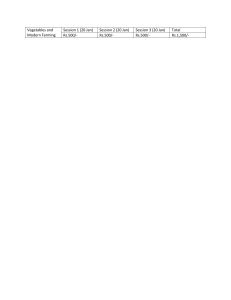
study notes for agri: video on agri notes https://youtu.be/U4RrC1_paMo 1. *Conventional and Non-Conventional Farming*: - *Conventional Farming*: This is a modern approach to farming that uses chemicals, machinery, and technology to increase yield⁶. It involves high capital investment and technological innovations⁶. It uses chemical fertilizers to promote plant growth and sprays pesticides to get rid of pests⁹. - *Non-Conventional Farming*: This refers to methodologies which use different approaches, from hydroponics to vertical agriculture and urban farming, agroecology, permaculture, and organic production⁷⁸. It aims to farm products that are 95% free of chemicals, hormones, pesticides, or other harmful methods⁵. 2. *Careers in Agriculture and Their Roles*: - *Agricultural Engineer*: Improve current farming methods, design new equipment and machinery using computer-aided technology (CAD)¹¹. - *Agricultural Economist*: Apply microeconomic and macroeconomic concepts and theories to understand economic decisions¹¹. - Other careers include biochemists, plant and food scientists, veterinarians, sustainable biomaterials specialists, ecosystem managers, agricultural science and business educators, crop advisors, pest control specialists, and environmental engineers in agricultural applications¹². 3. *Problems and Solutions in Agriculture*: - *Climate Change*: Fluctuations in atmospheric carbon dioxide, temperature, rainfall, and the intensity of climate occurrences such as drought, flood, and excessive heat is a major problem faced by farmers. Solutions include rainwater harvesting, precision farming, and modification of livestock habitat¹. - *Budgeting*: The cost of a farm can grow out of control over an extended period. A proper restructuring of finance systems and the reduction of interest rates attached to loans will direct agriculture to a brighter path¹. 4. *Importance of Agriculture in Jamaica*: - Agriculture contributes to 8.68% of Jamaica’s economy¹⁹. It is one of the pillars holding up Jamaica’s economy¹⁹. - Agriculture is an essential contributor to the Jamaican economy, accounting for nine per cent of Jamaica’s gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020¹⁷. - In Jamaica, agriculture continues to be integrally related to rural development. Its contribution to containing crime and maintaining social stability in both rural and urban areas continues to be significant as it helps to reduce problems of rural/urban migration. problem and solutions: Climate: Climate change is causing extreme weather events, air pollution, and species extinction. Solutions include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting sustainable development, and enhancing the environment. - Topography: The challenges of topography include managing sloping plots and erosion. Solutions involve different architectural and land management approaches to deal with landscape. - Rural Infrastructure: Rural areas face challenges like poverty, illiteracy, unemployment, homelessness, and crime. Solutions include improving infrastructure, providing better access to public services, and implementing rural development projects. - Praedial Larceny: This refers to the theft of agricultural products. It's a major issue affecting farmers' income. Solutions include legal reforms, public awareness campaigns, and improved law enforcement. - Land Tenure: Many farmers work on land they don't own, leading to insecurity and potential loss of livelihood. Solutions include legal reforms to secure tenure rights and equitable access to land. - Loss of Agricultural Land: Urbanization, desertification, erosion, and salinization are causing loss of agricultural land. Solutions include sustainable land management practices and policies to protect agricultural land. - Access to Finance: Many individuals and businesses struggle to secure financing due to various reasons. Solutions include financial literacy programs, simplifying the process of obtaining valid ID for financial services, and consumer protection regulations. - Coral Reef Destruction: Coral reefs are dying due to warming waters, pollution, ocean acidification, overfishing, and physical destruction. Solutions include reducing pollution, promoting sustainable fishing practices, and restoring reefs with more heat-tolerant coral. - Availability of Workers: There's a paradox of high unemployment rates alongside businesses struggling to find enough people to hire. Solutions include policy changes to encourage workforce participation and innovative benefits for employees. - Aging Farm Population: The average age of farmers is increasing worldwide, leading to concerns about who will continue farming in the future. Solutions include encouraging younger generations into farming through education programs and making farming more appealing as a career. - Limited Participation of Youth: Young people are often not involved in decision-making processes or in sectors like agriculture. Encouraging youth participation through education programs and making these sectors more appealing can be part of the solution. - Food Safety: This involves ensuring that food is free from harmful substances and safe for consumption. Regular inspections, adherence to safety standards, and public education about food safety practices are common solutions. - Natural Disasters: These can cause significant damage and loss of life. Preparing for natural disasters involves improving infrastructure resilience, developing effective early warning systems, and educating communities about disaster preparedness.