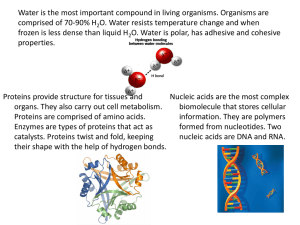
Pumpkin Seeds & Macromolecules Name: ____________________________ Date; __________________ Pd: ______ Pumpkins not only give us delicious pies and jack-o’-lanterns, but they also give us seeds that can be roasted. The roasted seeds have a rich, almost peanut-like flavor. Pumpkin seeds are highly nutritious and help protect against various health problems. They are rich in antioxidants, vitamin E, iron, zinc, magnesium, and many other nutrients. An ounce (28 g) contains about 150 calories. Pumpkin seeds have been shown to improve heart health, blood sugar levels, and sleep quality. They may even protect against certain types of cancer. Their rich nutrient content may provide other health benefits, such as improved energy, mood and immune function. What’s best, they can easily be added to your diet as a snack or as an ingredient in meals or baking, allowing you to reap their many positive effects. The shelled pumpkin seeds are often labeled as pepitas, meaning “little seeds” in Spanish. Proteins Carbohydrates Pumpkin seeds are a good source of tryptophan, zinc, and magnesium – all of which help promote good sleep. They’re a rich source of amino acids, especially tryptophan. Tryptophan is an amino acid that can help promote sleep. Zinc helps convert tryptophan to serotonin, which is then changed into melatonin, the hormone that regulates your sleep cycle. In addition, adequate magnesium levels have also been associated with better sleep. Whole pumpkin seeds are a good source of fiber. Half of the carbohydrates in a serving of pumpkin seeds come from fiber. Fiber supports healthy digestion and helps people feel full longer. Diets high in fiber are associated with many health benefits, including a reduced risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. A diet high in fiber can promote good digestive health. Lipids Nucleic Acids The fats in pumpkin seeds are of the more heart-healthy type. Pumpkin seeds have high concentrations of monounsaturated fats, as well as polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids. Unsaturated fats and omega-3’s have cardioprotective effects. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation and may help lower risk of heart disease, cancer, and arthritis. The word “pumpkin” comes from the Greek Pepõn, which means large melon. It’s in genus Cucurbita with muskmelons, cucumbers, and watermelons. Cucurbitas have large genomes with 20 pairs of chromosomes, compared to watermelon’s 11 or cucumber’s seven. Once deciphered, the genome sequences are an important resource for further scientific research and breeding of Cucurbita crops. By analyzing the genomes, researchers will identify many genes associated with the pumpkin’s desirable traits, including resistance to disease and temperature extremes, fruit quality, and nutrition. How to Roast Pumpkin Seeds: https://www.tasteofhome.com/article/roast-pumpkin-seeds/ Pumpkin images from Pixabay.com Pumpkin Seeds & Macromolecules Name: ____________________________ Date; __________________ Pd: ______ Read the information about pumpkin seeds and macromolecules. Then use your class materials as well as the pumpkin seeds resource to answer the following questions. Proteins 1. Proteins have many functions. List several functions of proteins. 2. What type of molecule is tryptophan? 3. How is tryptophan beneficial? 4. What type of molecule is formed when amino acids are linked together? 5. What elements do proteins contain? Carbohydrates 1. What are the functions of carbohydrates? 2. What are the monomers (“building blocks”) of carbohydrates? 3. What polysaccharide is described in pumpkin seeds? 4. Fiber is really cellulose. Where is cellulose found in plant cells? 5. What are some benefits of dietary fiber? 6. What elements do carbohydrates contain? Lipids 1. What are the functions of lipids? 2. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids? 3. What type of fatty acids are Omega-3’s? 4. What are some health benefits of Omega 3’s? 5. What elements do lipids contain? Nucleic Acids 1. Compare the number of chromosomes in pumpkins to the number of chromosomes in humans. 2. What are the functions of nucleic acids? 3. What is the monomer of nucleic acids? 4. What are two types of nucleic acids? 5. What elements do nucleic acids contain? Pumpkin Seeds & Macromolecules Name: ____________________________ Date; __________________ Pd: ______ Read the information about pumpkin seeds and macromolecules. Then use your class materials as well as the pumpkin seeds resource to answer the following questions. Proteins 1. Proteins have many functions. List several functions of proteins. Ex. structural, contractile/movement in cell, transport, storage, hormones, enzymes, protection 2. What type of molecule is tryptophan? Amino acid 3. How is tryptophan beneficial? It promotes sleep when converted to serotonin and then changed into melatonin 4. What type of molecule is formed when amino acids are linked together? Polypeptide 5. What elements do proteins contain? C, H, O ,N Carbohydrates 1. What are the functions of carbohydrates? Energy storage, structural 2. What are the monomers (“building blocks”) of carbohydrates? Monosaccharides 3. What polysaccharide is described in pumpkin seeds? Insoluble fiber / cellulose 4. Fiber is really cellulose. Where is cellulose found in plant cells? Plant cell walls 5. What are some benefits of dietary fiber? Digestive health, reduce chances of colon cancer, diabetes, and obesity 6. What elements do carbohydrates contain? C, H, O Lipids 1. What are the functions of lipids? Energy storage, insulation 2. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids? Saturated fatty acids have all single bonds in the carbon chain 3. What type of fatty acids are Omega-3’s? Polyunsaturated 4. What are some health benefits of Omega 3’s? Cardioprotectice effects, reduced risk of heart disease, arthritis, and cancer 5. What elements do lipids contain? C, H, O Nucleic Acids 1. Compare the number of chromosomes in pumpkins to the number of chromosomes in humans. Humans have 46 chromosomes; pumpkins have 40 2. What are the functions of nucleic acids? Storing genetic information for production of proteins 3. What is the monomer of nucleic acids? Nucleotides 4. What are two types of nucleic acids? DNA and RNA 5. What elements do nucleic acids contain? C, H, O, N, P All images used in this resource are from Pixabay.com