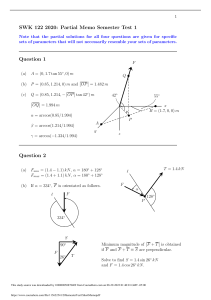
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT RECEIVABLES MANAGEMENT PROBLEMS – SOLUTION PROBLEMS Accounts Receivable Balance Dina Corp. sells on term 3/5, net 20. Total sale for the year are P912,500. 40% pays on the 5th day and take discounts; the rest pay on average of 40 days after their purchase. What is the average amount of accounts receivable? (use 365 days/year) 65,000 Note: • Average amount of accounts receivable asks in this problem is the same as the amount of receivable that we may be able to arrive using the formula of DSO discussed in the FS analysis. • AR will be computed by multiplying the DSO by the Daily credit sales. • What is somehow new in this problem is that DSO is not given as a concrete no. of days – we need to compute or estimate it based on percentage of buyers who pay on certain date. • 40% of customers paid on the 5th day and 60% paid on the 40th day – arriving at 100% of the customer. • Use the number of days per year given by the problem. This study source was downloaded by 100000871823805 from CourseHero.com on 10-16-2023 07:14:05 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/63012222/Receivables-management-SOLUTIONSpdf/ Change in AR balance Mike Co. budgeted sales for the coming year is P40,500,000, 80% of which is expected to be credit sales at terms n/30. Mike Co. estimates that by relaxing credit standard, credit sales will increase by 20%. The average collection period is expected to increase from 30 to 40 days. By how much will the proposed relaxation of standards increase the Accounts receivable balance? (use 360 days/year) 1,620,000 increase Note: • “Relaxing credit standard” means the company will shift its credit standards to more accommodating one so that the company may be able to grant more credit to the customers. • Again, the AR is computed by manipulating the formula of the Days Sales Outstanding (DSO). • The problem is basically asking how much will be the additional receivables that that the company will have resulting from the proposed relaxation of credit standard. • It is appropriate to compute first how much is the AR balance under the old policy. Get the credit sales first by using the info given (40,500,000 * 80%) • Under the new policy, DSO will now be 40 days. The credit sales is derived by multiplying the credit sale of the old policy by the growth rate of credit sale (* 1.2) • Get the difference of the AR under the old and the new relaxed policy, This study source was downloaded by 100000871823805 from CourseHero.com on 10-16-2023 07:14:05 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/63012222/Receivables-management-SOLUTIONSpdf/ Investment in Accounts receivable Moo Corp. has annual sales of P2,500,000. Its average collection period is 45 days, and bad debts are 3% of sales. The credit and collection manager is considering implementing a more strict collection policy, whereby bad debts would be reduced to 1.5% of total sales, and the average collection period would fall to 30 days. However, sales would fall by an estimated P300,000 annually. Variable cost are 75% of sales and the cost of carrying receivables is 10%. Assume the tax rate of 40% and use 360 days/year. What would the decrease in investment in receivables be if the changes were made? 96,876 decrease Note: • The use of the above format facilitates a more convenient way of comparing different Credit policies. • The fist column is the Before (liberal or relaxed policy) and the seconds is the Implementing (strict policy) • DSO is given by the problem under the two policies while Daily Credit sales is appropriately computed as well using the days of the year given by the problem. • The AR is computed by multiplying the DSO by the Daily credit sale. As you observe above, that format of computation is convenient in comparing the two policies. • Variable cost is multiplied to the AR balance computed to arrive at the Amount of Investment in receivables. The AR is multiplied by the Variable cost Ratio because its concern is only with the out-of-pocket costs, the relevant cost is the variable cost. This study source was downloaded by 100000871823805 from CourseHero.com on 10-16-2023 07:14:05 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/63012222/Receivables-management-SOLUTIONSpdf/ Impact of change in credit policy to profits 1. Fast Inc. is considering shifting its credit terms from 2/15, n/30 to 3/10, n/30 in order to speed up collections. Currently, 40% of Fast Inc.’s customers take the 2% discount. Under the new term, discount customers are expected to rise to 50%. Regardless of the credit terms, half of the customers who do not take the discount are expected to pay on time, whereas the remainder will pay 10 days late. The change does not involve a relaxation of credit standard; therefore, bad debt losses (per peso sales) will remain at status quo. Currently bad debts expense is 2% of sales. But more generous cash discount terms are expected to increase sales from P2,000,000 to P2,600,000 per year. Fast Inc.’ variable cost ratio is 75%, the interest rate on funds invested in accounts receivable is 9%, and the firm’s income tax rate is 40%. Use 360 days/year. a. b. c. d. What is the Days Sales Outstanding before the change in credit policy? 27 days What is the Days Sales Outstanding after the change in credit policy? 22.5 days What is the incremental carrying cost on receivable? 843.75 What is the incremental after-tax profit from change in credit terms? 68,493.75 Note: • The computation for (a) and (b) here is similar to the computation used in Accounts Receivable Balance problem presented previously. The days is multiplied by the percentage of customers who probably pay on that day. This study source was downloaded by 100000871823805 from CourseHero.com on 10-16-2023 07:14:05 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/63012222/Receivables-management-SOLUTIONSpdf/ Note: • The format above is used when determining the Investment in AR and Carrying Cost of AR, as well as in differentiating or comparing such under a new and old policy. This format is similar with the one used in Investment in Accounts receivable problem presented previously. • Accounts receivables has a corresponding cost imbedded into it. Analyze this: when we grant credit to customers we record AR in our books which represents a right to collect from customers, however when we do not grant credit to a customer, the company immediately collected cash, record the cash in the books and invest it immediately to an investment facility that earns a certain interest. The bottom line here is, if we grant credit, we may not be able to get the cash immediately and invest it to earn interest and that forgone benefit of investing it is the carrying cost of AR. This study source was downloaded by 100000871823805 from CourseHero.com on 10-16-2023 07:14:05 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/63012222/Receivables-management-SOLUTIONSpdf/ Note: • Applying the Aid Format for analyzing and computation of Profit Impact of Changing Credit Policies, above is the solution. • Be careful in each component since one error could lead to wrong computation of the incremental change in Profit. • The change in discount has a cost as well, since there is a change in the credit term, the projection of the customer who will avail the discount will differ. Since more discount will be granted based on the projection under the new credit term it is considered as a deduction to the CM generated from the increased in sales. This study source was downloaded by 100000871823805 from CourseHero.com on 10-16-2023 07:14:05 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/63012222/Receivables-management-SOLUTIONSpdf/ 2. Juan Corp. currently has sales of P1,000,000, and its days sales outstanding is 30 days. The financial manager estimates that offering longer credit terms would increase the days sales outstanding to 50 days and increase the sales to P1,200,000. However, bad debts losses, which were 2% on the old sales, would amount to 5% only on incremental sales. Variable cost is 80% of sales. Juan Corp. has a 15% receivable financing cost. Use 360 days per year. What would the annual incremental pre-tax profit be if Juan Corp. extended its credit period? 20,000 Note: • Analyze carefully the problems since not all the variables used in the computation should always be present. E.g. The change in discount is 0 since it is not stated in the problem that discounts will be affected by change in credit period. This study source was downloaded by 100000871823805 from CourseHero.com on 10-16-2023 07:14:05 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/63012222/Receivables-management-SOLUTIONSpdf/ Impact of change in collection policy to profits Worldcom Inc. is planning to modify its collection practices. The new procedures are expected to make the collection period longer by 10 days, although there will be no change in bad debts. For the coming year, Worldcom Inc. budgeted sales is P32,400,000 or P90,000 per day. Short-term interest rates are expected to average at 9% per annum. a. Worldcom Inc.’s average Accounts receivable will increase (decrease) by due to the change in collection policy? 900,000 b. To make the change in collection procedures cost-beneficial, the minimum savings in collection cost for the coming year should be? 81,000 Note: • Collection Policy is different from Credit Policy; the former means the procedure in collecting as well as the length of days granted o the buyer before the eventual collection. • In letter (a), the increase or decrease is computed using the formula of getting the AR using the formula of DSO. In this formula you can use the incremental change in DSO and Daily credit sales to arrive at the incremental increase or decrease of AR. • In letter (a), the increase in AR if further multiplied by the interest rate to arrive at the minimum savings in collection cost. This study source was downloaded by 100000871823805 from CourseHero.com on 10-16-2023 07:14:05 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/63012222/Receivables-management-SOLUTIONSpdf/ Net Credit Position Coral Food Corp. normally take 25 days to pay for average daily credit purchases of P100,000. Its average daily sales are P120,000, and it collects accounts in 27 days. Use 360-days. What is its net credit position? 740,000 Note: • The Net Credit position is simply the AR balance less the AP balance. • The AR is computed the same way as we compute the AR on the previous problems. • The AP is computed using the manipulated formula of the Payables Deferral Period (PDP) or Age of AP. This study source was downloaded by 100000871823805 from CourseHero.com on 10-16-2023 07:14:05 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/63012222/Receivables-management-SOLUTIONSpdf/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)