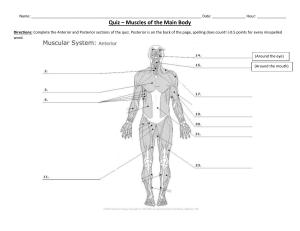
Muscular System Quiz Revision Booklet Name: Class: Introduction Welcome to your review guide for the upcoming quiz on the muscular system. This booklet is designed to help you reinforce your understanding and prepare effectively. Dive in, engage with the interactive elements, and get ready to ace your quiz! Muscle Types Overview Muscles are specialized tissues that contract to produce movement. There are three main types: Skeletal Muscle: Attached to bones and responsible for body movement. They are voluntary and have multiple nuclei. Cardiac Muscle: Found in the heart. They are involuntary and have a single nucleus. Unique feature: intercalated disks. Smooth Muscle: Found in organs like the stomach and intestines. They are involuntary and have a single nucleus. What are two facts about cardiac muscle that makes it unique? Actin & Myosin: The Dynamic Duo Actin and Myosin are proteins present in all muscle types. They work together to produce muscle contraction. Myosin "walks" along actin filaments, pulling them closer together. This interaction is fundamental for muscles to contract. Quick Check: Sketch a simple diagram showing actin and myosin interaction. Striations and Muscle Appearance Striations are the visible lines seen in skeletal and cardiac muscles. They are due to the overlapping of actin and myosin. Smooth muscles, however, do not have these striations. Reflection: Why do you think smooth muscles lack striations? The Role of Calcium and Other Proteins Calcium plays a crucial role in muscle contraction. When calcium is present, it binds to a protein called troponin. This binding causes another protein, tropomyosin, to shift and expose binding sites on actin, allowing myosin to bind and contract the muscle. Think About It: Why is calcium essential for muscle function? Sarcomeres: The Building Blocks Sarcomeres are the basic units of muscle contraction. They contain actin, myosin, tropomyosin, and troponin. When sarcomeres contract and relax, they give muscles their striated appearance. Quick Activity: Label a diagram of a sarcomere with its parts. Voluntary vs. Involuntary Muscles Muscles can be controlled voluntarily (by conscious thought) or operate involuntarily (without conscious control). Voluntary Muscles: Skeletal muscles. Involuntary Muscles: Cardiac and smooth muscles. Discussion Point: Why might it be beneficial for certain muscles to operate without our conscious control? Quiz Preparation Tips Active Recall: Test yourself without looking at notes. Teach Someone Else: Explain concepts to a friend or family member. Visual Aids: Draw diagrams or use flashcards. Rest: Ensure you get a good night's sleep before the quiz. Sample Quiz Questions 1. Which muscle type is found in the heart? 2. True or False: All muscles operate under voluntary control. 3. What role do tropomyosin and troponin play in muscle contraction? 4. Why do skeletal muscles appear striated? Note: These are sample questions. The actual quiz may contain different or additional questions. Conclusion You're well on your way to acing the quiz! Use this booklet as a guide, but remember to review your class notes and ask questions if you're unsure about any topics. Best of luck!