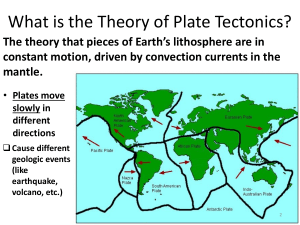
NAME:_________________________________________ YEAR & SECTION: __________________ GENERAL DIRECTIONS: Write your answers in capital letters. No erasure. Erasing in any form means wrong answer. Test A. Multiple Choice. Read the questions carefully. Write the letter of the correct answer in your activity notebook. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth? a. crust b. inner core c. mantle d. outer core 2. The crust and upper mantle make up Earth’s __________. a. asthenosphere b. continents c. core d. lithosphere 3. Which statement about the Earth’s crusts is CORRECT? a. Continental and oceanic crusts have the same weight. b. Continental crust is heavier than oceanic crust. c. Continental crust is thicker than oceanic crust. d. Oceanic crust is thicker than continental crust. 4. What do we call the continuously moving part of the earth’s crust? a. fault b. fissure c. fracture d. plate 5. Which theory states that the entire crust is broken and is continuously moving? a. Continental Drift b. Plate Tectonics c. Seafloor Spreading d. Titanic Theory 6. Which of the following is NOT a result of Plate Tectonics? a. earthquake b. fault lines c. landslides d. mountains 7. How are tsunamis created? a. A submarine earthquake causes a huge amount of water to be displaced. b. Differences in temperature cause hot seawater to rise. c. The gravitational pull of the moon causes the ocean water to rise. d. Topography underwater causes disturbances in the oceans’ current. 8. A landmass that projects well above its surroundings is a mountain. What do you call a chain of mountains? a. b. c. d. mountain area mountain chain mountain range mountainous 9. It is the location on the Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake. a. center b. direct center c. epic center d. epicenter 10. Plates float on the surface of the mantle. Which plate pushes the Philippine Plate toward the Eurasian Plate? a. Cocos Plate b. Indo-Australian Plate c. Nazca Plate d. Pacific Plate 11. If an earthquake begins while you are in a building, the safest thing for you to do is _____. a. call home b. duck near a wall c. get under the strongest table, chair, or other pieces of furniture. d. lie flat on the floor and cover your head with your hands. 12. Why is it important to be aware of places prone to earthquakes? a. to identify what crop must be stored b. to identify when to evacuate c. to locate where to stay best d. to perform necessary precautions 13. Which statement does best describe the location of most earthquake epicenters relative to the location of volcanoes around the world? a. They are far adjacent. b. They are always 3 kilometers away from each other. c. They are situated at the same location. d. They are not necessarily relevant. 14. How will you relate the distributions of mountain ranges, earthquake epicenters, and volcanoes? a. Mountain ranges are found in places between where volcanoes and earthquake epicenters are also situated. b. Mountain ranges are found in places where volcanoes and/or earthquake epicenters are also situated. c. Mountain ranges are found only in places where earthquake epicenters are situated. d. Mountain ranges are found only in places where volcanoes are situated. 15. Plates move apart at __________ boundaries. a. convergent b. stable c. divergent d. transform 16. a. b. c. d. Plates slide past each other at ________________. subduction zone divergent boundary convection current transform-fault boundary 17. The boundary between two plates moving toward each other is called a _________. a. divergent boundary b. transform boundary c. lithosphere d. convergent boundary 18. Seafloor spreading is located at _____________. a. transform plate boundary b. convergent plate boundary c. divergent plate boundary d. Indian plate 19. Plate Tectonic Theory states that continents have moved ________ to their current location. a. vertically b. horizontally c. quickly d. slowly 20. The East African Rift is an example of a ______. a. mid-ocean ridge b. convergent boundary c. rift valley d. transform boundary 21. The Himalayan mountain range of India was formed at the __________. a. divergent boundary b. convergent boundary c. hot spot d. transform boundary 22. The __________ is an example of a transform fault boundary. a. Appalachian Mountains b. Mid-Atlantic Ridge c. San Andreas Fault d. Himalayas 23. When magma in the earth’s mantle develops a great pressure, the ground above it is pushed upward. If this happens in the middle of an ocean, what landform is produced? a. mountain b. volcanic island c. volcano d. continent 24. The tall landform created when two continental plates converge is called_______. a. mountain range b. volcanic arc c. rift valley d. Oceanic ridge 25. It is a plate that dives down under a less dense plate during subduction. a. subducting plate b. continental plate c. mantle d. overriding plate 26. Materials in the mantle flow up and down. Which of the following best describes the mantle? a. a solid layer b. partially liquid c. a metallic layer d. very hot layer 27. Which of the following happens when plates diverge or move away from each other? a. The crust is destroyed. b. New crust is produced because magma rises, then cools off and turns into solid. c. Earth’s size changes because mountains are added on the earth’s surface. d. The mantle rises. 28. A rift valley is formed simultaneously with which of the following type of plate boundary? a. Convergent b. Divergent c. Transform fault d. Both convergent and divergent 29. How do the plates move when we feel that the ground is shaking? a. toward each other b. away from each other c. slide past each other d. all of the above 30. It is otherwise known as an underwater mountain. a. oceanic ridge b. trench c. hill d. volcanic island 1. stress 31. It is a chain of volcanoes developed parallel to a trench or a crack under the ocean. a. mountain range b. volcanoes c. volcanic island arc d. mountainous 32. It is formed when ocean water flips upward, sometimes up to certain meters high, due to the great push caused by convergence of plates. a. wave b. tsunami c. tides d. storm 33. It is the point where two plates meet or collide while converging. a. collision zone b. sinking point c. subduction zone d. meeting point 34. The place where a subducting plate reaches the mantle during convergence. a. collision zone b. subduction zone c. mantle plume d. magma 35. The word used to refer to the shaking of the ground due to any activity in the lithosphere. a. intensity b. earthquake c. Volcanism d. Wave Test B. Matching Type. Match the following words in Set A with the corresponding definition is Set B. SET A SET B 2. fault 3. normal fault 4. subduction 5. trench 6. reverse fault 7. compressional stress 8. primary wave 9. tensional stress 10. love wave a. a depression on the ground caused by subduction b. pulls hanging wall down relative to the footwall c. this wave causes the rocks they pass through to change in shape d. hanging wall moves upwards, relative to the footwall e. force leads to a smaller volume f. one plate dives under another plate g. fastest seismic wave h. rocks are pulled apart or stretched i. has horizontal motion that is transverse j. force applied to a rock and may cause deformation k. zone of fractures between two blocks of rock Test C. Fill in the blank. Choose the answer inside the box. continental theory geologic divergent lithosphere plates subduction convection current slowly denser toward two continental plates two oceanic plates oceanic plate-continental plate transform fault (1) _____________ is made of earth’s crust and upper mantle. It is subdivided into portions called (2) ___________ that move above the mantle. The two kinds of crust are (3) ______________ crust, which is thicker but less dense, and oceanic crust, which is thinner but (4___________. A (5) ___________ that the Earth’s crust is made up of plates moving (6) __________ and interact in various ways is Plate Tectonics. The interaction of the plates produces earthquakes, mountains, volcanoes, and other (7) ________ features. (8) _________________ from the Earth’s interior makes the plates move above the mantle. This movement causes the formation of three types of plate boundaries which are (9) _____________ boundary, two plates sliding each other; (10) ________________ boundary, two plates moving away from each other and convergent boundary which plates are moving (11) ________ each other. Three types of convergent boundaries are (12) ______________ convergent boundary which forms volcanic island arc, (13______________convergent boundary forming a continental volcanic arc, and (14) _________________ convergent boundary wherein there is no (15) ___________.