Here of and and – everyday travel benets tourism for work and journeys or leisure. negative It effects the will of longer also tourism. present of relevant vocabulary collate and information language sequences expressing of detail grammatical from and speech, opinions a variety abstract of short and longer spoken texts, material answering with structures and, spontaneity as and appropriate, asking uency. holidays Transport are the some words words in the caravan to do with transpor t. Match each picture to one box. coach underground/subway cruise train ship (tube) limousine motorhome bic ycle steam train Hint: canoe inter- city tram ferr y 106 and to: complex extended questions, 7.1 and some the use travel may learn organise involving and of will understand S3 about people some R3 L3 Travel all and train tandem houseboat cable car four-by -four hot air double-decker (oroad balloon vehicle) pedestrian bus Make sure of not pictures. have your Word the you meaning know words Book. Add that the do them to Unit Time Make How to notes far you ✪ the travel ✪ the local ✪ longer With the you do your questions and speaking do for have mode done of over the transport last did year you or use? so. Consider: day in your example leisure for time family visits. talk par tner, to you W hat ever y you journeys, to travel travel? travel Time Thinking think about did 7: keep talk the about the travel conversation you going. have For done recently. Ask example: REMEMBER: To keep a ✪ W hat is your ✪ How do ✪ W hy did ✪ W here journey to school conversation going, you should ask like? questions that need more than a you get to school ever y day? yes/no answer . Use: How …? When you travel by car? …? Why …? Where …? questions. 7.2 do Going you on like a to walk? holiday Useful Time to words: self-catering, get think away from it all, go sightseeing, Make some notes about holidays you have been on, holidays you would activity holiday, package holiday, like to tr y and what you enjoy doing when you are holiday. holiday of a lifetime, off the beaten track, places of interest, Time to talk holiday resort With a partner, take it in turns to ask and explain what the phrases in the ‘Useful words’ box mean. Ask one another about the holidays you have been on or would like to go on. 7.3 My Before Find a you a come picture internet to dream or of draw holiday to class, the a prepare holiday rough to from sketch a talk about travel that will your brochure, help you ‘ideal’ print talk holiday. one about o your the ideas par tner. Time to think Challenge Spend a few minutes making notes about your chosen picture. W hat Choose makes it your idea of a per fect a Time With for a to talk par tner, them. dierent another Be or ideas. to a small ask Consider person’s group, one why discuss another one your questions person’s ideas to dream and your explore holiday reasons might minute to your be the holiday tell your holiday from and talk internet. then about class. To give the make a two- holiday the talk more challenging, imagine are salesperson and a give you a nightmare! talk After wards, fantastic brochure/the Prepare in ready a holiday? the group class how talked far you were able to agree on the dream buy to persuade this the class to holiday. about. 107 Unit 7: Listening LISTENING In this section, you ✪ listen to and ✪ listen to a learn understand longer information ✪ will: some spoken from a shor t text recorded and collate conversation (gather together) it useful vocabular y on this topic. Exploring… e listening text is a conversation between a teenage boy and his mother. Spend a Audio A you choose W here 2 the the mother? a inside b at c on the a a the will need He has not c He will need is the to the beach to see an c to visit you of are and then listen to prepare before to yourself, background ✪ facts ✪ health ✪ instructions ✪ any thing and his or For questions c. phone conversation with cave asked her abroad to the to son this to come before send some phone and home collect without money his out at this time? him. family. to him. afternoon? mother give her son? skills hear who a star ts b questions. caves your taking a going does tourists he a, these galler y some going answer parents her art advice to his boy b ✪ 108 questions mountainside been a Read the cafe mother He group through answer, when entrance b W hat say son busy Developing To correct a Now reading listening, peaceful has W here 4 is are his W hy 3 minutes 7.1 As 1–3, 1 few are talk a recording about with group on a a to of visit par tner visit. a tour the guide Great about speaking Wall what a of to China. tour guide might Consider: information safety information else. through section B on page 109 and then listen to a Audio 7.2 Unit 7: Comprehension B Listen complete Lowest to the the tour gaps below. temperature: Highest time of year Best time of day Pur pose Star ted: -20 temperature: Best of the 2000 guide’s to to years will degrees around visit: visit: wall: You talk and hear write the the words recording that twice. C ____________ degrees C ____________ ____________, to avoid crowds ____________ ago; completed around the year: ____________ President Deng Xiaoping began to restore the wall in the year: ____________ Became Great a World Wall Warning length: for Reminder: Listen four e of the a explain b make c persuade d inform e show f give g argue in h of the the about the the not of the and wear year: ____________ height: ____________ ____________ or ____________ recording tour the visitors the km in ____________ statements pur pose Great to Do because Bring: Site 21,196 tourists: ____________ C Heritage below guide’s wildlife feel visitors visitors one are talk found pleased to how buy the last time. W hich correct? is to: near about the their Great Wall visit souvenirs workers built the Wall that facts the Great about that the the Wall age Great is of and Wall is world size the of impor tance the best Great tourist Wall site China give visitors safety information and advice 109 Unit 7: Grammar Grammar In this section, ✪ review the ✪ review how you will: difference verbs in between the active passive and form passive can be in forms the of past or verbs present tense ✪ recognise of Active In and the the The wall the can add formality to the tone was action the here would of the a word the subject you you by The the used saying ‘The Chinese the Chinese people built the wall’, people.’ passive been verb) use the form object becomes the people The the the verb of of the the subject ending in active be -ed normal – to The verb ‘to sentence of the build’. (which sentence The received (the do-er was subject the be wall by 2,000 the people passive the years object ago. 2,000 years ago. form: of the verb becomes wall followed – the started normally verb to started was the would of the wall from that the show the wall The verb the Note: by have version: normally • built version: change • of verb). Passive • instead said: that Active 110 verbs passive speaker word To passive recording, guide ‘The of how writing. by the past participle of the verb – started by using a phrase starting with by – people. normal was subject started may 2,000 be years missed ago. out completely, For example: Unit 1 Look verb at these active or sentences The b Another c The students d The caves e Several f The g Unfor tunately, 2 e a teenager rst The phoned phone call had a these one was mother made by have his in lost underlined verbs. Is the sentences needed a from the to the their teacher. the 19th way abroad. caves. centur y. in the caves. holiday. lug gage been by coach discovered fantastic has people his travelled were explorers Change the Grammar passive? a boy with 7: was from done huge lost for on the the way active home. into the passive. you. wall. A huge wall was needed by the people. b The c Visitors builders d Hikers e The f Some g Visitors wore tourists of used bought the enormous lots of stones. souvenirs. down the stones made the path tourists top of the wall. slipper y. spotted photographed on foxes wild in boars. the area. 111 Unit 7: Grammar Active The and passive Active Here them form are will word a The wall b The last c The wall d The stones e Ever y f It 112 the some a was the in be – past in the present past the more have or The tense: A A fox present chases mouse fox mouse a mouse. the by the fox mouse. chased passive word tense. chased the was about the is chased underlined change present the The sentences the to past tense: tense: past and tense: present changing You or in can the in form out, verbs. in form Passive 3 verb form Passive Active passive Great verbs order by the Wall. into and fox. Write active maybe two. is recognised par t was day, of the as wall designed were the used wall completed is by a World was by by built the local climbed the Heritage by the Chinese people by to for Ming keep in by 1644. UNESCO. Dynasty. out building tourists. emperor Site enemies. houses. add REMEMBER: the verbs Check you use. the tense of Unit When to Using The the lively. reason There to are the passive active and • use voice As do a two makes usually general so, for other better rule, only example times writing to when for making use the sound you sound more your passive more might The castles Great visitors • to Wall were stress were the has is built near been not the visited wall. formal. writing when clear , you direct have a formal. want to when the do-er of the verb is unknown or not Many Grammar passive form is 7: (Who thousands use the passive important, built of them times. form: for example: is unknown.) (Who the important.) person or thing receiving the action of the verb, for example: Ten tourists were hurt yesterday. (The main point is that ten were hurt.) e following information might appear in a hotel room. If the hotel wants to sound more formal and polite, these sentences might be in the passive. Ac a bre kfa st e: ssiv Pa be Note: by 4 e you information before 10 p.m.’ be does not because fore Bre d ere ord ak be need ‘ by er ord st mu u Yo e: tiv 10 t fas fore to you’ . p.m st mu say: is . p.m 10 ‘Breakfast must be ordered understood. Copy and complete these sentences, putting the verb given in brackets into the passive form. e rst one has been done for you. a Extra pillows can ____________ from Reception. (collect) Extra pillows can be collected from Reception. b Shower c Snacks can d A must e Dir ty table gel has ____________ ____________ towels by ____________ should in the phone. in bathroom. (order) advance. ____________ (place) in (book) the laundr y bag. (leave) 113 Unit 7: Reading non-ction READING In this section, ✪ read a ✪ learn ✪ select has ver y an some and remote. example. all be about a vocabular y about nature relevant popular tourist destination conser vation details. about… easier e It But aware text present become scener y. will: non-fiction Think It you NON-FICTION is at and easier Galapagos a great the visit Islands, thing same to for time, places just people there are o to previously the see coast of amazing negative eects thought Ecuador, animals that we of as are and should of. Exploring… Glossary Read the text below and then answer the questions that follow. in danger danger Why are the Galapagos Islands of These There 106 of remote are are the now giant tourists A 1 islands around The can and tourists? were and in really these complete Number animal b c e the close this the mouse of that year types may when of die the Name two become 3 W hy extinct, are visitors approach 114 kinds the of have no about the text Galapagos types of animal out soon islands were Galapagos the animals to animal the closely? that text. Galapagos so fear above. Islands able to have Of in 1835. these, species disappeared them. table. according to Some have discovered 2 Darwin islands. extinction. Galapagos to about dierent of Charles on there Number there of on by animal Galapagos questions Facts a of danger the animals get discovered species considered Answer Copy 450 tor toise completely. so with extinction in out so species popular of dying of humans type or kind of animal Unit Developing Here is par t naturalist of your a who ar ticle presented by many Sir David nature Attenborough, series on a British REMEMBER: be television. useful the I first and visited in fact everyone the last for realisation Galapagos returned six that when there on Islands my they are in 80th first 1978, arrive albatross filming bir thday. and and I Life think step pelicans off on Earth, These what knocks the just… boat is sitting mean the on there. … really understood what Darwin must have seen in 1835. There are the tor toises in different you of first them marine the to see the on iguanas at they the par ts of the Galapagos are world, with is rocks. If lizard especially the …; … you’re watching this are dramatic black been bottom rocks the swimming. having the in them sitting coast there unique but what It a there is – a are most are another fish, lizard! claws, – these you sea huge 20 feet grazing come lions down, idioms they meaning. raining cats that appear – to can make interesting. phrases they it to not mean have For and do example: dogs.’ this just means In it’s and very hard! When herds to see round and green … writing, are visibly iguanas. fascinating swimmer, trigger long marine use surface raining obviously When more what English, giant to writing ‘It’s I Comprehension skills magazine has 7: so on the on and holding on seaweed. Glossary knock means you for ‘takes six you (literally means out’, in like a an by ‘to idiom knock boxing that surprise’ you match) B For a, b or each of these questions, choose the correct answer, marine c. the 1 According to the ar ticle, which of the following can be found only a 2 in 3 or to do with one of a kind Galapagos? giant W hich a in on unique the living sea of large these b phrases marine tells you iguana that c marine trigger iguanas sh crowd together numbers? huge W hich tortoise herds b statement a ey chew b ey can’t c ey nibble Extending on go about bits of obviously the marine rock that under water, on your marine but plants, unique iguana they eat c is hold cows feet down tr ue? in seaweed like 20 their in claws. shallow eating pools. grass. skills C Answer 1 According tourists 2 Look there at at to and this the W hy these the text, which two sights are most likely to amaze why? extract bottom does questions. is David this the lizard ar ticle: – a Attenborough a It is exciting b It is a c It is frightening shock from to to see see to what what see he use the like an a ugly – 20 word expected looks such lizard! to feet ‘ lizard’ nd land down on the animal creature on twice sea here? oor. on the sea oor. the sea oor. 115 Unit 7: Grammar Grammar In this section, ✪ revise ✪ learn ✪ revise link use in this The Here and in to join pelicans ten to you make complex to show which and learned future, sentences ways to use compound sentences and can to vary main cer tainty sentences (two clause of varied. conjunctions sentences (a level be (joining or with more one words) main or more clauses). example, are book, clauses subordinate when verbs ways conjunctions clauses) For modal different Earlier to will: conjunctions to Revise you this the is a two come complex sentence that uses the conjunction clauses: along commonly when used people are selling subordinating sh. conjunctions: REMEMBER: after although because before if since until when where You can also put the while subordinate main clause before the clause: Work with a partner to check you understand what these conjunctions mean. When people are selling sh, the Look up any words you are unsure of and write them in your Word Book. 1 With the box your partner, make up a sentence for each conjunction in pelicans come This add to above. can your notice 2 W hich Use a than conjunction dierent one Main could conjunction possible you for use to each link pair. these ere pairs may of be clauses? along. even sentence the after clause. more answer. clause Subordinate clause a tourists love the Galapagos Islands the animals are so tame b people like to travel to the Galapagos they have seen Attenborough’s T V programmes c d e 3 take care not to step on a marine iguana people go swimming the Galapagos are a popular tourist destination you walk across the rocks the marine iguanas graze on the seabed it costs a lot of money to get there Now write the sentences from question 2 out in full, but this time write the subordinate clause rst, followed by the main clause. You don’t have to use the same conjunction. Remember to use the comma correctly. You can change some words if you need to. 116 variety writing! comma subordinate more But the Unit Modal Look People these if no save they might chance People sentences: could to, People a must the want save they question will the the they tortoise giant save save – giant from extinction. (could = have the to) tortoise them giant have a – but tortoise strong from it’s extinction. not from (might = there is certain) extinction. obligation to save (must = there is them) Oak People tense will – save yes, the they giant are tortoise denitely from going to extinction. save them (will – = Tree small because They will verbs they can are change express called the modal meaning meanings such verbs. of as the how They verb are hurray!) that denite very is Welcome after that them. The something tea 1906 happen. popular still Choose an appropriate modal verb to use in these sentences. are a sentences may have more than one possible W hen you iguana, swim but in that’s the not Galapagos you W hen I am older I ____________ see a marine with a visit the If people had been more careful, they with Tourists nothing ____________ have saved David 5 ____________ take care when they visit, or there’ ll be way Attenborough at area walls which atmosphere. itself chairs carved is lled and tables. tablecloths offer to be After left. islands, Look the The green, is Crisp complete the scene. a wide range of Mouse. understands that people ____________ the no matter tourist sentences what leaet are he says. on varied. the you you With a partner, so have will choosing cakes. right. teas, something there to is tempt selected have the sure you. your hard task visit of the place. It the tea, e fashionable dark elegant different d in became Galapagos. We Galapagos opened peaceful dining luxurious c was gentlemen. special beautiful definite. ____________ the Room. answer. white b to Tea immediately painted The a it and creates Some Tree room and ladies 4 Room important comes it Tea future Oak These Grammar verbs at ability 7: notice Why one not of visit special occasion? a time! great our us You delicious for will that have Find: Finally, visit our souvenir shop next to the a a simple sentence c a complex b a compound d a rhetorical sentence tea room. sentence question Here, small e an exclamation g a passive i a modal f a statement h a command j a modal bought at verb reasonable verb to show possibility verb to show future prices. 117 Unit 7: Reading non-ction READING In this section, ✪ read a ✪ learn ✪ select ✪ collate, the some unspoilt tourism about tourism connected information organise relevant from detail with a tourism longer and non-fiction present it for a text reader. about… like to tourists they has text vocabular y relevant people more will: non-fiction Think Many you NON-FICTION visit visit become. been areas these Over that quiet, the developed to are unspoilt last tr y quiet 30 and and unspoilt. places, years or protect the so, the a Of less new course, quiet kind places: and of ecotourism. Exploring… First, read the Glossary words understand what and the answer and they phrases mean. questions in en that the read Glossar y. the Make ar ticle sure about conservation you ecotourism nature and follow. that aims natural – how does it a not guides causing as organise little visits damage to as places of possible. help what preserve funds for places, same trips the to events them for to these the conservation time, chance makes beauty T ourists aim ear n see a is such as to living wildlife. future projects environment the places and help with are – the may traditional help the aim helped that The these they becoming of lear n perhaps, At have or to raises at make sure the endangered animals and are mixed attractive. money coming visitor and the in. In this way, more Ecotourism local is inhabitant tourists designed will to visit be of good cultural has that, some Galapagos ecotourism. means that closely. and All never have twice visitors – Some as the have they are all people many on go taken boats, and to have the think this tourists who lives at something the same time, disadvantages encouraged benet and so benefit keep to of of help to both people the preserve the keep safe alike. developed arrive tourists tourists meet there. Islands where the ones 118 The world surroundings NOTE: The person blessing groups remain natural the organising the of there the present inhabitants survive risk extinct inhabitant mutual to the to special there. They oppor tunities dances. and live people. hotels, be tourism to Ecotourism protect animals local running There special, generations. to the so of harm work? environment understand type to environment endangered T our of wildlife ecotourism Ecotourism protection and their and when different own they get so twice that well, the on go places impression works kind sleep can at boats. be that income. are they This watched different they his article, Attenborough of the In times the only should golden eggs – story about golden that will if talks goose this refers a eggs. you lose your lays to goose The kill about that a child’s that idea the lays here goose, source the the of is you money. Unit David Attenborough That will destroy always the blessing to the there islands would lesson who of live It looks as a, For b 1 2 or left of but if it’s lays the people around … temptation, there the on evil, is is the fact did now. are ecotourism your each the that local places tourism, though Developing A the nothing such So be Galapagos and be to goose conservation in doomed. seem the Comprehension writes: golden for 7: the is, not It a if get far was any all is that a not income be unless of the evil you mixed tourism from gone. It is it, the people conservation, necessary way so T ourism there that side best push would world the to eggs. you’re … forward. skills these questions, choose the correct answer, c. W hat is the main a to tell b to explain c to persuade you the point how the W hat is to introduce benets main b to explain c to show to how to so the of give point you why the ecotourism you a of of first can paragraph save the for second tourists Galapagos for ar ticle? animals tourists conser vation and locals projects paragraph? Attenborough’s many the endangered ecotourism money in work love succeed to in as a visit using naturalist the Galapagos tourism B Answer 1 According in 2 the Give a 3 the 4 In to the tourist three living W hy these is it ar ticle, how does ecotourism help the wild animals destinations? ways from questions. in which the ar ticle sug gests local people can earn ecotourism. quite easy to control the movements of the tourists on Galapagos? David Attenborough’s Galapagos Islands and opinion, their what animals, if would there happen were no to the tourism? C Answer 1 Find hope 2 one for W hat there’ these word the does questions. that David Attenborough uses that means ‘ without future’. ‘they all have the impression that they are the only ones mean? 119 Unit 7: Writing WRITING Writing In this ✪ about section, revise the tourist travel you use and tourism will: of modals to express r ules, regulations and advice in a context ✪ gather ✪ develop together the ideas writing for a piece process of of writing gathering , giving advice organising and revising. Exploring… Read help this visitor preser ve Notice how permission an the leaet, modal and which endangered verbs degrees of Welcome 1. You must always 2. You must travel gull symbol. You must 3. bears 4. You to in can feed stay the stay on in in in the to help tourists imaginar y) the leaet bird – express understand the ‘golden how to gull’. obligation, possibility. to only aims (and Golden your the group ocial marked led by boats trails for Gull an ocial with your Island the guide. golden safety – there may be forest. take photographs of the animals, but you must never tr y them. 5. You may camp in the eld next to the beach, if you have permission. 6. You 7. might even see the know time Developing Work with a you on your giant golden gull! to three 2 Give one thing that it 3 Give one thing that the Give one will that happen, thing have island! answer Give probably will a fantastic Welcome! skills partner things the 1 120 rare You should see some wonderful birds on your visit – most people do. We 4 extremely that are is these absolutely possible writer although the writer to ver y forbidden. do. much they is questions. hopes cannot sure is will promise going to happen, it. happen. and Unit You are now Time ink cave, the a ✪ W here ✪ Were ✪ Was ✪ Were ✪ Was there heard about. the visit, the wildlife Make these in a go any small and safety things that Your safe or have park , verbs advice a visited nature your what leaet for a visitor. as a tourist, reser ve or a for example a zoo. ask one answers. was it another For questions about example: like? instr uctions? you were you that not could you had allowed do, to so to do? long as you followed a rule? do? skills you job work is and the to not whatever for group, in that any thing stay notes or your imagine own talk any thing there your you wildlife you there there Applying a that modal did write Writing think to Use to place par tner, visit. Now a museum, Time With to about a going 7: sor t one write do was of for a any of the leaet places for damage to you visitors, the talked to place, about help the them or enjoy buildings, there. thing you might put into your leaet. Use headings: ✪ Rules/guidance for safety ✪ Rules/guidance for enjoying ✪ Rules/guidance for making sure the place or wildlife does not get harmed. Time to write: leaet the to place advise Use your notes to help you write your leaet. Try to write between 100 and 200 words. e leaet on the last page about Golden Gull Island can give REMEMBER: you ideas – but use your own, if you can. You don’t have to use numbers – Bullet points can help you you might decide to write it as a paragraph or two. Or you could use bullet organise your ideas if there points – one bullet point for each separate idea. Make up your own title. W hen both the you use a have few nished modals writing , to help look you at one express another ’s your leaets. ideas? Did you Did you var y sentences? are some you want and you have complete given your one another a few helpful ideas, work to Modals can shades of concise W hen short ideas or a list include. help you meaning express in a neat, way. separately leaet. 121 Unit 7: One ONE step further STEP FURTHER Think In this unit, tourism. detail how read be pairs, of of with for from can a on dierent consider the aspects this people further living in of travel and see popular and in a bit tourist more areas. partner about how the Galapagos while preser ving three most the when Share about to aect extinction. times animals? going tourists, decide saved think thought now previously attractive In are tourism Talk You you’ve You the your W hy needs ideas you the are make and animals decide people with Islands animals impor tant did of the on in you these conict the area environment. think three? with should Can the you needs class. Read e in mountain the world. To national park improve the Local as guides or cooks. food set but and this the has one e had an set tourists – so the a a gorillas most gorilla, on unique for benet, such of tourists used as e endangered Uganda the system for are too, the impact up enjoy Prots projects, of mountain Uganda culture. other is accommodation projects up Uganda save provide conser vation Uganda – help of situation, people Ugandan gorilla created people living ‘community and animals get there. To tourism’. employment experience, education, a sampling health or too. Batwa Trail: http://www.ugandawildlife.org/explore-our-parks/parks-by-name-a-z/ mgahinga-gorilla-national-park/activities/item/85-cultural-encounters-in-mgnp The For Batwa generations, Batwa: for forest they the are and Trail, home on park to heritage. was their dense forests fierce were warriors established low-impact, re-enter which while and home who to the depended indigenous on the forest medicine. abandoned permitted Batwa cultural food national and ancient 122 Mgahinga’s hunter-gatherers shelter , When the Trail their visitors enjoying Batwa cherished will nature the nomadic discover walks and were evicted lifestyle. forest the is as magic learning The tour of the about from only the time guides on Batwa’s the Unit The to Batwa make women and demonstrate bamboo of the leaves Part of cover the 1 Tr y tour with work b cherished Imagine invited a you b the arrival sense of goes directly to guides books, and improve meaning of the notes in research OR: e ‘fading Trail Batwa You a member the Cave, echoes this fading musicians and once eerily a plants refuge around the and for demonstrate the Batwa, depths of the how where dark the cave, culture. the rest goes to the Batwa community fund to livelihoods. following , and then use a dictionar y to check . of the national Batwa tribe. With a partner, decide how you feel about: park tourists the an headings ar ticle ‘Positive feelings’ and for a In this ‘Negative and unit, feelings’. check you: recommending when may website on do man thoughts or and you talks of Imagine changes of medicinal ✪ talked about journeys ✪ learned ✪ listened ✪ understood ✪ reviewed active different uses and being a tourist or visitor holiday some some useful vocabular y about travel and tourism extra to some recordings of a conversation and a tour guide rst. culture’ people. and Reect magazine Uganda. richness their Garama which out tourism. under Write Batwa sacred song point further lifestyle Write the the the honey, step partner the of of community travel the sorrowful moving and are creation EI T HER: to gather One culture the Make are perform nomadic a c techniques, a a out low -impact, fading with fee fees a c 2 to Guests community guests school Talk cups. hunting 7: the you about woman. have gathered and information passive verbs, from and a spoken learned about text their Batwa are feelings and the an old Write about seen. Do ✪ read ✪ revised ar ticles ✪ learned about endangered animals on the Galapagos your conjunctions and ways to var y sentence structures the about modal verbs to show future, and level of you cer tainty feel optimistic about this as letter – the you a to or pessimistic future? diar y your decide. or You an could ✪ learned how to ✪ wrote leaf let give clear advice in writing write a and a travel ar ticle or diar y/letter. imagined grandchildren Check you necessar y, A sk for feel go help confident back if you to the need about all section these and things. revise it If carefully. it! 123 My UNIT In 8 this unit, learn, the dislike In this unit, make W3 texts, S3 the their will learn organise accurate and use and involving asking around you produce will subjects understand L3 you about collate, R3 Schools studies questions, study, where and young what they people like present vocabulary and information complex sequences and relevant detail grammatical from language of speech, expressing a variety and more of with short abstract answering opinions structures and, and longer appropriate, spontaneity and Look at the where dierent people kinds of words: learn school or elementary college in the box on the Time a school 8.2 to My one in you the ✪ what ✪ how ✪ the tests ✪ the stage 124 ages the countr y. school, you dierent If you and explain been to you ink these any of dierent them? talk been about about go in to an your the system about: each stages schools enjoyed children always uncer tain could examinations you schools have feel star t different different or Have system, children the the group, country experienced. ✪ small the or kind, or schools change as children most stage, are and school called you take of get at why. older each stage kinds school, school, school, secondary school, middle school, private school, state college, a think countr y ’s have in about home international home or another. to notes your talk home Time Make to par tner infant primary right. boarding With uency. world kindergarten, Places spoken material as Useful 8.1 and studies. collate extended they about to: of some think of school, day schooling school, sixth-form school, home Unit Time Prepare in your Give a in 8.3 in and your the in a the to group par t) of of ✪ a teacher ✪ a grandparent. are not Take going ask small ve Find of you out to give ‘self ’ – how is the a as you much the own the school system have as you dierent heard can the about school the systems what a ✪ an point you your your details the of topic view – of ‘homework’. you to thoughts. new ‘self ’ suppor t Here agree your are going But to you imagine you ✪ have you ✪ organise it are some with any ideas of about these? views. Homework to role employer because: learn the parent in makes on people: ✪ on take think. would and should following prepare far person discussion your good practise of would to examples Each learned it about when between age have minutes Homework ✪ group questions group. ve. your to new homework ✪ of going your ink to dierences one student what a think a are to part ✪ You give ready your Time Work to world. Play (play Be speakers the talk countr y. talk. similarities is should bad do because: your schoolwork school causes too much REMEMBER: stress group your time ✪ there’s no time for you have to take or responsibility it stops you wasting as important time ✪ it spoils ✪ it’s relationships unfair to some at home children, Use it improves your example grades. encourage nod or those who might quiet space at have your smile. talk but give discussion as a group. Each person talks minute, then they ask one another questions. for can about Remember these your own ideas – imagine what your character would the group discussion agree that going there for should between be more ve and ten homework? think minutes. Or – to idea, us an add and did to Show to another you help – by have asking not to Can help to catch for them them expand example: example the of ‘Can that?’ discussion, ‘I see what you If you want to on you You for …’. mean, disagree, say. do Keep as are I not one carefully example: one listen language home. their Now a it not out, to have for questions have Time to body and listened ✪ you discussion, activities on speak. ✪ When class other is ✪ Thinking and speaking talk shor t home the other to 8: your it ‘I’m respectfully, afraid I can’t for example: agree with you.’ less? 125 Unit 8: Listening LISTENING In this ✪ section, listen to about you one will: shor t and one slightly longer text and answer questions Useful words: Verbs about learning: to learn …, them to take a course in …, ✪ listen out for information and details, and practise recording these to in various study course ✪ learn some useful vocabular y on the topic of ‘my Exploring… text you give School are going students, Sameera following the to and listen Jan. to ey is a are conversation at an between international in learning studies’. to e …, to …, …, up UK curriculum. ey have to choose three study at A Level for the last two years of helps if you spend time reading through the hearing prepares the you recording. for the sor t is of helps you ‘tune information you to or Economics, Computer you are You listening will hear to the Audio 8.1, recording Geometry, the answer in topic listen a gap in sure out for. of phrases. Use or W hich 2 To 3 W hat might 4 W hat university will 5 subject did did Jan Jan Jan decide write study a at course not to study at A Level? letter? university? does Sameera, at the moment, think she follow? Copy and students need to complete have be in the chosen any table for to their par ticular Subject show A which Levels. subjects The the subjects do not order. 1 Subject 2 Subject 3 Jan Sameera Developing Now Jan you and their First, of your going Sameera. to skills hear ey go the on rest to of the discuss discussion the reasons between for choosing subjects. look page 126 are at 127. the know a these and phrases With few a useful words to describe school subjects at the to the top or up a words and dictionary add any your partner , make word whom you meaning new Word take it in sentence between. 1 course and these with vocational advance to minutes ’ Technology, school. should twice, Social Science, four A As Geography, Science, needed questions. …, school questions in’ drop Geology, Make of a stop two Philosophy, It to subjects: Archaeology, to to … Literature, subjects follow ways phrase. if words Book. turns for each Unit To prepare par ticular yourself, talk with a par tner about the benets of studying Useful W hy study English ✪ W hy study Mathematics? ✪ W hy study Geography? get good grades’ is Literature? not words: Negative useless, words: uninteresting, a satisfactor y answer! Positive keep the conversation going by asking about the subjects that both time? some studying Give of at reasons the the why vocabular y moment. someone in the Do any might subjects disagree seem with a waste you. Tr y of to the questions rst and use box. the sor t of answers you will Make give. en listen carefully to sure Audio 8.2 and answer the you of challenging know these unfamiliar the words. ones to Add your need Word to creative, your meaning consider useful, stimulating, you any Read difcult words: relevant, are pointless, irrelevant, fascinating, Now Comprehension subjects. ✪ ‘ To 8: Book. questions. B Answer 1 Choose Jan they b he c 2 the chose a he Copy these knew the help him and each in the to complete because would them table to answer subjects they found answer correct his will questions. his most then question him career. a great ar tist. thought-provoking. put – sentence. … future make the one Jan, tick (✓) Sameera in or Jan W ho thinks studying W ho W ho a is no pur pose row to of show the them. Sameera neither in Ar t? says world there each neither Histor y safer says can make the place? Science has no useful pur pose? W ho explains the value of studying Science? 3 Jan explains examples 4 why that According to he Jan, he thinks tells how people Sameera can should study Ar t. Give two about. studying Histor y improve the world? C According learning to the audio, what are four benets of people Science? 127 Unit 8: Grammar Grammar In this ✪ section, revise help ✪ prefixes build practise Prexes In Unit of letters 4 meaning help you Some and your suffixes un-, dis-, you learned that or can par t be of give im-, about added new learn suffixes il- how understanding meaning. word them can and For be with spelling. ir- and root about help opposite also help prexes the Knowing the can to and some to words, words prexes opposite and speech. understand but and vocabular y prefixes prexes the will: using adjectives, give you to suxes change prexes you spell meaning. added to and small groups word’s suxes will correctly. Often, verbs, – the these nouns words and are adverbs to Spelling As + happy unhappy general add im- with (adjective) im • add il + allow disallow + possibility + + impossibility responsibly words p. mature il- l. to that start For example: ➜ immature words For legal that start example: ➜ illegal add ir- to words that start (noun) with ir to or (verb) • im m + with dis rule: example: • un a hints irresponsibly (adverb) ir + r. For example: rational ➜ irrational However: • 1 Use prefixes meaning. to Look give at the the following ‘ Spelling words hints ’ the box to opposite help rules practical b are some c natural d necessar y e legible f relevant g satised h regular i moral j literate k polite l interesting Use a them your dictionar y understand 128 in to what Word check all the Book you in are words for unlawful, words to the example: take unreal an in- appear prex. Write exceptions above, unpack, you. • a there groups, correct. mean. under At the the correct same time, prex. check you For example: in + formal ➜ in + complete informal ➜ incomplete Unit Sufxes The -ly, sufx -ly is thoughtful -tion used to sufxes The most -tion and common -sion make But you For example: add -sion comprehend -sion one collection evade adjectives into adverbs. For example: is are (notice to root used tion, for there words to make verbs into nouns. example: is that only end one in t) d de s or se. comprehension evasion REMEMBER: have the 2 3 -ly Add to these adjectives into b happy c soft d hopeful e crazy f noisy Write down spelling question -tion Add the a you had to to change dictionary to these check verbs your b irritate c pollute d protect e confuse f explode g extend h erode the a correct root Jan word wanted university. b Sameera noun in to Jan to d was his use to these sentences, using his at (educate) it hard of was Ar t. to reach a (decide) sur prised Sameera in continue found love by Sameera’s (react) looking of for ward her to studies. the REMEMBER: (complete) e e Sameera enjoys all arithmetic, of f high even numbers. when Remove the de or the necessary. the (divide) Jan knew he would have to spend long hours on his g of word. brackets. . c you spelling into imitate the root the spellings. a Put Sometimes change 2. -sion or Use rules to adverbs. clever nouns. 5 make a answer 4 Grammar thoughtfully The collect and 8: They .(revise) both study. needed a lot of to (persuade) 129 Unit 8: Vocabulary Vocabulary You can expand more common bio means – -graphy micro- -logy 1 ‘life’ means 2 the a a autobiography c biochemistr y d automatic e microscopic some Work ✪ Tell each ✪ Use a 130 a the sufxes. Greek word, meanings For as of some example: do all the following: the the story of words suffixes someone’s below. and root Use life. your words to help. dictionar y. b ✪ is of prefixes, autograph Word from biography meanings of with are comes learn and ‘writing’ a Below you ‘self’ knowledge Check it if prexes ‘small’ example, E xplain vocabulary words, ‘study’ means for – means means auto- So, – your root with a subjects par tner another dictionar y Book. a Biolog y b Zoolog y c Archaeolog y d Psycholog y e Microbiolog y f Geolog y a to you to might decide sentence check if study what using the the necessar y, at university. words mean. word. and add to your Unit 3 Copy the a and root words Sameera’s she b He loved loved d Jan Jan of f 4 The W hat that 5 learned to in become rock study Use this a word section based to fill an on one each Vocabulary of gap. because histor y. many facts about the Ear th as he formations. instead tiny life of Medicine, as she forms. some details about his life such as his bir th. became human have sentences. studied gave date e to these decided ancient the Sameera you sister learned studied c complete 8: a as he was fascinated with the mind. word suffix ‘zoo’ is shor t for ‘ gardens’. in question 3 turned a noun into ‘someone in question 3 turned a noun into an who studies thing ’? W hat suffix adjective? 131 Unit 8: Reading non-fiction READING In this ✪ section, read a you NON-FICTION will: non-fiction text about why it is impor tant for young people Glossary to do spor ts and games at school bonds ✪ identify relevant ✪ organise close curriculum and relationships information present the information in different ways. what about… things that normal Parents and teachers will encourage you to study hard. ey expect responsibility is to learn you for how to your to do homework own manage learning. your time and, An as you get impor tant older, par t of at you school activities do outside hours (notice the will prefix probably learn school extra-curricular Think you to and suffix) take this process fine motor abilities eectively. for skills using example thread a physical small using movements, fingers to needle Exploring… good We all need to balance mental lear ning with physical team works Read why the ar ticle spor ts page are below, good which for you. is from en a school read website through the player someone who activity. and well with other people explores questions good on work-life balance right amount of work right amount of leisure just and the just the 133. so you gross have a motor healthy skills activity, mind physical abilities using the whole body, for Why students should have to do sports at school example learning to kick a football A lot of teenagers, should be simple – forced and to through sometimes take sport, part in young their sports people parents, at our too, school. develop in ask why The mind teenagers answer and in is body. quite mental to physical help just to at foster the school, physical but and throughout mental their skills lives. Let that me everyone explain needs this in do with the mind Sports – to do with the body not more detail. social skills abilities that help you to get on well with other people Firstly, we regularly. they too can late all know continue – how Teenagers to start important who play through this a it is sport adulthood to are into eat properly starting old age. a and habit It’s never develop. In class, students are working hard at developing skills. There are many opportunities while they draw, or learn musical instruments. But they have to sit Sports allow young men and women to develop early that – or still most what motor of the time. are known as ‘gross balance, strength, which will help them lead healthy lives. sports help their fine carry out experiments, skills’ – the whole-body skills. Through structured such as swimming or football, students develop 132 exercise too habit. Now for my second reason. Think of the physical skills that motor exercise of physical activities, agility and Unit The third skills. solve in a Many with here Colleges on or is a and – on and of taking days other basketball practical need you people. team? reason, universities like in a to be How In in to sport a is how good better addition, form. position denitely of not One case see Extra-curricular a part to develops team learn you’ll it player these learn to social and skills Comprehension to than develop close teammates. application took Last these with your balance. your you jobs football Next, advantage problems bonds life big 8: – haven’t are example you already candidates activities good leadership, least I that such as should always of these team do convinced have a is a good good thing sport, you. work- to put especially if captain. sport because it’s fun! A Now 1 read ‘Spor ts needs.’ 2 W hich help word 4 foster of in to 1) the have According habit to article (paragraph teenagers 3 the no the first in about 2, a why answer and what paragraph choice par t and physical Explain paragraph taking again, mental this tells it questions. skills that ever yone means. you whether is the good or that not for in this they school do school spor ts. students to create a spor t? Give two examples of activities the writer says develop fine motor skills. B Answer 1 Choose The these the word are b take c are correct 3) sug gest planned place In paragraph 3 According can to be ver y inside difficult 2 who answer ‘structured’ (paragraph a questions. 3, and find in the that complete phrase the the following ‘str uctured activities sentence. physical activities’ … carefully. a building. challenging. one paragraph good to ‘team word 4, that why do players’? means ‘the employers Give two ability these to days move want quickly ’. workers reasons. C Answer 1 Choose The a 2 the word ‘ bonds’ ar ticle five questions. correct physical This List these answer in ties. b explains different to complete paragraph 4 emotional why it reasons is means links. good the the for ar ticle following sentence. … c economic students to connections. take par t in spor ts. gives. 133 Unit 8: Grammar Grammar ✪ ntences ✪ within ragraphs ✪ in different using ng as . of If the the not of ere engine, Without links writing words to var y are and way. the one the e links the be links, , weak , Sometimes ma each these are clunking tr y sting. paragraph connective train. it. kward, will a piece them. a owing nt a li the e train n best to ma ake ks a ar e obvious. s s 132–133, which er. s e for writer each stead, the lists cou d paragraph, writer us stron ng have us u se ed d an nd d connectives. f the article ntences or again. phra Find n es s hat an nd d lin i k phs. A lot of teenagers, should be simple – help at to forced through foster school, Firstly, but we regularly, sport are all in the sometimes take sport, part physical know order into old how to a and their habit of It’s a their sports people lives. is healthy exercise never too our skills Let it parents, at me to in that eat early The or why and this in and too more – – quite Sports not detail. exercise who continue late is body. needs in Teenagers can teenagers answer everyone properly they – ask mind explain lifestyle. that too, school. develop mental important achieve age. in young throughout starting adulthood and to to play a through start this habit. Now for develop. 134 my … second reason. Think of the physical skills that sports help just Unit 2 Now go through phrases that Connective Connective 3 they You use Below is box. one a To the Do of before as make a mixture of with to get vegetables get oil is hot, keep a drop stirring the 4 frying down Here is There and the are your so cook phrases or words and it healthy a a ‘signposts’ paragraph, healthy words could phrase a ve fit rst too. lunch. and more the clove them or put oil as phrases in more than in than once. step then minutes lunch pan to of vegetables mixture the known inside ingredients chop tablespoon the , sit the , Put to after including your ideas nally sensible, warm. or word stage you list writing. connective this all sometimes and healthy get is the any nex t and paragraphs. the how words use onion. It through about doing the article lunch wok the the doesn’t garlic into your into into up together: of and small and put plates one pieces. it on into the the to pan. the pan. burn. will stove. oven be is With a bit of to luck, ready. , eat. first four paragraph sentences of the here. text With a from the partner, last talk section. about Hint: not how each sentence is linked to the lot of teenagers, be simple – help just to at more forced through foster the school, and to sometimes take sport, part young physical but in and throughout their sports people our skills lives. in that Let too, school. develop mental their parents, at the connectives ‘signpost’ words are – the next. find should Here, simply links A Grammar phrases sentences the not the phrases are you link gaps is a and to Some soon and guide of remaining paragraph place. nex t as help rest the words them Complete the link words because can the 8: ask The mind why everyone me explain in more subtle. Can you them? teenagers answer and are is body. needs this – quite Sports not in detail. W hen you practise come using to the writing connectives in section your on own pages 138–139, you will writing. 135 Unit 8: Reading non-fiction READING In this ✪ section, read at a you NON-FICTION will: newspaper repor t about the number of hours children spend cited school ✪ learn ✪ identify Glossary some useful and vocabular y present about relevant education referred as Class/Grade/Year evidence a year group details. competitive the when worldwide jobs Think to or taking part competition college in (for places) about… Countries around the world organise their education in dierent ways. ere is no right or wrong way – ever yone is tr ying to nd the best way contentious which is issue likely to a subject cause an argument that suits their countr y, their education system and the funds available. correlation with link to Exploring… disadvantage Read the children newspaper in India ar ticle spend in below, school. which en is about read the the amount questions on of time page reduces the rote kids spend too much school? … Arriving the globe. authorities education a at … ideal to make than School in hours Mexico Bir school hours such Arundhati ‘It is time more well designed … Why extra 136 to of not in their on any gadgets and rote that hours?’ she High will our of the existing as stated that stayed the as globe 777 hours School the help in issue the for US around United longer. for States US students school … only them with hours per with education in were at shorter secondary a year to students those in year. points better time learn. of out learning Today system that longer education. ‘We or think children needs to ¿nd which Parents’ Teachers’ Association working the hours makes activity-based suggests. little correlation extending learning introduce open by that learn ways to says. president than 2009 students 1,167 hours classrooms important utilised not Podar school schools across as gruelling RN in a contentious been cited students. spending learning,’ she Chavan, had have their their signi¿cantly a remained hours keeping Duncan have regarding children … vary up may on for Chinese Finland principal be informally guide then like Avnita keeping case and spending shouldn’t a has school disadvantage’ as Indian countries hours longer secretary Arne ‘competitive hours school India’s days of are extended learning planned school. or Our hours demanding learning time utilised at … properly academic seem recreational like a says: and is burden. activities in of that success 137. gruelling Indian something chance the used or learning tough by heart Unit 8: Comprehension A Read 1 Find of 2 the and the article copy the again phrase and in answer paragraph the 1 questions. that means ‘in all countries world’. Choose the correct 2, answer the word to complete tells following In paragraph a that the writer thinks the Mexican system is b that the writer thinks the Mexican system sounds c that the writer has opinion no ‘gr uelling ’ the on the you sentence. … a good Mexican one. harsh. system. B Answer 1 Look a at these the Thinking children b Thinking According than they of about to children 2 table questions. children attend about to to statistics for for Arundhati need be for in the children attend (numbers). in the classes least classes most Chavan, many 2–3, which number of 6–7, which number why Indian do countr y of the children expects its expects its hours? countr y hours? extra and hours their seem worse parents? C Answer 1 Give one children 2 3 word may Ar undhati might be ‘India’s 4 spent. to sentence to are two by the to idea sug gestions sug gest of more for how that Indian hours the at extra school. hours they? hours a means b spend less c spend the time time same children needs sor t W hat down Chavan case that have for the been cited by keeping their schools US government the United open wants States for longer.’ American … more W hat Ar undhati makes school spend system by weighed make a ‘ Today used feel longer children questions. Chavan authorities This these of at in school time learn to school, find at like than school informally ways learning do children Indian as on their guide … you think this in India. children they to do do do. now. gadgets such and our education learning.’ refers to? 137 Unit 8: Writing WRITING Writing In this about section, ✪ learn ✪ revise ✪ practise Unit 7 formal. and you make sure informal writing idioms connectives/signposts. learned this also and about… you In of using studies will: formal use Think In you about the my unit, read you a use about you heard more the using two formal correct the passive students repor t. level of to make chatting W hen you writing quite write, more casually you need to formality. A With of your formality, 1 a I would partner, from like to ver y be put these formal to considered groups ver y for a of sentences in order of those casual. position in your establishment. 2 b I want a c I would a Give b It job in your like to apply me one would be delicious 3 4 of – a it’d job be in yummy great! your shop. cakes. appreciated if you would give me one cakes. Please, a Please b I’m c Sorr y, a You’re b You are c It excellent is for those most c can I have accept ver y shop my sorr y, can’t but on I’m to the extremely to of those apologies, come really one lovely but afraid I I cakes? cannot can’t attend come to school. school. school. ball. aler t. see how perceptive you are. B Work 1 Decide with if your these features ✪ using idioms ✪ using longer ✪ using impersonal with Look these 138 at ‘It the are to answer formal words constructions 2 partner star ting questions. informal: ✪ using ‘slang ’ ✪ using the ✪ using polite ✪ using shor t …’ passive phrases forms (abbreviations). sentences features or these were in section used. A one more time and see where Unit Time You are to going Each account Here are ✪ You the to write should on a two be trip and accounts about informal of the 100–150 same event. words. to a museum organised by a company. ✪ The transpor t ✪ The exhibition ✪ The restaurant ✪ You were Now formal Writing facts: went local write: 8: write they tired two arranged was poor. boring. was and was poor. got accounts home of the late. event: Hint: could ✪ Write one version that you send as an email to a close friend. ✪ Write one version as a letter complaining to the company. calm Here use are in some your before the idioms you writing: storm the quiet, peaceful period before a moment You can add ex tra details. For example, what was wrong with the of great activity or mayhem transpor t? W hat did you see at the museum? W hat was wrong with cost the restaurant? W hat did you eat? W hy were you late an arm and a leg was very home? expensive W hen you have connectives also linking to the nished link your your writing , ideas paragraphs – not check just that inside you each have used a paragraph, few felt under feel very a nal, improved version of your are some never connectives that might rains be one of To show ideas show the or addition events and, besides, addition, on progress next, through time eventually To position above, show not lots of see eye also, top of afterwards, ahead below, of me, on in bad but it other thing pours! things happens, go wrong too. useful: to someone To did writing. When Here weather well themselves. It Make the but not only … but also, the the after other a side, long agree with something in everything nally, eye over time, the last in series a straw of the last problem problems directly background, behind us REMEMBER: idioms if informal in a not sound check spelling If use and and too a writing you situation, REMEMBER: to to are piece. formal to Try you few an are writing take care casual. Always remember correct your punctuation. 139 Unit 8: ONE One step further STEP FURTHER Think In this unit, section, and you’ve you are considered going to look dierent in more aspects depth at of your how studies some – people where, what overcome and great why you study. diculties in In this order to study learn. Talk Some with people condition may that a partner nd means In pairs, ✪ how schools ✪ how school education they learn dicult at a to slower access – perhaps they have a physical issue; or they may have a pace. consider: can make buildings life can easier be for made children accessible with for mobility, all, for hearing example or other including issues ramps for wheelchairs. If you face this sort of diculty, include your experiences. Or talk to friends and relatives about their experiences. If you do not have any experience of this, tr y to imagine how it might aect you if you did face diculties. What would help you enjoy school life in the same way as ever yone else? Read Helen Keller was born in 1880, in Alabama, USA . At 19 months, she had an unknown illness that left her deaf and blind. Keller was However, of using the extremely she began signs as communication e birthday to she conversation. intelligent By realize did. the became of her and that Feeling age so of tried her their six , urgent to understand family members moving Keller that later these lips, wrote soul March 3, 1887. Later Keller would call this day her “soul’s birthday.” … few young women would have persevered through the tempestuous rst weeks of the relationship. Keller hit, pinched and kicked her teacher and knocked out one of her teeth. Sullivan nally gained control by moving with the girl into a small cottage on the Kellers’ property. rough patience and rm consistency, she nally won the child’s heart and trust, a necessary step before Keller’s education could proceed. Sullivan … ngerspelled the names of familiar objects into her student’s hand. She also innovated surroundings spoke ew in outbursts Anne Sullivan came … to be Helen’s teacher on 140 she her her to into one a through another rage when autobiography, occurred daily, with she “the touch, their was need sometimes smell mouths unable of to some hourly.” and taste. instead join in means of Unit 8: One step by incorporating Keller ’s favorite activities and her love of the natural world into the lessons. Keller this “nger play,” but she didn’t understand until the famous moment when Sullivan spelled further enjoyed “w-a-t-e-r ” while pumping water over her hand. Keller later wrote: “Suddenly somehow I the something it free! ever y … felt object myster y that was wrote that I which of built the Talk I language had days a over that … a as was my name, of to did that with to Helen’s forgotten I knew word gave – a then to a new but her explore constantly, love of language, … them joy a in the order impatience meant gave As it we the light, and wonderful hope, returned to joy, the cool set house my hands coached and and her grace as in a learn the the name of give-and-take writer and public ever y of speaker partner rage and soul, thought; foundation. Explain when returning “w-a-t-e-r ” my with 2 into of thought. and Explain these phrases to one another, using a dictionar y to help. ew that awakened birth 1 a thrill life.” nothing ngerspelled believe me. living name quiver “I to at each followed, something revealed hand. and seemed Sullivan people this with of touched Many upon consciousness owing touched; conversation. were misty Ever ything object Keller a b patience why she Helen would fear and may have relief rm have felt consistenc y felt these them in the fr ustration c innovated emotions, text, 1 and to put 6: suspicion Write Reflect EI T HER: Write a diar y In from the teacher, point Anne of view and check entr y of this unit, you: Helen’s ✪ talked about ✪ learned ✪ listened ✪ practised ✪ learned ✪ read your school experiences Sullivan. some useful vocabular y about education OR: Research a person who has to recordings about choosing the right subjects achieved a great deal despite a understanding and gathering information from texts physical issue. Write an article about prefixes and suffixes for a school magazine about that webpages about school spor ts, a newspaper repor t on person. Examples: Stevie Wonder, education in India and an extract from an autobiography Claude Monet, Stephen Hawking, about Helen Keller Christopher Reeve, Frida Kahlo, ✪ revised ✪ learned connectives how ✪ wrote diar y linking sentences and paragraphs Evelyn Glennie. to write formal and informal pieces OR: Read Helen Keller ’s a entr y, ar ticle or book repor t. autobiography and then write a Check you feel confident about all these things. If book report, saying why you would necessar y, go back to the section and revise it carefully. or would not recommend it. A sk for help if you need it! 141 Life UNIT This 9 unit through variety In this R3 unit, make to the life day what you school about the collate, W3 is of around at at you school school, leave. life is It from the explores like for rst the young day wide people world. will learn organise accurate understand and use and to: present of relevant vocabulary collate and information detail grammatical from a variety structures of short and L3 longer spoken abstract texts, involving some complex language and more material produce extended sequences of speech, answering and, as appropriate, S3 asking questions, and expressing opinions with spontaneity and uency. Starting C hildren rst may time. – family 9.1 Learn you’re want to rst carers talking be a be mix ture safe and around storm my I them. in by has a life idioms at to matching been done school add Each 142 in butteries with idioms the in may two. their Suddenly each for with interest. idiom Up all friends, First that with in a to my (in below you might to its your meaning. mouth my tummy) I felt ner vous I felt really feeling scared ver y calm talk par tner, shor t sentence their changes! practise take sentences should it in to turns show contain the to you practise using understand word because or these them. when for ner vous until home it school be you. teacup was Time Now, star ting others Meaning hear t had of secure Idiom a about excited; idioms about some one emotions will think understanding e felt some to use will have and Time dierent children many they own If have Some fr ightened moment school the or Unit 9: Thinking and speaking Memory 2 I remember going for my 9.2 First-day memories school dinner. Our rst lunch was chicken, peas and gravy. I remember balancing some peas on my Time to talk fork, and watching them wobble because I was so Work with a par tner. Take one of these memories ner vous. en somebody nudged me and the peas each. Read it silently to make sure you understand it went ying across the table and landed on the and then read it aloud to your par tner. Now discuss girl sitting opposite. Whoosh and splat! Peas and how you think each of the children felt when these gravy were all over her nice clean school uniform – things any of happened your to them. Do these memories trig ger I couldn’t believe it! own? Memory 1 Before I started school, Mum told me that my teacher’s name was Mr Bateman. I was scared I’d call him Mr Batman! I kept practising it as we walked to school. Mr Bateman. Mr Bateman. Mr Bateman. e more I said it, the more ner vous I was. Oh, it was awful!! 9.3 My rst Time Spend can’t You a to few memory minutes use some How were ✪ W hat ✪ W hat were other children? was you back home? back another these was name impressions feel about to your your memor y prompts W here teacher ’s your did of you? your How thinking choose ✪ ✪ old school think remember, could of to your and of help day use and did at school school early your what they classroom, day at your or school what the first rst from own did look the it if you ideas. look like? like? teacher when – schooldays. you and the got REMEMBER: Make a few notes to help you organise your ideas. When you give a talk describing something that has happened, try to use your tone, Time to your voice and your body language talk to make the story interesting. Now give a shor t talk to your par tner about your early school memor y. It might be sad, funny or just Tr y to talk for a couple of minutes. interesting – but make it lively W hen you keep the en it’s have nished, conversation your going , par tner maybe can ask asking you for questions more to help you and keep talking as smoothly as you can. Don’t worry about saying details. ‘errrr’ or ‘ummm’ – everyone does your partner ’s turn and you ask the questions after wards. Don’t that, even professional speakers! ask yes/no questions – they don’t lead anywhere, except to silence! 143 Unit 9: Reading non-ction READING In this section, ✪ read ✪ identify, a rst organise day children. children will: non-fiction Think e you NON-FICTION about children’s present relevant first day of school information. about… of W hat be text and school will can the be a school worr ying be like? time Will for the many other friendly? Useful Dierent countries have make transition dierent ways to help It the from home life to school words a little is traditional/customary a There Exploring… birthday is candles many years or in customs one are countr y. actions that Sometimes have been people carried forget how out the but they still do it a Read this children First In ar ticle settle This gifts, ago, Other is ‘Admissions year, the sides red is the in all it is to a in The with bag’. countries help young to (the rainy an school black for and is the it with soon, of first is a day of schultuete. made sweets, around at small one of small 200 least as it is a in boys. colours. known) as among bag, gifts to example. season) bags, the fact, star ted end umbrella These on if years the it! India special In traditions children stuffed tradition school. shapes their tradition unlikely the Austria, give shape, include and sizes, some world and ‘school do follow into randoseru. girls, ways (praveshanotshavan often a a monsoon usually called for come 144 the parents gift also step Day’ of as cone anything countries Republic suchlike. popular impor tant – grandparents large and so have beginning Czech and a traditional school translated it’s pencils but children that be and the school. of the parents can paper, into the My family has tradition anyway. skills about day Ger many, school, your tradition on birthday Developing well the past, These celebrate As is often as the gifts. backpack the to with were days, the In cake. of putting cake. for tradition the star ted, phrases: easier. have Traditions and children the school Japan, sturdy coloured bags cake. always of followed eating Unit Other countries first day of The children ceremonies for the single In the at the day in The receive a instead a small known smar t school. but with is as clothes, and children balloon of a gift for the teacher. ‘Knowledge there often in are bring retur n. bouquet, the and a The Skills Day’. speeches flower take and bouquet Kazakhstan children Comprehension has a a flower. USA, it ter m was with tradition began children from The persists for the Russia up and tradition, school fees. in dress teacher, similar mark school 9: their in apple the poorer image to traditional an this most of day. 1800s, homes a for for shiny Many red children teacher. when who US outstanding young the It apples States as a to star t thought were otherwise apple is available could not healthy, have a the that to afford tasty Golden new the school treat Apple Award teacher. A For 1 According giving 2 schultuete will children give children enjoy c It is a large phrase ‘a a contain b are made c are large only cone from in be their children 2 Give day three of W hat C the gift these the Look at W hat is school at a with children sweet ice with 2 …’ can cream many sug gests tradition c. of sug gests that the cones … eat. wafers. things. that monsoon in India always parents want this day to c sturdy give their happen in children Russian an umbrella? schools on this first year. children receive in Russian schools? questions. 2 and point giving 3. traditions might or remember? that paragraph first-day W hy main the the b questions. paragraph regards Look the these the that a, parents. stuffed top parents things Answer as to b do their paragraph celebrate some unlikely answer, out? the thin, up do it correct it. things word W hy to is the cone. lled Answer why die it W hich one choose ar ticle, e 1 3 the e B 2 to b a 3 a question, a The 3 1 each of 3. dierence between these two paragraphs gifts? W hat of teacher paragraph of is Russia be the and given a main difference between the K azakhstan? golden- coloured apple in America? 145 Unit 9: Punctuation Punctuation In this section, learn: when ✪ how to use inver ted ✪ how to use brackets, Unit 2, question there 1 In you and other with the italics revised marks were Work use will ✪ In to you a a to show b to make dashes the use of punctuation to in is another commas basic for parenthesis. punctuation marks. In the – text commas, you have full just stops, read marks. answer schultuete it’s and exclamation partner ar ticle, commas in these italics. three questions: W hy? language REMEMBER: you read it ver y when c to emphasise you The it. 3 phrase ‘Admissions Day ’ has inverted commas a to show they are a b to show they are the c to show someone ‘the words in beginning the of translation title said ar ticle the of them have monsoon a book in a conversation brackets (the around rainy them, season)’. W hy? a to show the words in brackets are b to show the words in brackets are in brackets an c to explanation show are an the words afterthought comment 146 around W hy? Some are only writing use on italics a it computer 2 You loudly or a translation for example: when you or word are processor , writing by not hand. Unit Inverted Inverted ‘ Punctuation commas commas ’ can “ Inverted 9: be single or double. They always come in pairs. ” commas can also be called speech marks or quotation marks They • can the He • • title love a used words said, the I be a lm, song quotation, you then spoken in a conversation, for example: ‘Hello ’ of the commas show: actually write as shrink a ‘We for Shakespeare When to will or a rock song, for example: you’ example: wrote, out a marking it book ‘To be or not conversation, out the to you actual be’ should words. think Think of of a the inverted cartoon bubble, down. How are you? He asked, ‘How are you?’ REMEMBER: If you always think you’ll always put in the right of the places. the bubble, comma punctuation Here the and the the question speech inside The put the other a marks, speech thing comma to just mark just go as You need before the to put a words spoken. capital He H just asked, ‘How are you?’ inside they went bubble. remember before the is to words spoken. 4 Write out these sentences, putting in any necessary punctuation. a We went about b I a went My d I e e to cinema a school quotation brother ran the to watch Harr y Potter, my favourite lm school. on famous c to said school teacher trip To Have a singing asked to be see or good Oh, How are Hamlet not to day what you be at a and all was the waiting for the time. school. beautiful morning! today 147 Unit If 9: Punctuation the speech comma. I said to For the is not the end of the sentence, the full stop becomes a Challenge example: teacher , ‘Thank you,’ as I left the Make room. up some sentences Question stay as marks they are. and For exclamation marks inside example: the speech marks the I asked, ‘Are you OK?’ as I came makes meaning. in. partner . 5 Write any a b out these missing father got home. My brother me c Hello d e putting in punctuation. My saw sentences, said, I hear asked collapsed said the teacher Are in boy asked you you the fun tired when when he he chair. sitting the had girl next Can to I me. see your picture? e 6 She exclaimed love E xplain the pairs sentences. a i of My My b i ‘I I ii ‘I I said, his dad read his all all ‘Pedro these came home and ‘Pedro came home,’ and book. my my enjoyed ate between book.’ said, enjoyed ate painting difference dad read ii 148 I at school,’ I said, ‘and school,’ I said, and lunch.’ my my day day lunch. at pairs your placement marks the of of a of own the where speech difference Try them out to on a Unit Brackets You put include for the around sentence. If an extra you take piece away of information the words in you want brackets REMEMBER: Using brackets can using too to (or stop the sentence will still make complete can use brackets. a For pair of dashes or a pair of and makes many the sense. meaning You you ‘in commas, parenthesis’), Punctuation parenthesis brackets in 9: commas instead of a pair clearer . of example: Giving an apple to the teacher (a popular US tradition) began in the 1800s. Giving an apple to the teacher – a popular US tradition – began in the 1800s. Giving an apple to the teacher , a popular US tradition, rst began in the 1800s. 7 Use a brackets Parents their for give In America, c In Russia, d I e Japanese f had e a gifts you rst take children drink black ver y small in sweets, these pencils sentences. and notebooks to children. b and parenthesis a cup children for day boys of an take of apple a milk a with traditionally to big owers shiny huge my one to your bunch to their teacher. teacher. lunch. take a new backpack red for girls school. school in Russia ‘Knowledge and Skills Day ’ is special. 149 Unit 9: Listening LISTENING Glossary access In this section, you get ✪ listen to a non-fiction text about how an African countr y to learn education some for its practise more complex understanding vocabular y and (verb) about selecting relevant eating has been libraries of Lesotho is a small countr y in the middle of South Africa. working into to Money improve is life hard for to its come people by, by but the the introducing more you lack of difculties money of government schools. not the education words and phrases in the Glossar y on the learning time ministry right. of education department in education practical/impractical hard all school government Exploring… read the hardship by full-time another charge First at information. all – sleeping about… Kingdom countr y in, to caused e live education nancial Think to children go ✪ ability is and ✪ education school board improving to will: to do because of the Work circumstances with a par tner to check you understand them. oral of A Carr y out these tradition storytelling, Write five system. sentences Tr y to use about some of your the home words countr y and and phrases its in down education the to Now put the education its system weaknesses. Developing Before on en a few 150 you page Listen sentences to to the minutes’ the help carefully answer Use your star t 151 in aside. your listening in one of a par tner countr y, the words or small including you have group its about strengths been radio task , read through the talk between. given will by hear a teacher the practising. questions from recording Lesotho. twice, the and yourself. You stories next Glossar y. skills questions. gap own some prepare the Tell passes the part-time 2 tradition activities. generation 1 the where with education learning only some of the time (not full-time) Unit B 1 Answer W hat want 2 does to There 3 are that is to it job the for are do so the government young of are the people? transpor t available W hat it its modes about makes W hat 5 says Comprehension questions. Lesotho three Lesotho. W hat 4 the achieve speaker of these 9: to the the people they? countr yside hard to travel women itself around? mostly do, according speaker? What are the usual school hours? Choose the correct answer. 6 a 8.15 3 p.m. b 8 a.m. to 3.15 p.m. c 8 a.m. to 6 Give a.m. the W hat 8 W hy to three is p.m. three according 7 to it spor ts the jobs most popular with young people in Lesotho, speaker. is the impor tant teacher for these in charge children of to the be librar y able to trained read and to do? write English? C You your are home going to countr y instructions write and its a script for education a radio system. programme Follow about This with the map shows Lesotho the African continent highlighted. below. Challenge Time to write: radio script Work Before you star t writing your script, make notes on the following: to listen out ✪ what I like ✪ what I think about education could be in my improved with as may you the to find it help internet helpful you or to gather from work your other a ideas. people Find how. Read you it are aloud ready, to write practise your any par tner You you from could also the same research countr y or Take another turns reading scripts. this from things well interesting – you thought maybe some information or opinions. know. script. new one radio three Suggest W hen partner . countr y and with to your worked You a could difficult phrases and to become be three ways the script improved. as Consider: f luent Then as possible. make a Aim recording to of make your your talk. voice interesting to listen to. • the speed • the clarity • the details • the variety Make a nal, it was of spoken tone. polished version. 151 Unit 9: Spelling Spelling In this section, ✪ how ✪ what to use you will learn: apostrophes for missing letters correctly Hint: a homophone is: ✪ how to spell some A more common ‘School (a In the been text you written for missing listened down, to, you would starts letters heard have some looked full phrases like which, if they is phrase any short that isn’t easy there aren’t is ➔ not The For are speaking, isn’t letters are that example, in not have been isn’t, the run words together . For will in are to more show missed letter examples a ey ’re b is’ll c It’s which changing change o out has from not letters are shown been the have children’s the whole left by out an (omitted) from script. been is word ’ Challenge Write them out out go in for full: a run. in better start revising. He shouldn’t’ve He won’t done it. lives. countr y visit. unusual you try to help? For each of the following, put the apostrophe in the a didnt We b shouldnt c doesnt d shes e weve Write out these sentences, using shortened forms of the underlined words. Use an apostrophe to show the missing letters. a It is hard roads ey c Luckily, d are e At are using my home ey schools have going might eat horses school ever y break, with reach which do not have nearby. b go to to soccer close to stay are by so not I ver y am fast. able to late because they practice. children some them. which night. decided the is food who they in writing, the not couldn’t’ve was 152 write omitted. right place. 3 formal apostrophe. Won’t 2 In usually aren’t You’d full clock use example: Let’s Here the full. Write 1 of don’t many they ➔ for we had out people o’clock’. this: you When example 8 more). REMEMBER: this at homophones. O’clock Apostrophes difcult is are not have playing brought coming. seen what Unit 4 9: Spelling Write this out using apostrophes when needed. There are ten apostrophes missing. The schools in Lesotho arent ver y accessible. Often the boys REMEMBER: and apostrophe girls have to walk many miles to get there. Theyd like to go the evenings but this isnt always possible, Im sorr y to say. you home works they cant change themselves, things for and makes could. The speaker in Lesotho theyre months hard changes – to the at best said help a all time. of hes often it. Its a Theyd hoping its away from shame, do that, the but things in know the they’re apostrophe is in for a missing letter . family ever yone differently time, an and The standing fathers use it’s home when in Only for hell see if big people. Homophones Homophones are words that sound the same but are spelled Glossary differently. For example: aloud their, they’re and there its and not allowed 5 With test 6 a partner, one Choose these learn another the on correct the the homophones words, word from in spellings the the and brackets Glossar y. Then meanings. to fill each gap in sentences. a I bought b I nearly a fell asleep in class of shoes. because I was _____________. After school, an a bored not going _____________ the skatepark with ground-up a In each sentence, fruit He b From use a pair (or more) of homophones to the sky rule by a king or queen fill _____________ the top of the that ball cli _____________ you can the open _____________ window. correct, He went _____________ _____________ schools write put or down, for not but he is _____________ young when he ocean see use left class are studying under that _____________ tree over working hard for on paper your eyes past tense of throw remember. (preposition) from _____________. one _____________ words was through e or example sea threw ve, letters the _____________. d from gaps. a c wheat blossom water right the wood (to/too) reign 7 of interested my rain friends. plank two pear I’m clothing animal board pair (bored/board) c without bear ower (pear/pair) permitted bare our _____________ silently it’s _____________ side or end to the other exams. to (preposition) too two towards also/overly 2 153 Unit 9: Reading non-fiction READING In this section, ✪ read a ✪ consider ✪ collect you NON-FICTION will: transcript some and of of a speech the present made abstract relevant at ideas details the in United the from Nations speech the text. Exploring… e United that On of discusses 12 the July UN young were One of public to since countr y, the closing brothers child’s well bright peace It the about world Youth she her had she We of world was been of sisters, Takeover rst was section issues. education. known was future. and organisation Hundreds as and an ever around speak most speech is Dear of the rst place. from is impor tant the Yousafzai. home is took invited (UN) many 2013, people Malala her Nations travelling her we will education for rights we injured during on a an attack school in Pakistan, bus. speech: want schools continue our ever yone. and education jour ney No one to can our stop for ever y destination us. We Glossary will cause speak for our and will bring change through our voice. an believe must believe in the power and the strength of our words. Our change the in and to we we want are to all together, united for the cause of education. weapon and achieve of work to our goal, then let us empower ourselves knowledge and let us shield ourselves with make strong And lack of knowledge with or the to world. ignorance if people achieve empower Because that want words hard can idea We education unity together ness. illiteracy the state of being uneducated Dear are brothers suffering forget that and from sisters, pover ty, millions of we must injustice children are not forget and out of that millions ignorance. schools. We We of must must people not not unity wage that So our let sisters us terrorism wage and and a let brothers global us are waiting struggle pick up our for against books a bright illiteracy, and pens. peaceful pover ty They are One the child, Education 154 one teacher, one pen and one book can is the only solution. Education First. together , as one a struggle ght a battle Make sure these words you understand and our weapons. world. acting future. chang e and ideas. You most may power ful all forget need to use a dictionary. Unit A a, For b 1 or each of she wants her c she wants boys her says: shows hopeful afraid c indierent the first aiming To is the that they c that lack Answer is W hat a these ready 2, be for be can treated change the to … listen. work the because together. same. world.’ future. find one word that means ‘the place we of c the third future paragraph? … make is face many donations the biggest to problems. children’s problem charities. today. how says she she is ready chooses to words battle and for the phrases rights that of make it clear ght. think is the child which best c one weapon? Is a, b or c correct? writing word means that the problems facing children ever ywhere? No b Education c Shields Work come they sisters’ … children one 4, a C a these one the Malala b found of to can is have feel and questions. Malala shield W hich girls point food Explain does to destination must of paragraph can 4 about world’s paragraph children. In answer, future. ever yone b she correct future. main the a the paragraph, that In the at’. a B choose brothers relatives words b remind and Malala the journey W hat 3 for of and ‘dear listeners ‘Our that b a 2 family a are questions, listeners all In 1 her b Malala 4 calls a is 3 these Comprehension c. Malala 2 of 9: can sentences stop is are with the up the point of Malala’s speech? change. only powerful a sums way for ward. weapons. partner to answer these questions. 1 According speech, ‘enemies’ or Name four ‘enemies’ Name four things In problems paragraph ourselves W hat 3 Malala’s a b 2 to with does this Malala says do think you 2, facing that Malala the or the are a world’s number of youth. problems. can says: weapon there defeat ‘ let of us them. empower knowledge’. mean? one teacher she means can by change the world. W hat this? 155 Unit 9: Writing WRITING Useful at Formal words school: this section, you insightful, qualities, will: seeks condent, ✪ learn how to write a formal review and ✪ practise learn organising to check and your planning your leadership challenges, determined, helpful, repor t competent, ✪ progress writing effective, In about committed, ideas work . accomplished, successfully, adequate, inconsistent, reluctant, nds difculty improvement, Exploring… When you write a review or a report, you need to have a plan. Remember, with, needs conscientious, enthusiastic, reliable, independent learning, social skills you are not telling things in the order they happened. You usually need: ✪ to write an introduction to things the ✪ to identify the good ✪ to identify the unfavourable ✪ to offer opinion ✪ to use Adverbs: subject about the topic casual a formal or style judgement (unless the based review on is the for a facts reader a who expects a mean use less by check what taking them in a familiar Word your partner , understand style). Developing frequently, never things With an regularly, occasionally, it that these in turns sentence. words to you words to Add your Book. skills Most schools produce written reports on their students, to inform students and their parents or carers about the students’ strengths and weaknesses. e reports also oer suggestions about how the students can improve. ese have to be written in a positive way, to be encouraging. At the same time, they have to be truthful in order to help the young people. Time Here are Imagine of add two you them. can to invented are Aim any write: their for end-of-year students teacher. around details that and Write 100–200 you reports some an brief facts end-of- year words for each about repor t repor t. them. for each Facts – good lot class, at painting, in enjoys is captain basketball team, of Maths, very good homework done, does class, loves not at Physics sometimes like writing speaking stories. Layla 156 and not in and school loves Tai – History want. Music, Facts talks You Biology Yang a Unit Applying your Time Your to teachers for write: may college my have report to write a lengthy repor t on you when you or apply for a job. You are going to write this repor t – you don’t have to be totally tr uthful! You can write the would like to English, not Star t making by using e the how ( Your accurate notes under teacher it will judge it on the quality review to weigh or up report the of on each side, then make your is.) the headings below. en write the repor t subheadings. repor t Name on have. you repor t facts you A on expects yourself Writing skills REMEMBER: apply 9: of will contain the following sections: student: Job/course applied for: Strengths: Weaknesses: Recommendation (on Challenge suitability): When you reviews, Extending your skills and work read to write: school that your infant school (or another school of your from your early Find years) has asked former pupils to write for their school partner In your work: three golden words words which you – think a are review a through. own three choosing with your review • Imagine written them partner’s Time have a little unfamiliar but website. well-chosen. Make notes under these headings: • ✪ The school (for example what it looked like, the facilities, Then nd three signposts the – connectives golden three that help to surroundings) make ✪ The best aspects of the school (for example what you liked the happiest memories – choose one or ow, by best, linking your review ideas within a two) paragraph. ✪ The worst aspects of the school (for example what you liked • least, what you found hard – choose one or Lastly, links ✪ My opinion as I look back as a young adult (weigh up the good Your bad review website. Write Aim points Also, your for needs of to reach be in a it four 200–250 writing as must it be will be put balanced paragraphs, using on and an ocial school ow of linking your to writing. leave time notes to help you. If you one words. for golden ways has checking the punctuation well, in been can’t and spelling and nd another they with which made some between paragraph fair. your to where Remember three three conclusion). formal course, review around and – and the the nd two) by can kind one another . all these, help suggesting be added. in Then your produce a nal draft of review. 157 Unit 9: One ONE step further STEP FURTHER Think In this unit, dierent the of Talk help do your the about young of own children schools dierences, your and the life adapt to has a school, school educational world and life. systems shared a how You’ve around sense of the also the great think partner is the best system of education? Use these ideas to discussion: ✪ At what age should children star t education ✪ At what age should children star t taking ✪ W hat ✪ How the at education. with you help variety Despite impor tance W hat thought countries considered world. you’ve are the would most you impor tant decide which things in tests children education school? and examinations? learn system is at the school? best in world? Read Read this ar ticle, which is about the best education systems in the world. In 2015, the operation the to and world’s children which ey OECD Development) schools. in 76 countries found countries’ strength. (Organisation that ey had the there academic Perhaps a tests around best is is strong not in link and a report various the systems performance this Economic produced gave countries for world, of Co- on subjects to see education. between the economic surprising. Japan came second in the 2015 rankings. Again, the countr y expects hard work from its children. In addition, Japan makes more use of technolog y in education than any other countr y in the world. Another strong feature of their educational system is the part played by extra-curricular activities such as chess and sports. e government is convinced of the link between school success and outside activities – nearly all Japanese children are expected to take part Perhaps what is more surprising is the widely in these activities. dierent most spot is taken countr y education billion literacy – 158 South – its invests their is an write. Korea. great e work budget impressive leaves seems days deal result is used number It to seven yearly ever yone and a being e children school dollars. rate nearly read by attend education countries. expects children 11 of successful countr y e styles a of this hard: week. is 99.4 the one money that school in their per able cent to in Unit Finland 2015 list, spend to is in far many the topmost sixth less place. time in countries. examinations non-Asian e the ey until they countr y Finnish not reach take the the they students classroom, do in some compared any age the public of of formal tests, the teachers and to decide what to valuable next Talk 1 Find 2 a the with word ‘the richer b ‘the ability is it to Are any there are not education – on e can school schools take visits place and further believe outside eld trips, for carr y is hard teach for people to work out which is the best out of education when you can see how dierent each published can all gain excellent results. as partner phrase in countries to read dicult approach improve results a or a W hy 3 – countries. step 17–19. styles person many classroom form assessments in One example. It Instead are 9: to education got and in ar ticle better that means: results in the test’ write’. decide education, ideas the which according this ar ticle around the countr y to this that has the best ar ticle? you think could world? Write Reect EI T HER: your school about make your the Write a the school. ideas proposal board change to a or you headteacher would education You could included in like to system in use the and one In this unit, ✪ talked ✪ learned ✪ read you, though you have some it in more and If you look can, at the go about vocabular y of on school different countries’ the topic traditions concerning school learned about inver ted commas, brackets and dashes, and detail. on the OECD to punctuate ✪ listened to ✪ practised a direct spoken speech text about education in Lesotho internet website selecting and collating relevant information in for written yourself: useful memories to how OR: early to ✪ develop your of ar ticle will you: about star ting help check to and spoken texts http://www.oecd.org/ ✪ gave a talk ✪ revised on education in your home countr y education/ Choose an area of about that interests repor t on the you do the level same repor t, results girls in sug gest of the and OECD example, using apostrophes for missing letters and learned education write ndings. and boys Science? reasons tests. ✪ learned ✪ read ✪ wrote how to give clear advice in writing For a speech given at a United Nations Youth conference achieve In for homophones a about education or education systems. your the Check you necessar y, A sk for feel go help confident back if you to the need about all section these and things. revise it If carefully. it! 159 Education UNIT This 10 unit people is after education or it at further at evening this R4 unit, draw for L4 a Education will learn inferences, the variety extended of classes, you of years. at some education age self-study 16 or education recognise 18, (FE) in at open This kind in the or may of be college, workplace. education college to can continue university, apprenticeships or even home. to: make deductions language with and recognise increasing uency implicit and meaning creativity purposes purpose, implied meaning, attitudes and feelings in texts demonstrate S4 to opportunities of school, the manipulate W4 the age refer after through the at might Later , In about post-16 appropriate pronunciation and intonation. post-16 Glossary 10.1 Our choices 16–18 A Dierent and countries phrases in the have dierent Glossar y (your education school systems. may use Look dierent at the ones). words Make Levels and you understand these – you will come across them a lot over few Time a in the secondary list to of think people AP you know who are older than 16, and the dierent UK of (short learning they have done or are doing now. Make some the same kind of education you want for the next two years. Are or dierent? W hat are Use your some reasons of the for words these a and phrases Time to from the last US year what you both hope to do over the years. You conversation ✪ where ✪ what ✪ reasons 160 need going you you will for ask smoothly. hope hope to to to your be do choices. one You another could students two of following similar questions nd out: to a to qualication after a three-year next course two or schools curriculum; awarded out or by Level’ degree nd taken the talk par tner, Advanced course choices? ‘A a following they the Glossar y. With years notes secondary the schools for Placement) in about by two curriculum examination kinds taken nal years. the Make courses the of next for Levels) examinations students sure (short Advanced keep the at university Unit 10.2 10: Thinking and speaking Expectations Glossary Time to think and talk GCSE/IGCSE In what ways do you think education will be dierent been up to in the (short [International] two years of secondar y to use school school? these from Talk star ting how it about has your ideas in now, small since groups. the subjects you ✪ relationships ✪ homework You might Certicate of Education) – Secondary like points: taken by the British with subjects ✪ rules and ✪ clothing. the ages of 16 are taught (verb) to pass standard or college UK Can you to think your the after up to the school end of course equivalent school age of by looking at the photos successfully below. star t you or end? leave ink formal of examples education? you have at diploma gained (for 18) the by completing high all school seen. How? IB (short for International Baccalaureate) and to US secondary qualication conversation learning learn Time the learning courses does at the the university school the high W hen 18 discipline Lifelong for reach a students Prepare or required of Time and teachers high 10.3 usually learn examinations the following curriculum, graduate how qualications students between ✪ General star ting the ✪ for last set of – a course examinations taken talk by students in the nal two With a partner, talk about the dierent opportunities people have for years of secondary schools all learning throughout their lives. Be prepared to ask one another questions around the world and answer as fully as you can, to keep the conversation going. qualication pass required examination for a job or course qualify (for doctor) education example example (verb) you to to get need become as a the (for a doctor) 161 Unit 10: Reading non-fiction READING In this section, par t you ✪ read of ✪ learn ✪ understand some a NON-FICTION will: blog useful and vocabular y practise inference. Exploring… Read in this blog , Germany writes leave to about their which spend ‘culture home was a written year at shock’, countr y an by Judith something to Enders Australian study High ever yone who left School. her Here, experiences home she if they elsewhere. https://www.internations.org/magazine/culture-shock-a-personal-story-16175 Culture When one first year with the I shock phase also of I After … a to two host Many culture. experience I started I age was of the However , or happy soon and in enough my go to of feel friends High culture shock the that this to over School the shock feeling and didn’t before … last more head: more! ‘honeymoon Differences my with much culture family populated so so-called other odd. is for moon homesickness culture be increasingly to term months to started missing 16 completely frustration things thoughts the confuse weeks super months, Annoying people first are at family confusion, those you apparent. more. Australia foreign going about more a where was in with feeling to includes phase’ as live everything adjusting It arrived and However , forever . Glossary adjusting became fit and in changing understands me, my English is not good enough. … to find proper bread (‘proper’ in my opinion Why is it referring at Germany)? home! And I so wish on. public transportation would work the to same the next few way … I developed my own little cannot something honeymoon though, of you as … months, feeling because bread taken Over a so do from you better annoyance impossible that “Nobody frustration really so by a a romantic newly holiday married routine, couple learned to adapt unknowingly expect in most appreciate and made the ways dramatically – also and not of only many had my and my I own had in I had attitudes. vocabulary exclusively friends. phase’. adapted thinking dreamt new ‘adjustment situations, new thought … entered had behaviour My and what and English expanded English! slowly learned to inevitable learned had improved significantly but I over the meaning … started Every day I to felt make more sense and and more I understood comfortable moon ‘really Australian with my culture new better many new traits while also keeping idiom home. a period earlier ones from my of time, I my head filled home head country. This 162 I would process often which refer to occurred myself over my as ‘having last few a second months nationality’. abroad is a ‘stage’ populated adopted an happy’ … phase Things unavoidable to called traits characteristics my Unit the ‘mastery day remarked sound just I to want … acceptance 1 Answer W hat a, b is or us!’ out One is explain to say c to show W hat B was ‘You are when my dear Australian friend now, one Jude! You the rst effects for step sure of culture though: towards shock culture adjusting are different shock better is to a for inevitable foreign and culture. questions. point of paragraph 2? Choose the correct answer, c. to 3 that main b How moment conversation: thing’s the a 2 a happiest what that long that after made Answer early culture culture shock Australian arriving Judith these feel is shock nothing bread did is Judith fr ustrated feels like serious not ver y star t early to good feel on? uneasy? Name two things. questions. Hint: 1 In paragraph 3, how can you tell that Judith’s English has a high 3 what ways affected 3 In 4 Judith by Early Later 3, Judith this herself shock? how identifies complete of did culture paragraph Name can you different table, Give using change three tell that stages ideas stage of so that the phase ______________ phase Felt phase Had about Give you her two you B1 will less the more shock. to at Copy fill in home? to infer lines). text and yourself (read You work what between have the to out consider for answer is. and the gaps. frustrated ______________ Do C, ______________ Appreciated advice feels blog phase C questions section Feeling honeymoon W hat became the Judith culture from she ways. ______________ 5 answer and level? have In To reached and 2 Comprehension … these the My during like point everyone A phase’. 10: does think Judith give for Judith was positive experience reasons same for of living your in getting new ways attitudes over or as culture negative of an doing things Australian shock? generally Australia? answer. 163 Unit 10: Grammar Grammar In this section, you ✪ to identify ✪ to understand how ✪ to understand what noun Prepositional A phrase is a connected so The in the a words ‘head’. If over after the a the of noun words stay is a phrase. phrases under the a are neatly and concisely are. grammatically within single Unit 4 you like bridge before detail phrases that act add antonyms a word preposition, In can can and together expand ‘head’ months, phrases synonyms they phrase water , few noun and that a learn: phrases group prepositional prepositional will then sentence. that the learned adverbs. lunchtime called phrase how For (adverbial is is these example: phrases (adverbial of place) phrases of time) If the ‘head phrase. my The for lessons noun I 1 is a noun, then the phrase is a noun example: in French phrase and can be German the students subject of the aged 16 or more sentence, example: Students or word’ For the aged object enjoy Find my of 16 the lessons and copy or can sentence, in The 16-year-old b Judith learned c Judith loved for French the a Australian more noun girl go college. example: and German phrases. was brave. independence her to year-long and stay in self- confidence. an Hint: school. Sometimes phrase d Judith’s Australian host family were ver y might Learning a foreign language is a wonder ful phrase experience. at 164 noun a kind. prepositional e the include question 1c. – look Unit Writing noun can build a noun into a noun phrase neatly like phrases this: add Take a noun is detail be saying determiner or a number or both the two a Add a adjective prepositional phrase the two clever the two clever with Add a descriptive -ing word or phrase the black two with sentence of way to sentences. more interesting and can save words concise something. way of Sometimes, adds variety students writing to and more your sentence makes your interesting. students hair clever black over it neat, structures, an great your students it Add a noun students and a Using to Sometimes Add Grammar phrases REMEMBER: You 10: students hair sitting there informative. Add two or three these: ✪ determiner ✪ adjective ✪ -ing word a I have b I would c I shall d __________ was frightening. e __________ was ver y or lost ✪ number ✪ prepositional phrase Challenge phrase. __________. (bag) Can like miss __________. __________. (mobile phone) add to question (teacher) (book) exhausting. you extras with four the 2 to or all sentences pack ve in them information? (journey) 165 Unit 3 10: Grammar Look at number each and these in vocabulary sentences. brackets refers Find to and the copy number the of noun noun phrases. phrases e in sentence. a I learned b I appreciated c Slowly, I e My new and made ways started of to many new thinking make friends. and sense (1) attitudes. and I (1) understood Australian (1) adopted my adapt things culture. d to home many new countr y. happiest Australian traits also keeping earlier ones from (2) moment now, while was Jude! …’ when my dear friend said: ‘ You are (2) Vocabulary REMEMBER: Synonyms and same antonyms called 1 Write out the sentences below, changing each in to the another word with a similar meaning. similar widened only pleased Use the and jog obvious are happy to be in the Dierences other English exclusively 3 166 Give had in became culture. apparent. improved. en things My for each I vocabular y of a sad b shout c nice d horrible e scared Give L ater, star ted adapted had English. synonyms antonyms for Two words with adjusted to meanings each a love b dark c empty d sharp e tall of these words. these words. my behaviour. expanded. I For dreamt are are called example, feel cold 2 synonyms. progressed antonyms. My are example, words opposite odd. For the box. strange was with meanings synonyms. REMEMBER: I words underlined run word or Two antonyms. hot and Unit 4 Copy an and complete this table – the rst row has been done 10: Vocabulary as example. Challenge Word Synonym Make Antonym the friend comrade some words ashcards in the with table. You can enemy use inexpensive them including for different this games, ‘memory’ game: noisy careful Turn all then take the quick the it cards in synonyms. turns to nd face turns to Then the up, nd take it in antonyms colourful 5 Now add five rows to the table above and use your own You can few cards make can add as your as many or you want. You own words/ words. synonyms/antonyms You can use a dictionar y or thesaur us (a book that gives synonyms phrases) to (but check or they similar as are correct with your help. teacher rst). 167 Unit 10: Listening LISTENING In this section, how you ✪ revise ✪ learn ✪ understand some listening W hen you prepare listen is 1, By also such as what have your To this by closely text recognising then L ater notes to in in answer your implicit ideas questions, educational lectures to prepare can will in – this is you life, good should you will practice have for to that. star t have read by checking good the reminding range questions out of yourself its store vocabular y through, of of to noting the topic. words draw any on that on. key words where your have to have this is good answer this, by Other skills answer to skill, is ‘zzy incorrect, never A for think listen questions hard, to not Audio where just 10.1 the listen and answer for then the is not so answer. answer heard Now them. ‘ black listening drinks wrong: is a question: think e take brain and you practise meant listen you learned – to vocabular y is learned now, also obvious listening about… you when will for mentally. and Developing You to yourself means topic. You useful carefully Unit prepare texts. Think In to will: are coee or closely to named – but drinks’ are ‘o because it’s so of it until answer black the tea’. actual you knew limits’, new, You words and the knew spoken. these were ‘Aqualight’ listeners have now. these questions about Audio 10.1. REMEMBER: 1 W hat a, a b is or to the main pur pose of this talk? Choose the correct answer, you will implied c. help students stay t and to healthy help be c 2 to to How inform persuade can three 168 students you of students tell that the to the dangers buy of is spot examination to recognise Key this words sort of include: caeine Aqualight speech the meaning. you question b In asked drink aimed at college students? Give • What • Why • How is the does purpose …? ways. can you tell …? …? Unit 3 How can you generally 4 W hat a an b a c a from your is listen a this? to school answer the to to the questions group of people who the correct answer, a, b or c. radio a par tner not or in actually meaning to a expert Audio talk to radio on were the appealing A small spoken behind 10.2. a you had to think them. former 16-year-old – group. student, Naz , has students. Glossary exception below. does After a pause of two minutes you will hear the recording a second not Answer 1 W hich 2 W hat 3 W hen subject career W hen 5 for 6 to subjects questions. did Naz Naz career or you of taking up? what word does she use as for is about the your best post-18 subject place to get choices fur ther post-16? (to specic denite the former the latter advice work 1 W hat to keep It’s a b c 2 does to W hat mean to your the do) the rst the last for a it’s like short working time to see in a what about Practise with a using partner Word these and words add them to Book. when she says, ‘It’s good open’? your mind rst many making main a plan. times. choice. pur pose of the last par t of talk? a to warn b to describe c they questions. options before is follow what … rmly change wait her to How students explain hard 3 your good keep Naz see experience job your these someone someone education? certain subjects. What are these reasons that she considers poor? Answer rule a Naz gives four reasons that she considers poor reasons for choosing C that general quickly? choices, careful where needed on a ‘career ’? be Naz , decide thinking about ‘ job’ should According the is talking synonym 4 these something follow time. shadow B Comprehension research? the with answers words carefully to on is Choose medical answers ese the returned Now text documentar y lecture aler t! Now of speaker scientific advertisement health beyond the respect kind Compare Be tell 10: as can person? shows what that you you Give against making university university is a mistake really courses like are not as think tell that one Naz example is an of understanding what she says that this. 169 Unit 10: Grammar Grammar In this section, you differences will learn: ✪ the ✪ how to use repor ting ✪ how to use the Direct In and Unit marks Naz 9 ‘I am Sometimes Naz said apostrophe learned show said, direct the you that how she to repor ted speech show possession. punctuate direct spoken, speech, for using speech example: experience.’ want was to actually work might and speech words doing speech questions reported you to between to doing just work report what was said, for example: experience. REMEMBER: When you use reported be speech: missed Naz ✪ you don’t use speech marks/inverted said The out. she word For was that can example: doing work commas experience. ✪ you have ✪ you may (for 1 to change have example: Change these a e girl b e boy c Naz to the pronoun change am the doing was sentences said, ‘I love (for example: I she) verb into doing). reported speech. Histor y.’ REMEMBER: said, said to ‘I’m the afraid I students, don’t ‘It is know good what to I keep want your to be.’ options questions, reporting questions, modal speech. The verbs verbs change that when change you are move can, from must direct and to The could boy must asked, The boy asked The modal ‘Can if he I had have could to a may mix have of a may The boy Arts and of arts science and courses?’ that do not change yes/no if. asked, and science The boy mix of For example: ‘Can Science I have a mix courses?’ are would, could, asked Arts if and he could Science have a courses. courses. Notice verbs use might arts mix report reported of can you carefully. open.’ When Some When think should, there is no question mark might now. and ought to. When reporting questions with question words (for example, 2 Put the following sentences into reported speech. when, where, why ), use the a Naz said, ‘I could b Naz said to c Naz told the have become a lawyer.’ question word again, for example: the boy, ‘ You can change your mind.’ The students, ‘ You should choose boy asked, ‘How should I carefully.’ decide?’ d e boy e e girl asked, asked, ‘ W hat career ‘ W here shall should I go I do?’ to university?’ The boy decide. 170 f Naz g e asked girl the asked boy, Naz, ‘Do ‘Do you you want want to to study be a Medicine?’ journalist?’ asked how he should Unit 10: Punctuation Punctuation Apostrophes In Unit letters The 9 you had to show learned been to use missed apostrophe possession apostrophes out, stands for for example the to show isn’t missing is letter that short one for or is more REMEMBER: not. or of o ’ The apostrophe (possesses) something decision the choice the teacher Here, the boys’s 1 2 3 4 5 can of the using these class b the teacher c the advice d the opinion e three f the of the of of of why bit the elephant’s the cat’s d the students’ e the teachers’ in ’s owner immediately it. owns the owner of example: decision choice boys’ boys. teacher It does not have ’s because by using ’s or s ’. children of the boy are incorrect. Write them out correctly. trunks noses brain head difference a the parent’s b the book’s between view authors apostrophe a the books cover b the tables tops c our d my fathers fathers said the tail the said, ends is mother these c show that it awkward. subjects b after someone to word that parents the my lions’ Naz word A Abdullah of the the the show teacher his a ‘Naz ,’ comes a for boy’s the or apostrophe of, the phrases chosen ideas E xplain word boys sound the the the something an Naz’s the a E xplain that use boy apostrophe E xplain show You Naz of would Shorten Put also something. of to follows without the s’ in (one advice the ‘e boys, boys parents’ the books’ correct book, one tables, (many (one difference the the (many advice pairs of phrases. view authors place. cover) many tops) fathers) father) between ‘should should these make make these the the pairs of sentences. decision.’ decision.’ 171 Unit 10: Reading non-fiction READING In this section, ✪ read ✪ learn a case ✪ practise you NON-FICTION will: study some about useful drawing a young man who is studying Business vocabular y inferences and recognising implicit meaning. Exploring… If you or have relative, career e in text to a AP It Case is is a Explain case or a than an early actor, I’d age, I always why of IB. it. or Do why book a young He left world, you perhaps think you from would a friend enjoy a not. called Guide to Not Going to man school Birmingham, to Study: business about study in the careers the College rather of another from courses Business From one below business, an tell experience business? University. Levels, any UK . who after He decided taking hopes to not to GCSEs go take and straight A went into university. Adrian knew I Jarrett wanted wanted to to focus run on a my own creative business. career Being where Glossary I case could ear n a living, as well as gain total job satisfaction liaising study someone’s people. an actual of experience … entrepreneur After example with applying for the course, I was invited to the college for someone induction and I fell in love with the wonder ful facilities on (from French) an offer. who is inventive in The business relaxed a great For atmosphere reputation me, the ‘outside a best the business, also entrepreneur. fundamental business its par t box’. it was for It It of the not The to you with from it you College had a of nur tured are you settle an occasion shown to one which is more independent, inuences an who about your individual to have I in my made have overcome pushing myself this to by setting myself small was a from specific life people difference in helping me challenge, achievable responsible for goals me excel. liaising Aside a me helping and help school partly but when to in instrumental environment, around up knowledge on you think setting focusing in you mindset in-depth being the induction makes about the whilst and suppor t. that adopt principles jump is teaches you provides welcoming student course only allows business goals. extremely strong business-related units, we also get cooperating/ involved interacting with over fun activities £3,500 for Bir mingham during national Half the course; charities. Marathon. T o collectively, raise Crossing the funds, finish our I group took line raised par t was one in the of mindset nurtured proudest was moments such a to date. rewarding I still wear my wristband ever y day – have 172 been elder lucky brother to have and mind cared for experience. in my of it think I state my several teachers to strong name a influences few, but in my since life, studying a ‘outside different, the box’ creative think way Unit here … have to I can add different be been It’s The succeed peers career successful. experiences. me my so goals, great tutors far, to we to all be have their these influences want able also the to been knowledge, too. same lear n Whilst from from instrumental guidance the each and we 10: Comprehension all course – other’s in helping suppor t has fantastic. A Answer 1 A 2 career W hat are W hat is To 3 the before b while c after what he he he setting does the appealed last point actually was had to Adrian the started into about for two reasons. says small phrase the college studies. his studies. there he for a … while. overcame achievable ‘small 2? his studying Adrian these paragraph liked settling been 3, of Adrian myself Answer In main paragraph W hat B business explain ‘ by questions. they? a In 1 in these his problems goals’. achievable goals’ mean? questions. paragraph Adrian says ‘I can add my peers to these inf luences’. W hat 2 Look does at Adrian 3 a an b a cares C In the List he last paragraph. ambitious the team whole about this course why the mean? a phrase or a sentence that shows person. player. text, text, (the Adrian academic the reasons can why he was ✪ why he enjoyed Do not side) each satisfied the gives social for ✪ give how you tell that Adrian is a person who others? enjoyed four Copy is good From this the same reasons of aspects of the with social reason why college of he life, college was and satised the with reasons life. following: the academic side side. more than once. 173 Unit 10: Writing WRITING Writing In this to describe section, how you to will: ✪ learn ✪ practise using ✪ practise building ✪ learn useful use synonyms synonyms up to noun vocabular y to show add different variety and shades interest of to meaning your writing phrases on the theme of buildings and schools. Exploring… Earlier words that in can you house this unit have will might comfor table you learned exactly learn both to same recognise refer feelings the about to the meaning the place attached synonyms. to longer where it, the – Of there you you other course, are study live – no shades of English. but (house) is one two meaning Home (home) more and has factual. A Work with a partner to answer these questions. big/gigantic 1 Look at the synonyms in the boxes on the right. angr y/furious With a par tner W hich word discuss seems when you would use one, and when the other. ‘stronger ’? good/fantastic 2 Explain the differences between the words, whispered, shouted, muttered, screamed, bellowed. slim/scrawny 3 Read this sentence aloud to one another: cold/freezing ‘T ake How this!’ many underlined he said, as dierent words? he walked synonyms Write out towards can your you me. nd sentences to replace and then the read two them aloud Hint: how to one You you will read Read the paragraph below to your par tner. Then work together change replace use all lovely those for dream nice each words with different synonyms – (you on the sentence, the new words to you A to another. depending 4 need can’t have used. just one!). night out Challenge We had a nice meal in a ver y nice restaurant. The tables were nice, Turn and all the knives and forks were nice. Then the waiter came this paragraph nightmare serve us. He looked nice and was so nice to us. He brought to us ver y quickly, which was nice. We had nice salad cheese, then we had a nice main course with nice desser t we had a nice cake covered in nice cream. every We left tip for him after that nice 174 could read out your new versions to the class – Do twice. experience. help You A out. nice not with an repeat any nicely, of You can use a a dictionary nice night vegetables. word For a with antonym. nice of the Replace meal into to course! you. or a thesaurus to Unit Developing your page 165, you Writing skills Useful On 10: learned to use noun phrases to build up a words to describe description. buildings: Now do the same with one of the pictures below. Each picture shows a Parts school in a dierent par t of the world. Star t with ‘a of a building: roof, arch, school’. courtyard, interior , playground, exterior , entrance Construction materials: concrete, timber , steel, brick, stone Adjectives storey, to give the-art, spacious, ancient, simple, to show breathtaking, Make sure these words school? B 1 With Choose like. a one You Say of the could countr y! 2 partner, Your which Time it pictures include par tner schools to take you write: the has in turns above. to Describe surroundings to would guess or school play – which would ‘ W hich what but school not like the don’t to a 150–200- word You could description use this as a school of your school are attend the the and the to the Use help a few you noun add brochure/ Take Check in care an economical you same not have word. to not overdo it. repeated Use synonyms appearance/style to ✪ words plan: surroundings outside more Book. why. the ✪ other describe describing. way. ✪ you looks REMEMBER: for ve what What the brochure paragraph help Add information prospectus. know mean. Word phrases Write tranquil school?’. read you opinion: grand, you would your spacious, impressive, old-fashioned, to futuristic, elaborate awe-inspiring, a single- state-of- dilapidated, Adjectives words facts: traditional, avoid repetition, for example interior building/structure/construction. ✪ general You could impressions use a or feelings photograph or about drawing it. to add interest to your writing. 175 Unit 10: ONE One step STEP further FURTHER Think In this unit, invited to you’ve think thought even about fur ther dierent ahead – to types of university education or college after the age of 16. In this section you are life. Read Many international postgraduate statistics, life in to students studies. help QS have World students the whole University make an world to R ankings informed choose is an decision. from when organisation Here is an it comes that extract to their produces from their undergraduate lists ever y website year, about or using student India. https://www.topuniversities.com/where-to-study/asia/india/guide Fast Facts • Second • Seventh • Capital: New • Largest city • National • Around • Major • Around • The • Currency: • Popular • India • Climate wet • largest of the rupee the largest the most sizes, India’s subjects, Indian space and China) at 1.3 billion = 100 of Institute field and from largest but individual states have additional official languages. Sikhism and Buddhism. education in the hockey, is world football planning northern to (after its the (soccer), first southern system in in was the of ranked (IISc) the the US and China) basketball manned India, but space is and tennis. mission generally for split 2021. into three seasons: hot, world 24th of in the and a fast-growing expansion (after and state-run, for Institute world. China), rapid colleges some well-known Indian in (after undergone origins, (IISc) Science placing has thousands and the vegetarians systems are especially by of population system Science of as Christianity, system agency, There is English, paise) population education and higher and English. Islam, cricket, specializations well in education spearheaded as (after cool. second higher 2016, Indian world Hindi speak education significantly education Institute sciences, include: can Hinduism, rupee complex. higher Rankings (1 largest world’s of the … Standard invested higher own the higher in world Mumbai population include: GDP varies has the languages: largest of The of its in population: sports has the types, by religions 3% population Delhi (monsoon) India’s country official 10% India national largest third India With 176 about the China and the the universities others world quality Science over of (IISc) in … past US) economy, few – India and to it’s decades. to an choose unsurprising India now outsider, from, of has that one perhaps many one different private. in its the QS Higher education in Education System engineering and Strength technology Bangalore. Bangalore Bangalore global top … 100 performs for best chemical (among the engineering, top 50 worldwide) electrical for engineering materials and chemistry. ... Unit 10: One step further Mumbai Mumbai the … world, site of a is India’s home large The of city ancient food. is capital, of 18 million home in people. Mumbai to and the is one of Located India’s Bollywood the on fun Mumbai of buzzing cities. and is the and extremes restaurants theater , also Talk cultural There is are as home largest universities Discuss and to scene, great activities – lm … industry glittering well as some sights of some of India’s in the a weather , most world suit best using a at the the and highest and street of W hat are of the nightlife. this probably live one of music, India’s traditional universities, students. including The the language University of of Mumbai, instruction at Indian check unit, you: talked about different kinds of education for students aged 16 expansion above and ✪ read a blog written by a student ✪ learned some ✪ learned about noun ✪ learned about synonyms ✪ listened who studied abroad capital useful vocabular y about education scene phrases and and their use antonyms advantages/ of studying to the a recording of a talk given to school students about in subjects information ✪ given? it food, … 550,000 and choosing using make great instruction disadvantages India, including these nancial cultural language entertainment, interest, dictionar y: enter tainment buzzing and partner rapid commercial, any around and 2 and well-respected with ✪ d coast nancial English. meaning undergone c in skyscrapers beaches to India’s In b west cities simple-yet-mouth-watering and universities usually with the phrases, a the commercial, Reflect 1 largest India. contrasts fancy city … festivals one full populous harbor , millionaires markets, Mumbai’s most over natural entertainment number to most Consider why you not, like learned to understand implicit meaning in spoken and written texts might, or studying might in ✪ learned ✪ learned to punctuate speech and use apostrophes for possession Write ✪ read ✪ wrote an EI T HER: e about direct and repor ted speech India. website a case a study creative about piece a student including who studied descriptions, a business and an course ar ticle or inter view. https:// www.topuniversities.com/qs- world-university-rankings information like to Write study, an not your go to dierent money for from Conduct to if ar ticle information OR: about an for a to object. study. If magazine you on Using do the not city this website have you access would or to others, the most choose internet, like to study one city research in. where in Explain a you would librar y. why, using research. inter view or places no school your college inter view a was has with someone university. school Find you out know why who they has studied thought their at university, decision was a or with good someone one or not. who did Write up magazine. 177 Jobs, career choices UNIT and 1 1 This we In unit do this and unit, draw R4 is for you a for to What four or at I’ve to reasons why – the we do work it. to: make deductions language with and recognise increasing uency implicit and meaning creativity purposes purpose, implied meaning, attitudes and feelings in appropriate career pronunciation and intonation. choices done think ve example help these jobs, careers ambitions Time List about and texts demonstrate S4 11.1 of jobs different learn the variety extended and will about inferences, recognise L4 Speaking the manipulate W4 all ambitions activities hobbies home. In and each you have pastimes, case, done out spor ts write down of and the the classroom, games skills or you things need you to do do things. Time to talk REMEMBER: With a par tner, talk about your list of activities. Ask one To conversation ✪ what you enjoyed ✪ what skills you or have to disliked or think you don’t encourage questions have and ✪ which activity was most impor tant to you and use which you want to do to strengths Time Read the about 178 to careers. and weaknesses think extract at the one nd body to use ready another , out more language. correct pronunciation conversation My the be ask detail You top of page 179, which is will intonation again. and 11.2 going, why need ✪ keep another: from a book to for ow the easily. Unit It is very know But not hard about there are know based to the many about on know jobs we is deal of career parents jobs Here they kind our other them. whether what that a never list with and of would suit friends do consider different people, us or best. tell kinds things, of data or do hand-eye skills, that ideas. include work skills managing negotiating teaching, with involved and people, enter taining in working organising or with people, suppor ting and understanding people other work together speed help and to innovative people, might work skills include involved manual in skills making in using or the ability to understand constructing tools how or original and things working work hand-eye Data: work deciding Ideas: work designing down yourself a 5means a graph, best to in handling working to with present associated adapting things that accuracy having new things work or being your able hands to skilfully with discussing and having agreement figures and with things, infor mation on a or infor mation. innovative experimenting include computer communicate being might and might include investigating. think the headings mark 1–5 for ‘People ’, each area, ‘ings’, where 1 ‘Data’ and means ‘Ideas’. ‘not ver y Now good’ give and ‘excellent’. Time With involved skills or Time Write a how way sight coordination skills interpreting do the and ideas skills with reaching good to and creative, negotiating machiner y, hands people. manual Things: speaking might persuading giving coordination someone’s require People: and Glossary about. we work Thinking We us because 11: to talk par tner, which are your 11.3 Which Time to discuss which weaknesses. of these Give areas reasons for are your your strengths and answers. career? think Challenge Most jobs will be a mixture of skills. For example, if you are interested Prepare in working with people and data, you could consider jobs in to or management. If you enjoy working with ideas and things, a medicine or scientic research might suit you. One thing is the cer tain career to know yourself informed decision. Prepare shor t a and your own strengths will help you make an of about 2–3 minutes about your and reasons for choosing need to possible do dream admire but job - have doing. some You will background Consider: qualications you need it. it would fantastic to presentation career why Time a your considered the choice you research. talk give on – not getting class career a in and business be such a job talk In a small group or a pair, give your short talk. Use the talks as a starter for the salary not important. and why it is or is a longer discussion on the advantages and disadvantages of certain careers. 179 Unit 11: Reading non-ction READING In this section, ✪ read ✪ answer a ✪ practise shor t of star ted person shop. father, business Honda a understanding recognising successful themselves, Honda, from (1906–1991), Company, child, who and most Soichiro Motor As testing of implicit a text meaning. about… world’s their was Honda biography inference the Soichiro will: questions Think Some you NON-FICTION was he got spent also a and did worked not go their to university, way up. One but such Japan. the his people founder star t hours at and his fixing president father’s bikes and of bicycle the repair lear ning from his blacksmith Glossary … Honda’s glimpse of a Model T one day became a life-changing apprentice event: ‘I could not understand how it could move under its by power. And when it had driven past me, without even (verb) learn a trade own thinking doing the job, with close why, guidance I found 1922, myself that chasing love of it down automobiles the road inspired as far him to as I could leave run.’ home at In age 15 blacksmith to apprentice at Ar t Shokai, an automobile repair shop in makes The shop’s exper tise ‘At Art owner unusual Shokai machines,’ Honda saw said Motor theoretical … in in Honda one [Honda] knowledge an so he his was 1973 an worker processing elementar y much Kawashima, upon – hard only learned Kihachiro Company with a by school doing real who succeeded retirement. expert at all ‘He welding … Those of us who had only sorts studied education. work with Honda didn’t of the an academic In 1928, of Art Honda Shokai in standpoint completed just his Hamamatsu. couldn’t at just practical real the have Model rst trucks and a repair lift for began cars to the subject on T his and investors Undeterred, Seiki Heavy Shokai, he began … in 1936, made In other 1949, Type-D’ the storefront 180 of back where piston and opened building racing rings of expanding star ted at a cars into separate putting night. par ts for Honda Los Motor bicycle … In Company, … 1959, Angles It was in His a a branch everything using an Ltd., old company, full day and at the Ford rings – car the from parts a motor engine succeeded … released Honda Honda the hit But T okai became a Aircraft, first with Motor Dream, ‘Dream the Company by came after joining pieces airplane Ar t Nakajima immediate American introduced T from manufacturing. business T oyota an Model tasks him. after skill paper companies. public. in to supplier motorized Japanese dream Honda Industr y, 2,000-employee among to refused metal USA together engines, from mass-produced welding dump who compete.’ apprenticeship Honda things expertise of from person technical piston like a T okyo. 1964, using heat of metal Unit they were selling Japanese Trade auto and Industr y Never theless Honda 1972 Civic to … its in it ban first the U.S. month despite on 1973, won a – hatchback. 1974 opened 100,000 industr y new the … car of Motor was Year jumped Ministr y companies. Civic the Honda Japanese Honda The Car globally. a the Inter national introduced immediate Japan into Comprehension … Company an of 11: award. In hit, the and 1979, from Honda plant. A For 1 W hat 2 question, amazed Honda a that it was b that it could c that he This 3 each event a the b it c he In is other T car 3, correct when he was the b He could make c He knew the him rich and following studied the Honda became Honda set Honda sold won up the theor y piston theor y of rings and information his Car died Answer own motor right Honda the career. that made him better than and had in car mechanics. x engines. practical the text, skills. copy and complete the these questions. company W hat …’. paragraph 5, 1936, evidence creative is person? two in can Give order star ted ‘undeterred’ you tell that a separate mean? Honda was a person? there obstacles overcome Honda does how hard- working W hat motorbike Year in List cars. company ‘Dream’ ‘Undeterred, ver y 4 … apprentice rst of retired 3 an the Honda In T? 1906 Honda 2 Model Year born 1 a below. Honda C of c. famous. with the about because Event Civic glimpse or car ‘ life- changing ’ it a b road fascination was caught a, own down as answer, managers? had table its it his what He Using on made of he a B much the mass-produced chase start that paragraph the rst described the knew so move could Model was the choose in the two text pieces (difficulties) to be that of Honda was a evidence. Honda had to successful. 181 Unit 11: Grammar Grammar REMEMBER: In this when section, to use Modal you will learn more about modal verbs and understand may/ shows might possible, something is semicolons. You verbs for example: may/might get top grades. In Unit 7, whether you learned something about is modal possible or verbs. certain These (see small verbs REMEMBER can show can/ shows could the box). He someone ability, for can/could has example: drive well. They You can also must be not used walk with on the negatives, for example: must grass. shows strong obligation, I 1 With a partner, between A Zara the talk about following could become B Zara might C Zara will D Zara must a become the in car racing will driver. a become racing a car racing Work together to match and driver. one 3 the statements a Zara has the b Zara has no c ere d It is Write what all a it ability choice chance denite two the the is in of the modal and verbs has Zara statements in a to (A , will be a become one reasons your B C racing becoming about the 1 become she Zara sentences means – of that question to do something to happen, You will older . below to of car racing a a car car one her exams in June. driver. driver. shown, might An tense, will driver. car signs sentences. She driver. racing it future D). racing the why or shows example: take of to driver. for 2 that example: grow become or example: remember certain for need homework. shows is driver. car must my meaning sentences. racing a differences for be explaining used. example is Underline given on right. This sign means that you must not smoke in this place. You might nd this sign in a hospital. 4 For the following brackets would sentences, be decide which underlined word in better. Challenge a I have good exam results, so I could/must become a nuclear Talk scientist. with answers b I denitely c He will/might become a a good hand-eye coordination so he could/must become the 182 Students e In an would make to must/might exam you study must/might hard not if they talk to want other to go to people. the the player. d 4 – your what other a word tennis about question teacher. difference has partner to university. sentences? meaning of Unit 11: Punctuation Punctuation Semicolons e ✪ semicolon to ✪ join to looks clauses separate like that long ; this are items and closely in a it has two main uses: Hint: The a stop full use semicolon closely can show that the two sentences or clauses helps – As a at boy, Honda practical A full two As boy, W hich a sentences. worked during separates sentences a as skills stop are Honda practical 1 two skills of single closely during father’s bicycle shop. He learned a a Honda However , you connected in his looks a like comma. remember the and comma, full its reader two clauses it stronger is but not as or strong stop. many in father’s could use a semicolon, as the meaning: bicycle shop; he learned many pairs with REMEMBER: letter time. following learned you makes a of sentences semicolon? would Write be them after practical skills. is helped him There a is no capital semicolon. improved Hint: out. One question a of time. this sentence as his them. worked the in this top between sentences, related these it pause are than Look on list. This A semicolon related. throughout pair 1 of does sentences not need to in be his changed. working b W hen it c he moved All his made d ‘e life, car not 2 be the Make Honda 3 its Honda can in also enough wheels and broken motors; you and motor car. He was amazed that In 1936, he had two jobs and time. one of the rst motor bikes. Honda’s wife husband. used to separate meaning one and practical own spare your if a hardworking. was her saw power. of the very items semicolons understand repairing your his or commas sure was be make Honda own Dream’ to lear ned Write boy, parts helpful strong Find a supported Semicolons very was under Honda always be life. skills chains making why such on items when includes in using the they as a from both in a a list. comma comma sentence have mending bicycles; pistons sentence long clear , been already. below. used. metal; of commas can might punctures, welding scraps This fitting fixing metal. and semicolons. 183 Unit 11: Listening LISTENING Glossary cast In this section, ✪ learn some ✪ practise you will: useful doubt vocabular y relating to careers and questions, including those about and concentrate To help you your skills develop your develop as you need to e recording your of the features words skills wide a in English, vocabular y both as written you and spoken, talented and a careers phrases advisor. she is Before going to you use listen, in the look at be have Glossar y. these Choose three the box below that a talent with b aspiration are do beaten a chance possibility you and of to doing understand phrases. them to a in these Practise sentences by partner . gift ambition. dream aptitude air REMEMBER: There to for: vision 2 out are talking synonyms set skilled sure words from you something questions. words/phrases in any using 1 thing can. Make Answer A one ambition what overwhelmed to some on pur pose. achieving Developing feeling implied fullling meaning stop ambitions focus answering aside negative eight words or idioms in the box below. Sor t them out into Synonyms are words with similar meanings, for example goal, target, aim and objective are two sets of synonyms. all synonyms. support overwhelmed devastated be someone’s rock crushed overcome encourage be there for someone Challenge Research Try to and nd nd words three that sets you of think synonyms your – perhaps classmates will four the with three a partner sets of or in a small group to sort each each set. know. Write them out on pieces of card or paper . Then muddle Work in them up. other’s words into synonyms. REMEMBER: the You Applying your will carefully to this radio talk by a careers advisor who is You 184 ideas will on how hear to each about to use wisely. achieve par t of success. the talk You twice. will hear the talk through all 5 the minutes to questions explaining and her have time skills read Listen Remember preparation in two par ts. think hear the about them recordings. before you Unit Answer B 1 The speaker might 2 ver y early Tick two one of why the b ey do not have enough c ey do not have the d ey cannot to decide the you focus the one that makes b the one that is c the one that makes speaker should something b a c almost more The speaker spending b writing c going The three a Use b Take c Read people feel over whelmed W hat is in a to warn b to give c to tell can ambitions, which one to money achieve most be is happy ‘realistic ’. She explains this means … achieve. achieve. an about Olympic that a Audio athlete, 11.2. the speaker sug gests you metres. it helps W hat c to does give she 20 kilometres. yourself a small reward for sug gest? g ym walk telling that the a the main as of you people of refers and how it to have is this hard on it ambition be helpful? best positive has be summed up as: thoughts. succeeded. successful people. talk? is how ver y can who about of your mentions. someone can advice that about speaker pur pose practical people friend speaker imagination much the most the 400 photographs as many words ways your have one that goal. quiet can step need. at. achieve. to b time ways final some … small a the you you become 300 for aim you should sug gests each they to questions metres. what people money. easiest can than to if you target you running a Give you a these want meeting In the impossible Answer 100 that on? says have a by might talent speaker, should you dreams determination. what a If or following. much bit ambitions 11.1. on? have The Audio Comprehension them. speaker, not a 5 the do star t 4 Name about possible ey C 3 two a you 2 questions gives to of According 4 1 have. According 3 these 11: to to easy achieve achieve to success success achieve success 185 Unit 3 E xplain a to ere lack b We a partner may of all Some have As learned a in Bullet points used writing list, in not have last one, In item for the 4 as will doctor • lawyer • manager . with been a was food For are condence, lack sentences. of money or you want to write a novel, run a in fact they would stop at nothing to 31, are bullet single used pieces in of points word stories writing, can also items or or other such as be used longer for phrases. narratives. reports or They academic essays. usually or at introduced upper-case the have lesson end. a full we by letters. However , stop to learned write at a colon. Also, you the about this sentences full e So of The each must end these example a – to items item be can may or consistent. show it is the may The nal jobs: out find school show four lists punctuated. to using commas a in time and the to instead of giving and W hy for the chatting odours were collect change of have these. rst the the cooked wearing. these items a batter y a New of York K ansas Seattle and them. success the rewards task are as into Telling a follows smaller friend Focussing tasks Being Picturing person. of and different textbooks. explain are people unusual to not You spoon. achieve Breaking examples books few Do cafeteria of students had USA a the the wooden just how I college sounds dishes punctuation. letters. the the clothes successful reading the a yourself a and name of at went rod cities to stages as I correct capital experiment metal thing to and strange many with strange pans Science yourself Now, was the the bulb one when much and ve good stops ner vous visited on 5 page they formal Philadelphia d 2, History these the light I these mountain. usually partner clashing c not usually given time. b in points. Rewrite I a perhaps ambitious: Unit lists careers teacher a of used example: • bullet in semicolon • Work lack is lists lower-case a colon goal. whether more such with are for are Bullet-pointed start reasons: dreams: climb their items are or points you our people achieve Bullet many the Punctuation opportunity. marathon c be why 11: the there kinds In different a of lists pair ways or in your small they group, have been differences? 187 Unit 11: Reading non-ction READING In this section, ✪ read a ✪ learn ✪ recognise ✪ revise you NON-FICTION will: non-fiction some narrative vocabular y implicit metaphor relating meaning and text in simile, about to a making more and skilled craftspeople things by challenging identify Glossary their any text use in eye a without modern using measuring devices text. carpenter a person who makes Exploring… With a what people par tner, Does it do describe and some what crafts tools they from use. your W hat home is countr y. skilful about things from chisel a Explain the if it dies out? W hy, or why tool for craft? shaping matter wood wood or stone not? craftsman/craftswoman You are going to read an extract from e Sindbad Voyage by Tim someone Savarind. Tim, a famous sailor and explorer, decided to nd out if skilfully, ship built stories of in medieval Sindbad the times Sailor. could In sail the as described Sultanate of in the Oman, ancient he found who often could make a ship in the traditional way. In this extract, constructing the ship under the direction of shipbuilder from the Indian island of Mohamed a the description and then answer the questions that … to The they worked greenshir t imagine entirely carpenters possible in the by eye, worked blazing used to to drive into things the in with heat. a a happy, frenzy Their carefree that tools traditional way it been (made) for chisel. Whether cutting a thick lump of years manner. was difficult were hammer to timber medieval history in times a Europe, period size, or and 1500 (Middle the finest of sliver wood for a delicate joint, 90 percent Ages) of saw the greenshir ts’ work was done with hammer and chisel; only a tool cutting reluctantly fathers, before did that, had question as and had they Now, as if on, as and leave No tip their of accuracy, never Timber - Sliver long, – to them until no look before to missing shape There as at were a the like the friend or chisel never in into big of to no hand, the rose handle. switch and … or the to of fell was job was how the time glance They the It them matter even around any Much wood. … carpenters, machines. stop difficult. whose generations enough work, them, gaze been become told how hammer untold well-oiled bore job sliced craftsmen and were piece were to matter at it had also they a they seemed them, to They would soon unwatched wood thin run chat the … per for med work chisel while 2 to of saw they as point seemed the 1 they deter heads boatshed, 188 to scarcely the tur n or that work could them a great-grandfathers, carpenters. but men, piece up and been begun grown repetitive, at pick children Mohamed finished. they they grandfathers could rest with of used ver y the steady wood of between 2 shaping they hundreds 1 and as follow. of always, tool or Minicoy. have As a chisel Ismail, in Read very Tim nails a things traditional methods hit describes using people hammer who makes a for 500 Unit Eventually the ship was out to pulled There … was each a He … complete. wonder ful inviting Tim describes the moment the ship stood the top, Comprehension sea. the ‘Congratulations, She’s was 11: moment other to be Mohamed,’ I as the Mohamed first said. to go ‘You’ve and I down done at below a deck. wonder ful … job. superb.’ swelled The with whole chuckle and pleasure sensation gurgle of and of the climbed the ship tide back had running up to changed. past the leave … skin I me could of the alone. hear ship. I the put 3 my hand from so on the many craftsmen. Answer A which planking these My had vessel taken was so much time and care alive. questions. REMEMBER: 1 In a the first paragraph, the writer says the car penters worked ‘ with Severin real frenzy ’. is Although writing experience, comparisons W hat does this In the first paragraph, what does Tim admire about the three things. 1 In the oiled Give 2 In these second paragraph, Tim compares the team of feelings. his As Unit men to ‘ well- as is by called 4, a you the a comparison word like simile. If the comparison is made by saying one another , or acts thing is is if it another , a metaphor then it is as called ways in which he thinks the way they work is like a machine. paragraph with questions. machines’. two in introduced or Answer B and craftsmen? learned List uses show mean? thoughts 2 he to Tim about steady 2, Tim writes accurac y ’. a had grown careless b had switched c had become on This in ‘the unwatched was because their some work kind of hammer the men rose and fell … habits. machiner y. Challenge so used to the work over time. Complete these metaphors Answer C these Find the par t of the text where Tim and Mohamed show for one another. How do you they do two more At the W hat as a end of other living the word When extract, in this Tim says section his vessel shows that (ship) Tim ‘ was thinks alive’. of the as ship I W hy does thing? Tim say the ship is a living of went if creature, when he knows it I your for felt own. the nervous, … b The sun c The teacher the 3 with then this? interview 2 and their a respect sentences similes questions. write 1 or tiny was a … persuaded children to dance is like… just made of wood? d My aunt, rock 3 Strips of who band, sings with a … wood 189 Unit 11: Writing WRITING REMEMBER: have Writing In this for different section, you readers and purpose more learn to ✪ write for this some book ways be informal: recognise the different different readers and pur poses of Use abbreviations, example: writing you’re, for can’t pur poses. • Use idioms, for example: really on the ball. Think you to will: • ✪ In learned He’s (meaning he about… understands the situation well) In your daily life, when you meet people, you automatically decide how And you will speak to them. If you meet a friend, you may say, ‘Hi! some ways to be more How ’s formal: it going?’ But if you meet your headteacher, you are more likely to say, • ‘Good morning!’ and wait to be spoken to. In the same way, when Use full forms example: write, on you the change reader how and the formal or pur pose informal of your (casual) you are, of verbs, for you you are, cannot depending • writing. Use passive example: the forms, The test for was set by teacher . Exploring… You already use dierent levels of formality when you write. Another For is example, you might keep a diar y, which is just for yourself. to use way an to use slang (words more common in speech than in idioms. Of course, if you write a diar y as an exercise, you know will read it, so you’ ll make sure you include enough A them, blog don’t is while also know cause be to idioms In you reader to be 190 know how remember, write or a little articles factual in feelings by a idioms to lot someone for preparing in of and write: action, to it write will more informal be read by formally English. people so as not is who to as usually writing to accounts, well and are information. as people you to you – show don’t You make events words quite formal. might it to your make know, so You you will to read. your writing emotions. aim occasional interesting want so Your use might want be your careful slang. article is r unning you about example a your imagined newspaper about in and give comparisons read use describe, cook and stories, local ink to will reports some you them but, comparisons Time Your you understand include how – inform and short work informal you oence. Newspaper will showing burger. have 150 a a series seen words. police at of ar ticles work . Choose ocer on Write just directing a one ‘People at work’. description par t trac of or This ‘it’ and means not using referring a particular person or thing. information For for subject a to teacher formal writing ) the and more You’ ll construction. probably be impersonal a their of work fast-food example: thought It that is clear … that …, It Unit Time You the are to entering stor y of happened based and Time your did, and his to one diar y of at the the how Put these of writing them and the a one You have episode places, and of add been his inspired life details and by write about a what feelings. entry shown. ver y about Imagine busy the day. you are Include doing the this hardest job. Write thing you work. skills tasks 1 Imagine diary images felt competition. Imagine thoughts your numbering reach it. Writing story stor y Honda. on end you short shor t write: Developing 1 a Soichiro description Choose write: 11: to in 5. order from Discuss informal your order to with formal a by par tner and agreement. a a report b an c a on email letter a scientic inviting to a a experiment friend teacher to your explaining done at school house why you did not do your homework d an e a The article blog pur pose level of Some for about of the a local paper travelling writing or will about a a new librar y holiday affect what you include, and the formality. pur poses of writing are: ✪ to inform to persuade to repor t ✪ to explain to argue to review ✪ to describe to give to express advice feelings. Sometimes 2 Look writing again ✪ who ✪ what Time at the the more five intended the to has pur pose write: than tasks in reader of the writing one pur pose. question 1. In each case, explain: is writing for is. reader and purpose Challenge Choose one of the ve tasks in question 1. Make sure you use the and the Look correct amount pur pose of your of formality, writing. bearing in mind your reader and back make have what was, through a read. the who written of this the book texts Decide in each purpose of the the for informal list it text and was how you case text originally formal or is. 191 Unit 11: ONE One step STEP further FURTHER Think You have Now been you can generally. ✪ W hat thinking go Make is about fur ther some and notes impor tant in ambition think for your in about yourself life? For terms of ambition on these example, work in and terms career. of life questions: success? Wealth? Happiness? ✪ How do Talk Use some about You with of what are fable you the a going to you you’ve you, read to your life in 30 years’ time? partner ideas makes wants imagine a and been fable, think thinking others, happy. which about how about. How means far a With stor y money a partner, important with brings a is talk money? moral. e happiness. Read The A Old Man Traditional There was was near tackle When the he shing sh me If and a The old old could “Let me go the the 192 old that to the full that a of man all you up of died. will am give How you sh have and golden I and the to get continued golden the rope. rope, rope. to it the rope,” you.” pull boat you old to which shing boat lake. beside He began man to man go, pulled please?” said. asked. “ said the “Please! golden . “No, said. up The Let the After very and I put he long he won’t The can your shing rod into the lake sh. pulled the continued let man you then up old go. put the man to I pull am the shing thought up the going sh into to a rod, he saw because golden sell he rope. you. I think container , rope. sink it. be happy sh man “You lake. must very to me man rope, pull old sh. said. in the began continued a the The let old rope old the was of golden sh rod said up a The was The lake, dinner . shaking. golden man a and asleep. golden shing in rod There “Can the his center was you,” the The The his He was you?” get line. golden price golden to the man. eat eaten fell rope,” trust put shing he shed shing dark. to rod old to his had surprise, the going golden high while, shing to a he rowed going can are the the the the talk I a his always becoming and his To He brought after was After as shing. man sh boat sh. “No, the very up could to of water pulled get to to lake. a old sky the true? end pay I after , attached now will man go, listened see it man. me Is rope was wanted let the woke liked the lake the caught old minutes man not which the the of who day, used man and man lake, surprising, rope? someone As rod you few golden the man the more go. to center Fish Folktale One out old Golden old the begged “Golden a went shing Even an house. reached Suddenly, the once The in the Chinese his and lake. and into the Finally, lake his but boat he sank was too greedy completely into and still the lake, and Unit Talk W hat is know any another the with a lesson that other the partner stories this in or stor y your small wants own us culture 11: One step further group to think that about? teach a Do you lesson? Tell one stories. Write EI T HER: Write your ‘message’ of talking them. in OR: Retell own home OR: Write below to a your about that unit, Some know be a fables from your shor t have stor y with a animals reading or from your practised ✪ prepared ✪ read ✪ listened ✪ answered a about different speaking and to a way gave kinds clearly shor t in you like, using a text of one of the pictures to travel about testing work conversations talks text, spoken questions a larger text how a students fable achieve vocabular y, other group and to with success understanding and meaning ✪ revised ✪ learned to ✪ learned how reader any check biographical implicit in you: thought modal use and practised ✪ understood ✪ wrote or you necessar y, verbs bullet to change writing how retold feel go help points, your colons style and of semicolons writing correctly according to pur pose ✪ for you should ideas. and ✪ A sk It choosing. ambition you ✪ Check fable. countr y. give this own fable Reect In own to a different write fable, you to the need levels creatively, or confident back if with wrote about section formality using about all of ambition. these and comparisons things. revise it If carefully. it! 193 Practice UNIT 1 2 In this full unit, exam paper . might face Approaching For the ✪ There ✪ Read The ✪ Reading are and before ✪ Look or ✪ at then the W here in read on have in in your range task once each a Reading similar exams. of you for answer skills, might as each sure to questions through, the question answer, make a and difficulty your points’ you to answer marks spend are the opportunity paper format Make and to and to sure complete the you prepare the the ✪ There ✪ Follow write ✪ or each write a goes carefully. sure question, do without exam make you your for ✪ when ✪ what [1] type refer it at to a did text face. These stopping. can are the The on. var y Tr y in to style, get the length ‘gist’ and of sometimes focused specific number of on be the useful correct requirements. marks will If also to check skill a or task give the par t asks you down, always make sure you spell and is next of about. question the you to text. ‘tick guidance punctuate be clear Each each focuses case. If on the a different task set requires of you skills to or a box ’ on how in it correctly. what you write. write knowledge. ‘ between 30–50 words’, do not that. the and task friend highlight below [2] and about a or the note down highlighted family gathering the key elements you must produce. words: or celebration. [3] [4] [4] [2] ✪ where ✪ the audience/reader [3] it was people general [4] who were content there. [4] [4] specic details you must ✪ Always 194 it some Once again, check the number of marks for each task and allow an appropriate amount check topic. what ✪ specifically different to: happened you of than in carefully look [1] the to on. It you and that. answer tasks. carefully more letter must writing task you paper rubric example, Write You four the less Read For are ones task. to Writing Writing continue Although there are no marks for writing in this part of the exam, you still need to For two papers carefully write five to texts text a – the paper increase you ‘ list long four each texts Read the of have papers These practise sorts you papers your testing spelling , those punctuation skills. and grammar carefully, regardless of of whether include time the on each task is task. Unit Reading Answer ✪ The marks ✪ The maximum Read 1: all tried the to big mark for are this shown paper is in brackets 60 R aj to his friend Selima, and then answer questions 1 to 6. show speak main will be have It hall on is great this instruments. You Let team. buzz me the We from know as Oh, – so might term, me as We a I you already a want but said I the have so What in told take you you of catch term sports me he of is I bad! fun I can’t All I to Are to need you hear to a girls. cinema. your help. musical is would and as other any up you open enter now we rehearsing think? Did is apparently the play – it three need brilliantly – going with but you. and hall tickets part, know guitar much could routine supply wasn’t do I day the dance to as play night. nal place month’s lyrics, You before the take has – would big left on practising and you. the will message: good you show Tony prize sing of win. on a this thought even and started with but talent exams. of song performing soon a there’s heard I of for point great yesterday be already and real to day used has have me school going last being this at is the fun! is accompany real you Leonora written perfect to There is and Anyway, a questions from news? juggler , to English Raj everyone. I in Selima, the It for email talent I questions Selima From: Hi papers Email the To: Practice paper ✪ Text 12: we for someone be the would get it? possible. Raj 1 On what 2 W hich 3 W ho day room has will in the the already talent school star ted show will be take used preparing for place? for the the show? show with three friends? [1 mark] [1 mark] [1 mark] 195 Unit For 4 12: the following Read 5 the Tony B The C Selima wants tickets written main a if B To tell Selima that C To tell Selima when the main A To ask B To enter tain C To persuade Are 2: The Longest you fed after world’s which cliffs runs and the be of tribal the first per form exams and a is B or C in each case. true? jug gler. are where of this show. [1 mark] [1 mark] [1 mark] paragraph? with R aj taking the in the place talent in show show main will hall be email? beach overcrowded – ‘Cox’s Come to beaches? Bazar’ in Bangladesh! If so, you could do worse than try one of the world’s largely- Bangladesh. off standard one, There also known the Bay nature as of who stretch the Parallel There old Burmese beach pagodas history. where brought of Bengal. ancient and villages by of the and the everyone! other and the (an to and are ways new Beach. and the either. tourist February airport brand Laboni environment infrastructure many December five-star is Captain unbroken the of beach, Hindu also immigrants incredible things It to km visitors temples. cascading doing 120 settle or will 75 be really still totally does waterfalls, are there miles, a in in 1790s, you’re captivated offer game the case the by tourist park, coral it features wondering), towering an amazing islands and revered. fast put between 196 for the World? English along Developing the in multi-coloured, charming the with gems longest combination Don’t as statement A, advice longest up the W hich either theatre. the will down history Named the she of write show the purpose Beach undiscovered rich for 6), song point Selima is to the for ask W hat for enter To The to is has the to (4 statements. A Text A questions prize is papers following A W hat 6 Practice is in – of peak process Kamal Buildings speed hotspots, the the Sheik Yes, are there but over tourist of going up being at a but be power 100,000 season. international development, can local There upgraded cricket frantic many shortages tourists are from stadium, rate say and that now a visit some a are a to an at are throw about up including international long yet weekends hotels, stone’s this hotels area worried beach all better domestic is not the many which with and from the there one. the impact is a space area on Unit Ideal This or for is really eye can Martin’s. to welcome How 8 W hat 9 In In is the of W hat 11 12 13 see, you is the first the ideal can the this to for the claim sound its have waters like Bazar ’ name of the the sights. been and adult beautiful place for traveller somewhere you? coral If so, who does different. and seashells book your not Just mind imagine which ticket now. discovering a can stretch be the W hat papers seen paragraph, stadium this the things sand on for as islands will be him far as like delighted beach. writer does of Bangladesh beach? spor ts paragraph, this independent to record-breaking ‘Cox ’s second does spot rightly crystal-clear Does long some 10 the and St 7 Practice one herself, the 12: says which the has just visitor will been be built? ‘totally captivated’ says buildings are going up ‘at a frantic mark] [1 mark] by mean? writer [1 [2 marks] [2 marks] rate’. mean? Which of these best describes the main point of the first paragraph? A The beach was B The beach is C The beach and W hat is the To inform B To explain C To persuade Below Four is of a list these was on main A of B Cox ’s histor y families C There D Locals E There F The cricket G The writer H Coral is the nearby avoid no of of to in gives this the an seashells is Bangladesh. have a lot to offer the visitor. [1 mark] [1 mark] [1 mark] text? about the what the beach offers beach the correct. information Write down given the in four Text 2. correct answers. 1690s. longest and beach hotels near opinion can in captain. beach about are water falls stadium area visit the five-star English Bengal the world’s visiting an travellers statements settled Bazar of surrounding statements first and Bay purpose the It are the after independent A are named be beach. temples in wor th December visiting. and Januar y. yet. L aboni about found Beach. how at St suitable Mar t ha’s it is for island. the independent traveller. [4 marks] 197 Unit 12: Text Read 3 Practice The the world ar ticle Work popular career. it it all it’s has not – you’re you build if you you a issue but with boring, when you my taking work I work able that food to I suppose I believe I can I at on It dress another you experience – the a to will gain help is work getting in in are a work order to suited to you to to or a type but customers in your on job if their you CV . a short work. might handling work are designer? for of you or the very but experience the even that tried is software – work advance gain what figures, had called) experience see for of experience, business handle world order salesperson, talking out. There is discover problems, It also helps future. also give you that for Also, a the sometimes of chance unless give is business inside you – it nothing a be the may What a you may or employers is a false proper you longer, boss difficulties wanted Of scenes, and Such is in idea not a to impression of of job get real what on give give you the well work sometimes going you but cages I as they idea make didn’t of were what skills than you infor med own with the interns anything is job. you or After like? your situation, experience animals, do caring businesses more my with animals, transferable the from work sick such good that much to course, examined really smartly . out as types by can’t side that vet’s. rooms me to you for a explore fellow might volunteers worthwhile volunteer? vet the for get whether them these criticism stand and a for being timescale well! local behind can always the like if of ahead you found work. see our gave it human with as have as is contacts short intern Working start, experience there cleaning and the worked get to lots free Actually have weeks, the watch supplies. punctual 198 part, a about perfectly chance. goes operation, work only experience was at to an are for banking unimportant are own the in not being be? What make you to For 14–19. chance There want insight two them really For and (or entail? good with if great to like. might just - off an questions working up working short do workers it really really Another hit seems upsides. you skills However, all, is point something means marketing gives much that in does a people. cracked its answer experience usually interested time work then young Everyone certainly What work among essence is below of experience: Nowadays, But papers anything and for kept was are are lose. so I saw and in getting All choices very a had And to is worth get it some I had is career. an medical learned work but essential competitive your your the ordering experience in think demanding, of who involved. vital I managed lots animals in, I for jobs’ free, good and to be market. but Unit Select 14 the W hich Marketing C Selling D Teaching E Designing Being W hat is a the B To say explain to experience. 18 In the vital in a The B Skills you 19 In the you W hat star t does is not 15. mentioned in the ar ticle? five is the good is a jobs’ from for new are the says that work experience good and writer points five says and bad that bad points about transferable mean? [2 marks] [10 marks] work points. ‘such skills are market’. the describes point work what that the getting experience same the can writer a be job is means? almost impor tant impossible. when lots of jobs. point that you must learn new skills when [1 the mark] ‘cer tainly job. paragraph this popular mean? points the making is ver y writer this best making is mark] paragraph? [1 there below going first is does ar ticle learn are writer last job experience paragraph, writer people CV W hat statement The a competitive A C List the experience paragraph, fourth W hich what the of work work upsides’. According point what that second its of and papers [1 main explain the types 14 vet To In questions Practice software A To for following B has 17 the Banking C 16 of answer A F 15 correct 12: writer says ‘all experience is good mark] experience ’. [2 marks] 199 Unit 12: Text Read 4: Practice In the papers search text below of and Scylla’s answer cave questions 21–30. e following extract is taken from a collection of travel writing called ‘From here to there.’ In the extract, the writer is tr ying to nd the home of a monster named Sc ylla, and is ‘The that cave!’ I was here?’ were or the the and I to The down balcony a large cliff a bell brown set in rock. a as a Above walking I standing atmosphere They were offertory twelve was the me to of perfect olive until for I noticed on a and into was a the cave. The and den at the had been grotto were runnelled about like point thirty not into the wide, a again. cliff iron ‘The thought With up railing the I was a monster Antonis: eel: a the type of who cave sh is me something metal roof up to rail had were inspection unlocked on excitement The her to path cobwebs lair do with been two I to the welded waiting built saw fill the a the door church, out the the and door was overhang and, for and from windows that in concrete together, small feeling of like inside. a wax chapel, in any and was way. the Its streaked about gloomy but hole shape walls with fifteen scooped and were smoke feet in appears called the in St Greek my ths Anthony ’s appearance of a and legends cave snake Alice: the girl from Alice through the Looking Glass by Lewis Carroll, who enters a strange world through a mirror 200 he and the it grotesque. from was cliff the some face. It Scylla. now with crazy T urning, Tim Scylla: a I projecting through in cave!’ before hillside. sitting near understood. me. growing pushed realized fishermen be behind I cave The would they constructed I any track. led balcony masked cave I startled. persisted. Scylla, right tiled nail. stepped of the closer a melted of feet on turned of been an for up, there exasperation crag. these A I the leading was the On the the and of had key glass, on final at with me pieces back in recently pipes. face. iron up balcony metal which large was extra the Then footpath steps, The cliff wall highest for of looking It original and a of I ‘Is yelled Obviously balcony used I backs. gestured high looked asked, pronunciation shrug. reminded that two frame porch, led flight of a been their Greek of tree, spiders earlier. made sort found I knew short man-made the deep a cross blobbed feet road victims, door candles. ancient turned men They even Where?’ (Anthony). the some fat through of of cave?’ cave? irritated of The door in one the hadn’t clumsy ‘Antonis’ corner an an bushes. of the word of hung painted witnessed I They very hadn’t sort section my that ‘The disturbed. and had was question. once questioning some local shermen. ‘Where’s cave forth, crude Alice was I the that tarmac passing a be the and the which face out brought was the them. eel-spearing, the back the path there his branches between seize to hoping caught to to find general confer , make the zigzagged spun I just hurried such men back down would annoyed two beyond I cave?’ turned could sure some tourist, I shouted clearly Please, saw I so a mythical cave apparently Severin Unit 21 22 23 The why W hat the main a suitable point of in the title, the book given first is about the difficulties B To tell the reader about the legend C To tell the reader about eel the in At first the the of paragraph, correct end of Sc ylla’. the Frightened B Pleased In In it’s Give first How A In place. he right of the are two a feel of in cave’. extract. [2 the second looking finding the cave [1 of things that sug gest the examples. the [2 writer says the ‘fat spiders the third five the does he reminded were ugly B They were decorated the W hat were third does and this says he felt ‘ like Alice walking through mean? writer describes the features of the the writer describes the walls as [3 marks] [5 marks] cave. ‘grotesque’. unpleasant. brightly. enormous. paragraph, he the writer mark] mean? They They marks] this? mentions. paragraph, this the does paragraph, things third W hat mark] writer [1 paragraph, glass.’ marks] Sc ylla number about papers place A In line Sc ylla’s Disappointed W hat C first of fishing paragraph does the there search Practice paragraph? reader In ‘In the the List 28 is extract tell the 27 this the To C 26 is to A me 25 given Explain is 24 title 12: say that [1 the makes writer this is cer tain clear? he has found Sc ylla’s mark] cave. [1 mark] 201 Unit 12: Practice Writing paper ✪ Answer all ✪ The marks ✪ The maximum 1 Describe between 2 Your 3 for school or cause ✪ the place ✪ the time letter Write a when ✪ where ✪ what ✪ the it shown paper this is in brackets 60 photograph. Your description should be is are having to charity sponsor raising the a r un you. money will ‘fun You run’. must Write a letter to [9 marks] [12 marks] local mention: for happen star t. be blog between about a 50 trip and or 70 visit words. to Do friends not or write family. an address. You must refer to: went did people of this in them will or are was you diar y college should you for see where it English words. you diar y ✪ Think you asking the in questions mark 30–50 ✪ Your 4 questions what businesses Your papers or one who blog were entr y thing you with you should would be like or who you between to visited. 70 change in and 90 your words. local [16 marks] [23 marks] area. Explain: ✪ what ✪ why Your 202 you it would should explanation like be to change changed should be or improved. between 100 and 150 words. Glossary Glossar y abstract opposite things relating of or access adjective thing , a word adverb, A a word for or and examinations two years of relates seen, to a that of you that an or to ideas to (the physical touched get etc.) school person, beautiful, phrase for feelings describes so example: be ability meaning (shor t which can tall, changing the Levels that example: adjusting changes) – that education for adverb thoughts, ‘concrete ’ objects to to in place or modies or other slowly taken by Levels) students schools courses in the following work chisel a tool for referred climate competition nal the UK silently for examination or two of shor t especially by similar for close Placement) students schools to ‘A that (verb) is in course the following (for conjunction words, a last the (a piece a trade of to by or a bear an the device job, a disappearing person board (verb) school you board (noun) bored by eye close not are in stone change group in weather taking jobs or or par t that can clauses in conditions over a the used or to sentence, conjunctions) of worldwide places) be a conjunctions) issue in college and, although, nature join for but, or; because, and while wildlife drinking subject with link which is likely to cause to craftsman/craftswoman things ver y skilfully, often curriculum what cushioning protecting can altogether, dying larger protect live in, who makes sleeping and things from eating at metal the to a of wood you someone using learn (a at who makes traditional methods school cushion is something soft you) degree a interested using a at noun, general, any modern measuring devices waste, has slow been the remains of something broken break-down chopping qualication down trees or awarded after a forests three-year university determiner relationships without of deforestation course plank bits that decay bonds who argument debris extinct go to clothing out blacksmith year eating an mobile a consumption contentious animal becoming or protection that without want evidence conser vation year guidance bare wood as (coordinating US software), doing shaping word phrases correlation downloaded learn a Level’ ‘application’ one apprentice with taken secondar y curriculum; app Advanced people when (subordinating permitted (shor t and helps change allowed AP in time example: not believe that to curriculum aloud people achieve work competitive Advanced secondar y to that Class/Grade/Year (slightly verb idea hard charity cited better adjective, work an need unbelievable t cause a word usually for that telling example: disadvantage us a, gives information whether the, something it is about specic or ever y that reduces the chance of success carpenter case a study person an who example makes of things someone ’s experience cast doubt from actual wood economic to ecosystem aside stop feeling negative live and do with natural money place where animals and plants interact 203 Glossary ecotourism the natural emissions fumes, a type gases enthralling in aims not to harm in sent into the air, for example car curriculum, strong danger global of dying out good (from someone who is natural something world that not follow a general skill outside normal activities school things that you do and have just a graduate feinting features making nancial that a pretend hardship life blow diculties motor skills movements, for physical example in a ght caused abilities using by hammer lack of into using ngers to small thread a ower focus foe wheat one thing enemy food chain the links between one species and oil, sources were long ago foul (power ful adjective) worn cloth breaking frustration cannot do fullling out to energ y, from or a broken for living example things up it feeling disgusting up is of (when said to coal that a be or of education demanding ‘frayed’) because achieving what all the a US word for (dustbin/wastebin) 204 ‘rubbish’, as in tool and works well with right of amount leisure of activity, so end of a or reach college or abilities to kick a using the whole football tough (for you set time ‘garbage to hit a the together the US chisel way to do or to that drive nails someone ’s things equivalent students school that hands require up diploma to the romantic the of the age of UK qualication all courses holiday secondar y 18) at taken gained high by a by school newly couple large (shor t groups set or for of of people two years of Baccalaureate) taken secondar y by – students schools all a in course the around the world illiteracy the lack the of of induction an you of being way as or education uneducated they have been (made) occasion when you are shown around in unavoidable inuences in to for years settle dierence knowledge state traditional hundreds help can’ International examinations ignorance you used accurac y school inevitable garbage or completing in learning the learning a nal string do full-time 18 temperature examinations physical honeymoon IB dir ty piece annoyance ambition UK and or died something your skills successfully and frayed is of formed the amount at work hordes fuels that just the coordination married another fossil who the 16 course example sight high on Ear th’s of mind pass and school blossom concentrate right hand-eye high ground-up ages things speed needle our the the better money ne in – General following the someone standard motor for the healthy required body, make students balance (verb) gruelling facilities by Education) between rise player work gross hours [International] people university extra-curricular taken usually work-life the for Secondar y good you does (shor t warming team other French) rule expertise of qualications business environment GCSE/IGCSE Cer ticate fascinating entrepreneur exception that smoke make endangered inventive tourism environment factor y empower of my me life people who have made a to Glossary inhabitant person innovative creative, instrumental helping ITV a in you sur prise’ boxing lives having helping there new me Old or original par tly ideas responsible Trafford oral for over for television six an (literally channel idiom means that ‘to the means knock ‘takes you out’, you like by in a pair liaising litter left having no coastline cooperating/interacting pieces lying local land, in of a r ubbish, public or often open paper, bottles or cans, a being able to work with your hands skilfully marine a period physical to medieval between menace mental to from of of of mutual do period 1500 the with of the sea positive histor y (Middle in Europe, going mind Welsh prole mind education see government depar tment in some good that, at the same a pronoun (as T Ford – of help do with the to bad discussing neighbours rst mass-produced car both groups of people people or unpleasant the not some of the time ‘stage ’ body motor pollen lled good word that and and my or engine at plants head shows chemicals fer tilising pleasant pronouns example keep a object) the and home, that things relationship other under prevent words the in a tree food from safe word summar y that for me, (for and who reaching live next agreement to, or close rain it, can be example: of you that people can used (as to replace subject) you, a noun she, or they; us examination familiar, informal title for name of a chair, person, Tokyo, practical/impractical thing , to, your a person or place or idea, for fear hard reign rule or pass required for a job or do need as (for a doctor) example (verb) to to get become a the doctor) because of the from by a the the king sky or people queen who live in a par ticular throw out or make building area (power ful right correct, Robbie to example you water residents boy, a a with personal qualication rid example: only weapon things place noun a phrase, qualify home a a course negotiating nickname head do for education to happy ’ disadvantages USA benet negative next ‘really online noun something the one bad preserve actor the of spreading preservatives threat to from learning time, with nouns sentence: Ages) of par ts my to between education Model the to noun) a blessing T a with state has Model do or and Sheen ministry time, times 500 mindset mixed in (strong Michael charge do rings preposition living yourself education pollinating skills down meaning where beaten defending populated manual stor y telling , fruit piston nearby idiom stadium full-time) pear phase space stories an of football two parrying (not by United’s tradition passes moon part-time surrounded the overwhelmed match) landlocked Manchester tradition generation me UK-based knock who rote verb) or Williams learning not an disappear left English learning by pop star hear t circumstances nurtured cared for 205 Glossary saw sea a tool for cutting wood ocean sedate see calm use sele set used a shadow quiet eyes photo your they or your you pulse take a access photos, skills other you goal, reel squinting attempt away, as someone (to see what that the Unicef such can do Internet, that help things send you to such emails get on of or who roll of looking to succeeded see run as unruly utilised veld for money ve if you achieve kilometres with par tly closed in an former the latter think the the clearly a state the through tense it be of doing to box’ of think in a dierent, creative throw (preposition) 206 with a chance also/overly a on your Children’s Fund as one control a for to a word that example: describe devices suppor ted with evidence Africa word; being , used reason in or giving struggle shows to walk, something media up work one side or end to the longer to towards have any possibility of joining what that used it’s or pieces experience see write ght something no wrath from something (preposition) too is paper in to ‘doing ’ welding other to have only, action to cook, that not in or the to be exists in physical reality to past may throw kind together, argument waste rst way threw you you used volunteering last ‘outside can something your free time to help others after skilled the acting electronic eyes a grasslands wage talented ‘ Trash’ Nations of hard virtual string more came ‘rubbish’; well animal donate one etc. verb as the United all valid kind people in for 2 unity people or word excited denite sponsors spool phone abilities type specic US two pavements take your yourself make follow smartphone species trash unique sidewalks with of do) social characteristics computer racing someone traits a battle is disposed or got rid of once wanted of metal working in a together job for a using shor t heat time like anger put letters or words down, for example on Index plastic waste 96–7 A D abstract water details active shor tages 90–1 78 verbs 53 glossaries 110–11 determiners past and present diaries activities 38–9, 24, 67, possessive adjectives Blake, 190 William buildings ‘A poison tree’ technolog y 28–9 Culture shock 162 68 pronouns acting direct object direct speech 77 Do Indian kids spend too much time at as 170 school? 136 43–4 Ecotourism – how does it work? punctuation 118 30 E adverbs 19 62 54–5 digital adjectives 24 112 education post-16 160, 161, 169 24 Ecotourism – how does it work? adverbial clauses education fronted adverbials 60, 178–9 antonyms 166–7 154–5 OECD education apostrophes 53, Islands 114, 115 in Hints and tips for a healthy life! Lesotho repor t 150–1 home 158–9 post-16 and neighbourhood 82 homophones 160 Honda, 56 153 Soichiro 180 152–3 apostrophes ar ticles Galapagos 61 education ambitions 118–19 60 to show possession Culture shock 162–3 Indonesia expectations 161 Jarrett, 66 171 Adrian 172 190 Fast Facts Attenborough, Sir David 115, 118, 176–7 jobs, career choices and ambitions 119 Jarrett, Adrian 172–3 lifelong learning 179, 161 184 Kite Runner, e 51 B email Batwa Trail, Uganda Blake, William 22–3 natural poison tree’ species 100–1 Plastic soup 53 schools 150 190 exclamation brackets for parenthesis marks 30, 148 Should we save endangered animals 149 and plants? buildings 100 58–9 F bullet 96 18–19 examples blogs 89 122–3 endangered ‘A disasters points for lists 31, Sindbad Voyage, e 188 187 fables facts 192–3 32–3, 53, 157 social issues social media 72, 21, 73, 75, 78 23 C family career choices 2, 70–1 dierent charity work 72, 73, families 3 and my family 2 at school writing memories star ting 14 132 about family 18–19 Will your next best friend be a robot? school writing to persuade 4 84 142–3 Kite Runner, e 50–1 Yousafzai, Malala 154–5 26 gurative collective nouns 31, writing 30, inver ted Mike ‘Best 156–7 commas sentences 146, 26, sentences Friend’ 36 grammar 54–5 7 active and passive 26, verbs 110–13 your next best friend be a sentences var y 116 4–5 connective words and phrases 135 116 about friends adverbials 60, 16–17 61 connectives direct and 134–5 repor ted speech 170 139 words and phrases full stops fun runs 30 fronted adverbials 61 135 73 main types of sentence 26–7 28 modal coordinating to 116 134–5, words ways 116 26, fronted connective and 147–8 writing conjunctions connectives 38–9, conjunctions robot? context 138–9, activities 3 Will compound Gould, 148 friends complex 80 186–7 free-time commas idioms 95 formal conjunctions verbs 117, 120, 121, 182 26 G crafts A 17 ction colons Freedom, 18–19 childhood clauses to W hy students should have to do sport 78–9 me childhood Walk 178–9 prexes 128 188–9 Galapagos Culture shock 114–15 prepositional and noun phrases 162–3 global customs Islands issues 88–9, 104–5 164–6 144 endangered species 100–1 prepositions 60–1 207 Index pronouns subject 42–5, and verb subject-verb suxes tense 93 7–9, careers advisor charity work choosing 129 digital 98–9 or classes 24–5, 99 76–7 86–7 me, Hints and tips for a healthy life! my 107 home lists 153 Soichiro Hosseini, your 57 31, home talk locality e Kite Runner skills students 91 imager y 80–1, and my Walk to Freedom, A family 10–11 popular with tourists? 108–9 at school 62 accounts impersonal 4–5 lists 186 Yousafzai, nouns mobile 190 modal Nelson school? natural 136–7 77 58–9, disasters are negative neighbourhood italics writing 138–9 commas 146, 147–8 146 my 23, 121, 182 object newspaper jargon 53 Jarrett, 178–9, 172–3 192–3 K kampungs Keller, 58–9 Helen words 140–1 10, 28, 63, 168 L leaets 53, learning listening 54–5 diculties 125 140–1 natural disasters (Organisation and opinions 57 for Economic development) activities paragraphs passive 190 and 38–9 when 4 58–9 162–3 to 13 past progressive tense 13 past tense Plastic soup 9, 118–19 practice 113 98 Michael positive 40–1 96–7 23, 84 papers 194 reading paper Text 1 195–7 reading paper Text 2 197–8 First day of school – world traditions reading paper Text 3 198–9 144–5 reading paper Text 4 200–1 Have you ever thought of visiting writing Indonesia? 32–3 passive tense Ecotourism – how does it work? opinions the continuous school? 22–3 use 112 past Phelps, 136–7 110–11 present 66–7 Hints and tips for a healthy life! prexes 82–3 un-, paper 64–5, dis-, 202 130–1 im-, il- and ir- Co- 158–9 34 verbs past 57 and nouns 165–6 32–3 Do Indian kids spend too much time at facts phrases P 56–7 Culture shock email noun 84 buildings Adrian as 77 outdoor repor ts non-ction acting Old Man and the Golden Fish, e more 56 nicknames J 88 neighbourhood neighbours 164 pronouns O 21 120, 88–9 Indonesia? inver ted 208 there Have you ever thought of visiting informal key 117, operation now? 66–7 phrases 154–5 95 189 technolog y why 66–7 59, 45 OECD N Indonesia jobs A Walk to Freedom 176–7 object Malala 24, writing 69, verbs Do Indian kids spend too much time at indirect 23, possessive 14–15 190 constructions 132–3 Will your next best friend be a robot? 57 metaphors 114–15 W hy students should have to do sport 90–1 house 14–15 W hy are the Galapagos Islands so 108 noun 142 69 imagined India 115, 188–9 74–5 40–1 187 Mandela, 67, Aid Swimming – for fun or for medals? M idioms 100–1 Sindbad Voyage, e 50–1 I 172–3 96–7 and plants? 168–9 shor tages dream punctuating 180–1 Khaled friends guide water 70–1 homophones Honda, my tour 56–7, school 180–1 Should we save endangered animals 150–1 63 drinks phoning 39 holidays home 82–3 your view healthy hobbies to Adrian Plastic soup 28–9 Lesotho talk Soichiro Jarrett, 126–7 Soccer extending H 72–3, Honda, 46–7 Farel’s health in 184–5 subjects technolog y employer ’s whose talk 78–9 study education 12–13 whom word 92–3 agreement consistenc y verbs who, 48–9 128 192–3 Index prepositions 24, 60–1 prepositional phrases 164 W hy students should have to do sport mobile at school picturing 132–3 present continuous tense 12 Will your next best friend be a robot? present progressive tense 12 4–5 present tense pronouns 8, 98 42–3 possessive possessive adjectives relative pronouns pronouns 48 acting as repor t possessive acting as nouns 45 relative pronouns punctuation 30–1, 48–9 146–9, 171, 41, speech questions lists 103 spor ts 4–5 103 question 130–1 at school 5 marks 30, 148 147 158–9 subject memories 143 ction 50 reading 50–1 136–7 Lesotho 150–1 subordinating buildings -ly, rst at school semicolons 136–7 senses 118–19 sentences 22–3 opinions 32–3 ways Severin, Sheen, shor t Indonesia? similes Hints and tips for a healthy life! Soichiro Adrian Plastic soup 82–3 180–1 172–3 96–7 Aid 34 188–9 74–5 40–1 14–15 sentences -sion 166–7, 93–5 26 129 40–1 174 188–9 9 travel 8 122–3 Islands about 114–15 tourism 120–1 144–5 106–7 106–7, writing 122–3 about travel 120–1 26 Unicef 74–5 72 V 73 ourselves volunteering media 20, and and others charity 36–7 and touch 73 verbs 7, 24, active past opinions in 72–3 work 32–3 20 59, and modal 22–3 keeping 118–19, 118–19 U runs popular with tourists? Galapagos writing 74–5 facts 59 106–7, traditions tense 53 34 ecotourism 5 W hy are the Galapagos Islands so 114–15 sentences 140–1 words transpor t tense issues email 116 190 simple social sentences 75 present fun 96, people tourism 189 helping Swimming – for fun or for medals? Walk to Freedom, A 69, Aid agreement and sentences Toraja 30–1 e Sindbad Voyage past social Sindbad Voyage, e Tim simple and plants? 100–1 var y simple Soccer Soccer technical 26–7, to skimming in conjunctions Anne synonyms topic stories Should we save endangered animals subject Swimming – for fun or for medals? 183 Michael Have you ever thought of visiting 66–7 the 132–3 punctuation 144–5 Jarrett, 142 138–9 130–1 -tion, Sullivan, 68 First day of school – world traditions Honda, 143 21 Ecotourism – how does it work? and school 65, studies T seles school? facts school of W hy students should have to do sport 162–3 Do Indian kids spend too much time at email memor y star ting 58–9 Culture shock suxes 140–1 92–3 subject-verb my non-ction about 77, school? 144–5 Kite Runner, e 7, identifying First day of school – world traditions reading 153 diculties 76 in letters 132–3 Do Indian kids spend too much time at education R missing 124–5 writing 124–5, rst-day marks for 39 learning schools 147 W hy students should have to do sport S 186 scanning quotation marks studies Q questions 170 152–3 186–7 punctuating 34–5 68 homophones friends 21 inform apostrophes 170 rhetorical myself to 21 spelling 157–8 speech words speech 48–9 56 root 154–5 53 residents robot 183, 40, writing repor ted pronouns Malala pronouns relevance 43–4 writing specicity Yousafzai, technolog y 76 passive verbs 117, progressive present simple verbs 120, tense progressive past tense 110–13 121, 182 13 tense 12 9 209 Index simple present tense 8 writing about studies writing about travel 138–9 W subject and verb 7, 92–3 who, subject-verb agreement whom consistenc y Robbie for pur poses classes 24–5, readers and the 190–1 76 writing identifying 64–5, dierent 6 80–1 prexes tourism 75 writing Books 6 word idioms and 99 98–9 Word vocabular y whose 120–1 Williams, tense or 93–5 subject in to argue a point writing to describe writing to explain writing to inform writing to persuade of view sentences 130–1 102–3 76 root words 130–1 understanding suxes 65, the role of the 68–9, 174–5 object 130–1 52–3 77 synonyms and antonyms 166–7 34–5 writing Will your next best friend be a robot? formal writing 138–9, 34, 156–7 4–5 repor t volunteering 72, writing 157–8 Y 73 writing about friends and childhood Yousafzai, 16–19 210 Malala 154–5 84–5 Acknowledgements Acknowledgements p142: Nolte p143: CR S Lourens/Shutterstock ; PHOTO/Shutterstock ; FamVeld/Shutterstock ; Elena p144: p143: p144: p145: Africa Studio/Shutterstock ; joingate/Shutterstock ; Tsur ukame Schweitzer/Shutterstock ; continued p144: Design/Shutterstock ; oneo/Shutterstock ; Bori: p147: Denis Shutterstock ; p148: tobkatrina/Shutterstock ; Cristo/Shutterstock ; p147: ‘Culture reprinted Shock’ by from permission InterNations of the author magazine, and InterNations Hart: extract from ‘Soichiro Honda, Biography ’, A SME .org , June michaeljung/ 2012, p149: from bodom/ Marion Shutterstock ; extract www.internations.org , p145: p146: Judith Pavel L Photo reprinted by permission of e American Society of Mechanical and Engineers Video/Shutterstock ; p149: XiXinXing/Shutterstock ; Leitner/Shutterstock ; p151: Emir Leitner/Shutterstock ; p154: Jorg p150: Simsek/Shutterstock ; Reinhold p152: Reinhold Khaled REUTER S/Alamy Shutterstock ; ; p154: p156: Hackemann/Shutterstock ; REUTER S/Alamy ; p156: leungchopan/Shutterstock ; rui vale p157: copyright © p158: Stock Experiment/Alamy; p161: Riccardo Shutterstock ; p161: mykeyr una/Shutterstock ; p161: Samuel reprinted by p162: p161: Aleksandar Shutterstock ; Bojan p162: Todorovic/Shutterstock ; p163: chuckstock/Shutterstock ; p162: Fosenbauer/Shutterstock ; p163: p165: Matej p165: Monkey B L rights Shutterstock ; p171: p169: Monkey Shutterstock ; p167: hxdbzxy/Shutterstock ; Business p171: Pixels p175: Roman Manchinda/Shutterstock ; p175: Kholmov/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; p177: Ar tfur y/Shutterstock ; INTERFOTO/Alamy; p180: p173: p179: Jovanovic p177: Stuar t Ajay © School p180: ZUMA Press, Inc./Alamy; on Photoonlife/Shutterstock ; p182: Andrey Buttery Hunter/Shutterstock ; Maridav/Shutterstock ; iStock ; p188: p182: Emcev/Shutterstock ; p186: Tyler p180: p180: on Hecker/Shutterstock ; p188: © behalf Noci/Shutterstock ; p191: Vgstockstudio/Shutterstock ; p192: p191: authors and publisher are Ste UK copyright Museum, Blind, extract extracts 1998, of & K J 2004), Water town, from of Long Little Andries: reprinted and Riverhead, extract by R andom from an House ‘Helen permission Massachussetts, Walk Brown from and Severin the e from Sinbad e to Book Freedom Group 1983, Voyage Jason reprinted of www.perkins.org (Abacus, 2013), Ltd (Abacus, Voyage by 1998), (R andom permission of copyright House A M 1983), Heath & Co author. and Ron omas: www.kidc yber.com.au, and record Pictures p188: p182: USA/Alamy; p187: p186: amriphoto/ magicoven/Shutterstock ; Malala IT V for amount Ajax News & Feature Yousafzai: copyright extract reprinted from by ‘Indonesia-housing ’ permission of the extract for from Unicef ’s June work for 2016 press children’, release, ‘Soccer Aid www.unicef.org.uk Brown © Monkey p192: Business for Malala Group Ltd, extract from Yousafzai London on speech 2013, to the reprinted behalf of United by Malala Nations, permission of July 2013, Cur tis Yousafzai. p188: third par ty use of this material, outside of this publication, is Ser vice/Alamy; Interested par ties should apply to the copyright holders p191: indicated in each Although we case. Images/Shutterstock ; KieferPix/Shutterstock. permission to reprint have before made ever y publication eor t this has to not trace been and contact possible in all all copyright cases. If the notied, following Plc Penguin of M88/ studio/Shutterstock ; Keystone grateful Publishing division authors. holders e a Naturspor ts/Shutterstock ; wavebreakmedia/Shutterstock ; Bikeworldtravel/Shutterstock ; the Sydenham prohibited. p190: Group, Seymour-Ford for Tim Kidc yber, Any omas J permission Severin Shirley adam/ Tvm/Shutterstock ; Olson/Shutterstock ; Zovteva/Shutterstock ; Bloomsbur y Dream_master/Shutterstock ; p182: p183: 2003), 2003, Fotokon/ raises p182: by Severin: Tim Ltd Jenner/Shutterstock ; : of Publishing Histor y Mandela: copyright p175: ar fa Dejan/Shutterstock ; Tim Unicef Shutterstock ; LLC BaLL Matej p175: p175: (Bloomsbur y, Nitr/ Tsekhmister/ BCS/Alamy; Andrei Pressmaster/Shutterstock ; p168: Babakin/Shutterstock ; p175: by Publications Business p166: Maridav/Shutterstock ; p171: LLC/Shutterstock ; Shutterstock ; p179: p170: Images/Shutterstock ; Golden K astelic/Shutterstock ; Kidsada MarclSchauer/Shutterstock ; Runner TKR reser ved. (Perkins reprinted LunL a/Shutterstock ; permission Penguin McGinnity, Keller ’ Perkins Tr pjumnong/ K astelic/Shutterstock ; of All Nelson Images/Shutterstock ; Kite © Borges Milinkov/Shutterstock ; Stanislav e 2003, Mayer/ LLC. Paassen/Shutterstock ; from Hosseini Nikolai/ Shutterstock ; Regien extract Khaled sousa/ Titov imprint Photography/Shutterstock ; Hosseini: p154: the publisher will rectify any errors or omissions at the earliest material: oppor tunity. David to Attenborough: sur vive’, copyright Lonely © extract Planet Lonely from Traveller, Planet, 2009, ‘Galapagos www. Islands need tourism Lonelyplanet.com/magazine, reprinted by permission of Lonely Planet 211 International ENGLISH A Audio GCSE CD inside AS S E CO N D L A N G UAG E Mike The Gould only English as a ■ ■ Second fully to the Oxford specication writing , listening Audio CD. Build assessment with communicate reading , students’ packed suppor ts Language students develops Rene that Pepper AQA (9280), International for rst clearly speaking , ability condence exam-style teaching practice and with with and with an a thematic listening from extensive exam I approach skills. practice preparation on the chapter advice. Unit Where UNIT GCSE 2017. Enable that Lorna textbook September ■ and 4: Thinking and speaking live When we talk about where we live, we also use the word neighbourhood. is means the street you live in (if you This 4 unit is all about neighbourhood and your home, town, live in one), or the immediate area around your home – the local roads, shops, parks, elds etc. region. So, In this unit show R2 you key learn clear points, and of vocabulary, coherent details how and text ideas of and extended purpose length to 4.1 My and longer make S2 the and overall message spoken appropriate grammatical you describe your home and neighbourhood? present texts, and home Time to think ideas ink identify L2 would to: understanding produce W2 will and key involving accurate points some use of a in more a variety complex variety of of about some of the following questions: short ✪ How ✪ W hat long ✪ Have ✪ Did have you lived in your current home? language is it like? W ho lives there with you? Useful vocabulary people moved in or out while you have been rooms, you live somewhere else before your current words family, relatives, there? structures. upstairs, Also downstairs, home? available: street Check Time My home and to that neighbourhood meaning Spend a few you know the talk minutes thinking about these things and then take it of all these words. in Glossary turns is unit Look at is the about the photos place on you these call two ‘home’ pages. and ey the all area show you live places we in. local people who but look how dierent they talk and ask questions with a friend or group. live 4.2 ‘home’, to nearby would neighbours call are! next to, or close to, your My neighbourhood REMEMBER: home sensitive in nickname a familiar , informal Time to for a person residents the or place people who Now, live ✪ in think Does it about have a the immediate name? area (sometimes around areas where have you official live. have particular building or area names, and homes sometimes they How people are given local ‘ nicknames’ as be live ✪ many too many and W here to how long would do you count, you you say or know just have your a by name handful, been in be than or the point others) others to your area? depending on (There where at which, you ✪ ✪ ere are lots of ways to describe the building where you live – share do not want leave, begins you think and – ‘I ends? have (Think left the structure with its walls and roof, but the word home If you it begins W ho live something wherethey How how you long nd feel you else. family about or For or your your many friends, home family your neighbours and (but safety will have not also lived all), and be means your the your Give by what it relationship village or same a friend area as or your in, describe and some vocabulary from the of this group. for friends, do you agree on where ends? the that most (for people example in their because neighbourhood? their family has Is there lived a there longest)? place security. inuenced there, the residents of it the with live section. often the means in you other opening ideas and knows word my the reason physical if to. now ’.) talk your to not may the Now, do things there.) neighbourhood as and you area to be (some comfortable reveal neighbourhood to neighbourhood Time to say enough more REMEMBER: Use about you lucky well) they ✪ may bigger press a Remember what think people title is a shor t talk – no and neighbourhood. you lived more If you than ve would minutes prefer to – talk describing about a your home previous place like, in, that is ne too. with town. 56 57 Answers to the exercises in this book and transcripts for the listening activities 978-019-841716-3 are in the Teacher Pack, available separately. How to get in touch: IS B N 1 web www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk email schools.enquiries.uk@oup.com tel +44 (0)1536 452620 fax +44 (0)1865 313472 9 9 7 8 -0 -1 9 -8 4 1 7 1 3 -2 780198 417132