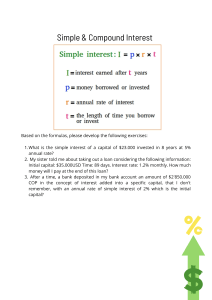
1. Durco Automotive needs a $1 million balance in its contingency fund 3 years from now. The CFO (chief financial officer} wants to know how much to deposit now into Durco’s high-yield investment account. Determine the amount if it grows at a rate of 20% per year (a) simple interest, and (b) compound interest. (1.34) 2. TMI Systems, a company that customizes software for construction cost estimates, repaid a loan obtained 3 years ago at 2% per year simple interest. If the amount that TMI repaid was $120,000, calculate the principal of the loan. (1.35) 3. The Nicor family is planning to purchase a new home 3 years from now. If they have $240,000 now, how much will be available 3 years from now? The fund grows at a compound rate of 12% per year. (1.36) 4. (a) At a simple interest rate of 12% per year, determine how long it will take $5000 to increase to twice as much. (b) Compare the time it will take to double if the rate is 20% per year simple interest. (1.37) 5. Valley Rendering, Inc. is considering purchasing a new flotation system for grease recovery. The company can finance a $150,000 system at 5% per year compound interest or 5.5% per year simple interest. If the total amount owed is due in a single payment at the end of 3 years, (a) which interest late should the company select, and (b} how much is the difference in interest between the two schemes? (1.38) 6. lselt Welding has extra funds to invest for future capital expansion. If the selected investment pays simple interest, what annual interest rate would be required for the amount to grow from $60,000 to $90,000 in 5 years? (1.39) 7. In order to make CDs look more attractive as an investment than they really are, some banks advertise that their rates are higher than their competitors’ rates; however, the fine print says that the rate is based on simple interest. If you were to deposit $10,000 at 10% per year simple interest in a CD, what compound interest rate would yield the same amount of money in 3 years? Solve by formula and write the spreadsheet function to display the i value. (1.40) 8. Fill in the missing values (A through D) for a loan of $10,000 if the interest rate is compounded at 10% per year. (1.41) 9. A company that manufactures general-purpose transducers invested $2 million 4 years ago in high-yield junk bonds. If the bonds are now worth $2.8 million, what rate of return per year did the company make on the basis of (a} simple interest, and (b) compound interest? (1.42) 10. The compound interest rate per year that amounts of $1000 one year ago and $1345.60 one year hence are equivalent to? (1.58) 11. The simple interest rate per year that will accumulate the same amount of money in 2 years as a compound interest rate of 20% per year is closest to? (1.59) 12. In order to finance a new project costing $30 million, a company borrowed $21 million at 16% per year interest and used retained earnings valued at 12% per year for the remainder of the financing. The company’s weighted average cost of capital for the project was closest to? (1.60) 13. Badger Pump Company invested $50,000 five years ago in a new product line that is now worth $1,000,000. What rate of return did the company earn a) on a simple interest basis and b) on a compound interest basis? (1.22) 14. Companies frequently borrow money under an arrangement that requires them to make periodic payments of only interest and then pay the principal of the loan all at once. A company that manufactures odor control chemicals borrowed $400,000 for 3 years at 10% per year compound interest under such an arrangement. What is the difference in the total amount paid between this arrangement (identified as plan 1) and plan 2, in which the company makes no interest payments until the loan is clue and then pays it off in one lump sum? (1.25) 15. A homeowner purchased a home in 1995 for $189,500. Eleven years later the home was sold for $240,000. What compounded annual interest rate was realized by the homeowner? (4-11)